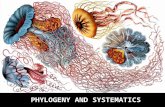
Phylogeny and Systematics Fossil record – Provides information about ancient organisms Figure...
-
Upload
ellen-mathews -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
Transcript of Phylogeny and Systematics Fossil record – Provides information about ancient organisms Figure...

• Phylogeny and Systematics

• Fossil record– Provides information about ancient organisms
Figure 25.1

The Fossil Record• Sedimentary rocks
– Richest source of fossils– Deposited into layers called strata
Figure 25.3
1 Rivers carry sediment to the ocean. Sedimentary rock layers containing fossils form on the ocean floor.
2 Over time, new strata are
deposited, containing fossils from each time period.
3 As sea levels change and the seafloor is pushed upward, sedimentary rocks are exposed. Erosion reveals strata and fossils.
Younger stratum with more recent fossils
Older stratum with older fossils

• The fossil record– Based on the sequence in which fossils have
accumulated in such strata– Fossils reveal ancestral characteristics

Figure 25.4a–g
(a) Dinosaur bones being excavated from sandstone
(g) Tusks of a 23,000-year-old mammoth, frozen whole in Siberian ice
(e) Boy standing in a 150-million-year-old dinosaur track in Colorado
(d) Casts of ammonites, about 375 million years old
(f) Insects preserved whole in amber
(b) Petrified tree in Arizona, about 190 million years old
(c) Leaf fossil, about 40 million years old

Convergent Evolution• Similar environmental pressures & natural
selection• Produce similar (analogous) adaptations
Figure 25.5

Peppered Moths
• Dark vs. light variants
Year % dark % light1848 5 951895 98 21995 19 81

The Universal Tree of Life • Divided into 3 great clades (domains): Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya• The early history of 3 domains is not yet clear
Figure 25.18
Bacteria Eukarya Archaea4 Symbiosis of
chloroplast ancestor with ancestor of green plants
3 Symbiosis of mitochondrial ancestor with ancestor of eukaryotes
2 Possible fusion of bacterium and archaean, yielding ancestor of eukaryotic cells
1 Last common ancestor of all living things
LUCA
4
3
2
1
1
2
3
4
0B
illio
n ye
ars
ago
Origin of life