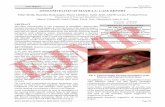
Pathophysiology of Osteomyelitis Diagram
-
Upload
kim-enrico-jumarang -
Category
Documents
-
view
145 -
download
3
description
Transcript of Pathophysiology of Osteomyelitis Diagram

Open wounds/ fractures
Microorganisms gain entry by way of blood
Microorganisms lodge into an area where circulation
slows
Microorganisms grow
Increase pressure
Vascular compromise of the periosteumIschemia
Infection through the bone cortex and marrow
Cortical devascularization
necrosis
Formation of new bone
Involcrum
Separation of devitalized bone from living bone Sequestra
Continues to be an infected island
Difficulty to reach by blood borne antibiotics
Enlarged sequestrum
Sequestrum move out to the soft tissue
revascularized
Removal by the normal immune process
Development of sinus tract
Turns to scar tissue
Site for continued microorganism growth
Remission and exacerbation
Chronic stage
Debridement
drainage from sinus tracts
fever, night sweats, chills, restlessness, nausea and malaiseconstant bone pain,
swelling, tenderness, warmth at the infection site,
restricted movement of the affected part
Systemic signs may be diminished with
constant bone pain, Swelling, tenderness, warmth at the infection
site
Excessive vascular insufficiency
Loss of organ function
Amputation
Healing
Predisposing factors:
vascular insufficiency disorders
genitourinary infectionsrespiratory infections
IV drug useimmunocompromising
diseaseshistory of blood- stream
infectionsIndwelling prosthetic
devices