Rds Patho (Dexsdad)
-
Upload
dexter-flores -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of Rds Patho (Dexsdad)
-
8/13/2019 Rds Patho (Dexsdad)
1/9
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Neonatal RespiratoryDistress Syndrome
-
8/13/2019 Rds Patho (Dexsdad)
2/9
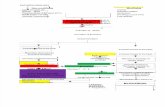
PREMATURITY
Surfactant
Deficiency
Structurally
Immature LungsAtelectasis
V/Q Mismatch Hypoventilation
Hypoxemia & Hypercarbia
Acute Phase Chronic Phase
-
8/13/2019 Rds Patho (Dexsdad)
3/9
Respiratory &
Metabolic Acidosis
Pulmonary
Vasoconstriction
Impaired Endotheliaand Epithelial
Integrity
ProteinaceousExudates
Respiratory DistressSyndrome (RDS)
High Fi02 & Baro or Volutrauma
Inflammation Cell
Influx
Antioxidant
Release
Cytokine Release Free Radicals
Lung Injury
Chronic Lung Disease or Bronchopulmonary
Dysplasia
-
8/13/2019 Rds Patho (Dexsdad)
4/9
Atelectasis- the collapse or closure ofthe lung resulting in reduced orabsent gas exchange. It may affectpart or all of one lung.It is a conditionwhere the alveoli are deflated, asdistinct from pulmonary consolidation.
-
8/13/2019 Rds Patho (Dexsdad)
5/9
the VENTILATION/PERFUSION RATIO(or V/Q ratio) is a
measurement used to assess the efficiency andadequacy of the matching of two variables: It isdefined as: the ratio of the amount of air reachingthe alveoli to the amount of blood reaching thealveoli.
"V" ventilationthe air that reaches the alveoli
"Q"perfusion the blood that reaches the alveoliThese two variables constitute the maindeterminants of the blood oxygen concentration.
-
8/13/2019 Rds Patho (Dexsdad)
6/9
Hypoxemia - an abnormally low level of oxygen in
the blood. More specifically, it refers to oxygendeficiency in arterial blood. Hypoxemia has manycauses, often respiratory disorders, and can causetissue hypoxia as the blood is not supplying enoughoxygen to the body.
Hypercarbia - abnormally high level of carbondioxide in the circulating blood
-
8/13/2019 Rds Patho (Dexsdad)
7/9
Respiratory acidosis -is a medical condition in which
decreased ventilation (hypoventilation) causesincreased blood carbon dioxide concentration anddecreased pH (a condition generallycalled acidosis).
Metabolic acidosis- is a condition that occurs whenthe body produces too much acid or whenthe kidneys are not removing enough acid from thebody.
-
8/13/2019 Rds Patho (Dexsdad)
8/9
Fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) - is the fraction orpercentage of oxygen in the space being measured.
Medical patients experiencing difficulty breathing areprovided with oxygen-enriched air, which means a higher-than-atmospheric FiO2. Natural air includes 20.9% oxygen,which is equivalent to FiO2 of 0.21. Oxygen-enriched airhas a higher FiO2than 0.21, up to 1.00, which means 100%
oxygen.[1]FiO2is typically maintained below 0.5 even withmechanical ventilation, to avoid oxygen toxicity.
Volutrauma - is essentially damage to the lung caused byoverdistention by a mechanical ventilator set for anexcessively high tidal volume; resulting in a syndrome
similar to adult respiratory distress syndrome. Volutrauma isseparate from Pulmonary barotrauma because themechanism of injury is excessive volume (volutrauma),instead of pressure (barotrauma).
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fraction_of_inspired_oxygenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fraction_of_inspired_oxygenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fraction_of_inspired_oxygenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fraction_of_inspired_oxygen -
8/13/2019 Rds Patho (Dexsdad)
9/9
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD - formerly chronic lung
disease of infancy) is a chronic lung disorder that is mostcommon among children who were born prematurely.Bronchopulmonary dysplasia results in significant morbidityand mortality. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia is more commonin infants with low birth weights and those who received
prolonged mechanical ventilation to treat respiratory distresssyndrome. The definition of bronchopulmonary dysplasia(BPD) has continued to evolve since 1967 when the disorderwas first described in publication, which resulted from effectsof oxygen and mechanical ventilation in premature infantswith severe respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). This is due tochanges in the population at risk.