Northern, Southern, Western...Northern Blot: RNA-DNA*(RNA*) •Alwine adapted Southern's method for...
Transcript of Northern, Southern, Western...Northern Blot: RNA-DNA*(RNA*) •Alwine adapted Southern's method for...

Northern, Southern, Western
Ed Southern:
In the 1970s Ed Southern of
Oxford University invented a
revolutionary DNA blotting
technique.
The Southern Blot allows the
visualization of one DNA
fragment from a whole
genome DNA extract.

Northern and Western
• People then applied the same technique
to RNA.
• They called it a “Northern blot”.
• Then other people applied it to protein,
and imaginatively called it a “Western
blot” Funny, eh?

3
Introduction Concept: reannealing nucleic acids to identify sequence of interest.
Separates DNA/RNA in an agarose gel, then detects specific bands using probe and hybridization.
Hybridization takes advantage of the ability of a single stranded DNA or RNA molecule to find its complement, even in the presence of large amounts of unrelated DNA.
Allows detection of specific bands (DNA fragments or RNA molecules) that have complementary sequence to the probe.
Size bands and quantify abundance of molecule.

4
Southern Blot: DNA-DNA*
Developed by Edwin Southern.
Uses gel electrophoresis together with hybridization
probes to characterize restriction fragments of
genomic DNA (or DNA from other sources, such as
plasmids).
Identifies DNA with a specific base sequence.
Can be done to detect specific genes present in cells.

5
Southern Steps
1. DNA to be analyzed is digested to completion with a
restriction endonuclease.
2. Electrophoresis to maximally separate restriction
fragments in the expected size range. A set of
standards of known size is run in one lane of the gel.
3. Blot fragments onto a nitrocellulose membrane.
4. Hybridize with the 32P probe.
5. Autoradiography.

6
Step 2
Gel electrophoresis
• Separates DNA fragments.
Soak gel in 0.5 M NaOH
• Converts dsDNA to ssDNA

7
Step 3. Nitrocellulose Blot • Cover gel with nitrocellulose
paper…then…
• Cover nitrocellulose paper with thick layer of paper towels.
• Compress apparatus with heavy weight.
• ssDNA binds to nitrocellulose at same position it had on the gel.
• Vacum dry nitrocellulose at 80C to permanently fix DNA in place or cross link (via covalent bonds) the DNA to the membrane.

8
Step 4. Hybridization • Incubate nitrocellulose sheet with
a minimal quantity of solution
containing 32P-labeled ssDNA
probe.
• Probe sequence is complementary
to the DNA of interest.
• Incubate for several hours at
suitable renaturation temperature
that will permit probe to anneal to
its target sequence(s).
• Wash & dry nitrocellulose sheet.

9
Step 5. Autoradiography
• Place nitrocellulose sheet over
X-ray film.
• X-ray film darkens where the
fragments are complementary
to the radioactive probes.

Characterization: Southern blot hybridization
-transfer of DNA from a gel to a membrane (e.g., nitrocellulose, nylon)
-developed by Edwin Southern

11
Southern Application: Diagnosis & detection of genetic diseases.
• Used to diagnose sickle cell-anemia.
• AT base change in the subunit of Hb
Glu Val.
• Development of a 19 residue oligonucleotide probe
complementary to sickle-cell gene’s mutated segment.
• Probe hybridizes to DNA from homozygotes of sickle-cell
anemia but not from normal individuals.

12
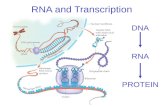
Northern Blot: RNA-
DNA*(RNA*)
• Alwine adapted Southern's method for DNA to detect, size and quantify RNA – 1977.
• No need to digest RNA with restriction enzymes.
• Use formaldehyde to break H-bonds and denature RNA because single-stranded RNA will form intramolecular base pairs and "fold" on itself.

13
Northern Steps
1. Isolate RNA & treat with formaldehyde.
2. Electrophorese RNA in denaturing agarose gel (has
formaldehyde). Visualize RNA in gel using Ethidium
bromide stain and photograph.
3. Transfer single-stranded RNA to nitrocellulose or nylon
membrane. Covalently link RNA to membrane.
4. Incubate membrane (RNA immobilized on membrane) with
labeled DNA or RNA probe with target sequence.
5. Development.

14
Step 1 Isolate RNA:
-To detect rare mRNA, isolate the poly A+ mRNA.
-RNA is both biologically and chemically more labile than
DNA. Thus eliminate RNases.
Step 2
Electrophoresis:
- Performed in formaldehyde agarose gel to prevent RNA from
folding on itself.
- Stain with EtBr to visualize the RNA bands.

15
Step 3 -Transfer single-stranded RNA to nitrocellulose or nylon
membrane:
Traditionally, a nitrocellulose membrane is used, although nylon or a positively charged nylon membrane may be used.
Nitrocellulose typically has a binding capacity of about 100µg/cm, while nylon has a binding capacity of about 500 µg/cm. Many scientists feel nylon is better since it binds more and is less fragile.
-Covalently link RNA to membrane:
UV cross linking is more effective in binding RNA to the membrane than baking at 80C.

16
Step 4 & 5 -Prehybridize before hybridization:
Blocks non-specific sites to prevent the single-stranded probe from binding just anywhere on the membrane.
-Incubate membrane with labeled DNA or RNA probe with target sequence:
Probe could be 32P, biotin/streptavidin or a bioluminescent probe.
-Autoradiography:
Place membrane over X-ray film.
X-ray film darkens where the fragments are complementary to the radioactive probes.

