Porifera
Click here to load reader
Transcript of Porifera

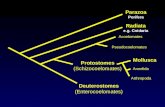
PORIFERAGeneral characteristics: -They feed through pores on their outer walls. -Cells are not organised to tissues or organs. - Different cells perform different functions. -They are both asexual and sexual. -Their skeleton is made up of collagen and spicules. -Porifera are also known as Sponges -There are more than 8,000 known species of Porifera in the world.

Classification of porifera:There are about 5,000 species of sponge, mostly marine and few freshwater
species. In sea they occur up to a depth of 8,500 m and mostly flourish in warm waters. Size can vary from a few cm to several metres. The body shape is highly variable.
Class CALCAREA (=CALCISPONGIAE) Small marine sponges with calcareous spicules.
Class HEXACTINELLIDA (=HYALOSPONGIAE). Marine glass sponges with 6-rays spicules.
Class DEMOSPONGIAE. Massive frame sponges with sponging fibres and siliceous spicules.

CNIDARIA General characteristics:
- All Cnidaria are armed with stinging cells called nematocysts.
- There are four major groups of Cnidaria: Anthozoa, Cubozoa, Hydrozoa, and Scyphozoa.
-They have radial symmetry.
- At some point in their lives they develop a medusa and a polyp stage.
-Medusa- a free-swimming bell, shaped stage, with tentacles extending below the bell.
-Polyp- Vase shaped, sedentary stage of Cnidarian life cycle.
-They have a gastrovascular cavity that serves as a mouth for eating prey and as an anus.
-They are free-swimming and floating at different stages in their life.

Classification of cnidaria:
Class Hydrozoa: Hydrozoas. Hydra, Obelia, Gonionemus, Physalia
Class Cubozoa:Sea wasps. Tripedalia
Class Scyphozoa:Jellyfish. Aurelia, Pelagia, Cyanea
Class Anthozoa: Sea anemones and corals. Metridium, Pennatula, Gorgonia, Astrangia

By:
Lizaveta Ramanouskaya
Cristina Gómez Herrero

By:
Lizaveta Ramanouskaya
Cristina Gómez Herrero