Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease
-
Upload
louie-kem-anthony-babaran -
Category
Documents
-
view
107 -
download
2
description
Transcript of Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease
Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease
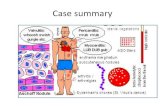
Activation of complement system, opsonic phagocytosis, production of NK cells to combat pathogensProduction of antibodies (IgG & IgM)Macrophages attack bacteria, and then present its antigen to the immune systemIncreased Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)RBCs stick together (rouleaux)Increased FibrinogenIncreased C Reactive ProteinStimulation of liver to produce acute phase proteinsHyperthermiaIncreased body temperatureIncreased thermostat point in the hypothalamusIncreased thermostat point in the hypothalamusRelease of Prostaglandin E2Production of Cytokines, TNF, Endogenous Pyrogens (IL 1 and IL 6)AMulti-systemic effectsPredisposing Factors:Family history of RHDAge (5-15 years old)Past history of Rheumatic FeverPrecipitating Factors:Environmental factorsLow Socioeconomic StatusGeographical LocationEtiologyGroup A Beta-Hemolytic StreptococcusBacteria invades the upper respiratory tract (tonsils and pharynx)Inflammation of affected tissuesImmune system cross-reacts and causes tissue injury to normal body cells due to Molecular Mimicry
AImmune system cross-reacts with Basal GangliaDisruption in motor signalsInvoluntary muscle contractions (Sydenhams Chorea)Immune system cross-reacts with Synovial membraneLeakage of plasma proteins and fluid Swelling of the jointCompression of nerve endingsPain and tenderness of the jointArthritis migrates upward to different joints Migratory PolyarthritisImmune system cross-reacts with SkinPresence of ring-like lesions (Erythema Marginatum)Immune system cross-reacts with subcutaneous tissueImmune system cross-reacts with myocardial tissuePresence of subcutaneous nodulesPericarditisIncreased permeability of capillariesShifting of plasma and fibrinogen to pericardial sacSwelling of pericardium CEndocarditisMyocarditisMyocardium loses its contractilityMechanical injury caused by inflammation and tachycardiaAggregation of platelets and fibrin along the valveDecreased Cardiac OutputDecreased PerfusionSympathetic Response: Increased Heart Rate, Increased Contractility, VasoconstrictionDEErosion of mitral valve leafletsFomation of vegetations along the edges of the leafletsB
CDBMulti-organ failureHypoxiaHypoperfusionDecreased Heart RateCardiogenic shockFDecreased CO despite compensatory mechanismsFCor PulmonaleDilatation/Hypertrophy of RVIncreased Pressures in the RV and RAPulmonary HypertensionIncreased Pressure in Pulmonary capillary bedPulmonary edema, dyspneaIncreased Volume in LAIncreased Volume in Pulmonary VeinDilatation/Hypertrophy of LVIncreased Pressure in LVIncreased Residual Volume of LVPericardial friction rub on auscultationSharp, stabbing localized painCompression of nervesIncreased pressure on parietal pericardiumPericardial layers rub each otherEMitral RegurgitationMitral StenosisPermanent distortions of the leaflets of the valveVegetations heal with fibrosis and calcifications
DEATH