Ethidium bromide is fluorescent in
UV light


19
Northern Application
• Northern blots are particularly useful for determining the conditions under which specific genes are being expressed, including which tissues in a complex organism express which of its genes at the mRNA level.
• For instance:
When trying to learn about the function of a certain protein, it is sometimes useful to purify mRNA from many different tissues or cell types and then prepare a Northern blot of those mRNAs, using a cDNA clone of the protein of interest as the probe.
Only mRNA from the cell types that are synthesizing the protein will hybridize to the probe.

20
Summary
Southern
• DNA on membrane.
• Digest DNA.
• Convert dsDNA to
ssDNA.
• Probe with DNA or
RNA.
Northern
• RNA on membrane.
• No need to digest DNA.
• Denature “folded” RNA
with formaldehyde.
• Probe with DNA or RNA.

Characterization: Western blotting
-transfer of protein from a gel to a membrane (e.g., nitrocellulose,
nylon)
-requires the use of an electric current to facilitate transfer
X Protein
X
x Buffer; requires electric current
X
React with
Antibody
X
Enzyme
reaction
or

Fluorescence in situ
Hybridization

Fluorescence in situ
Hybridization (FISH)
• FISH - a process which vividly paints
chromosomes or portions of chromosomes
with fluorescent molecules. Identifies
chromosomal abnormalities
• Aids in gene mapping, toxicological studies,
analysis of chromosome structural
aberrations, and ploidy determination

FISH
• Used to identify the presence and location
of a region of DNA or RNA within
morphologically preserved chromosome
preparations, fixed cells or tissue sections.
• This means you can view a segment or
entire chromosome with your own eyes
• Was often used during M phase but is now
used on I phase chromosomes as well

FISH
• Advantage: less labor-intensive
method for confirming the
presence of a DNA segment
within an entire genome than
other conventional methods like
Southern blotting.

FISH Procedure
• Denature the chromosomes
• Denature the probe
• Hybridization
• Fluorescence staining
• Examine slides or store in the
dark.

FISH Procedure

Probes
Biotin
Complementary sequences of
target nucleic acids
• Designed against the sequence
of interest
• Probes are tagged with
fluorescent dyes like biotin,
fluorescein, Digoxigenin
• Size ranges from 20-40 bp to
1000bp
Fluorescein

FISH Uses
• Detection of high concentrations of
base pairs
• Eg: Mouse metaphase preparation
stained with DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-
phenylindole) is a fluorescent stain that binds
strongly to A-T rich regions in DNA. It is
used extensively in fluorescence microscopy.

FISH Uses Centromere regions stained brighter - means they are
rich in A-T bonds
Also used in germ cell or prenatal diagnosis of
conditions such as aneuploidies (abnormal number of
chromosomes in a cell).

FISH and Telomeres • Telomeric probes define the terminal boundaries of
chromosomes (5’ and 3’ ends)
• Used in research of chromosomal rearrangements
and deletions related to cell aging or other genetic
abnormalities.
• Special telomeric probes specific to individual
chromosomes have been designed.
• Probe is based on the TTAGGG repeat present on all
human telomeres.

FISH and Telomeres
Application in
cytogenetics - can detect
submicroscopic deletions
and cryptic translocations
of genes associated with
unexplained mental
retardation and
miscarriages

FISH - Medical
FISH can be used in the
study of transgenic
animals (eg: Polly)
Selective markers show
if the human DNA was
inserted successfully
and pinpoint where the
human DNA is .


Diagnostic Applications of FISH • Prenatal diagnosis
• Cancer diagnosis
• Molecular cytogenetic of birth defects and mental
retardation
• The identification of specific chromosome
abnormalities
• The characterization of marker chromosomes
• Interphase FISH for specific abnormalities in cases of
failed
• Cytogenetic
• Monitoring the success of bone marrow transplantation

Other Human Disorders
• Sickle Cell Anemia –
– autosomal recessive
– Found most often among people of African
ancestry
– Blood cells sickle (change shape) when
oxygen-deprived (exertion, increase in altitude)
– Causes sickle cell event – pain and immobility
and death of tissue ( dangerous if in organ)
– Treatment – hospitalization and oxygen
– Carriers are resistant to malaria


Tay Sachs Disease
• Autosomal recessive ( Gangliosidosis or
Hexosaminidase A deficiency) .
• Genetic mutation of HEXA gene on
chromosome 15
• Found most often among Jews of Mediterranean
ancestry
• Child born appearing normal, but fat builds up in
brain and child dies by age 5
• No treatment, no cure

Huntington Disease
• It is a neurodegenerative genetic disorder that
affects muscle coordination and leads to
cognitive decline and dementia
• Autosomal dominant
– Symptoms do not appear until age 30-40.
– Death takes about 5-10 years
– No treatment, no cure – but there is a test to see if
you have it before symptoms begin
– Results in mental impairment and uncontrollable
spastic movements

Deletions • Chromosome fragment breaks off and is lost
• Cri du chat syndrome – mental retardation and
cat-like cry, delayed development, distinctive
facial features, small head size (microcephaly),
widely-spaced eyes (hypertelorism), low birth
weight and weak muscle tone (hypotonia) in
infancy.
• It is a rare genetic condition that is caused by the
deletion (a missing piece) of genetic material on
the small arm (the p arm) of chromosome 5.

The condition affects an estimated 1 in 20,000 to
50,000 live births, strikes all ethnicities, and is more
common in females by a 4:3 ratio

Prenatal Tests to detect
chromosomal problems:
• Amniocentesis – removes a little amniotic fluid
from around baby – fluid is then tested for
abnormal proteins and the cell in it can be
karyotyped.
• Amniocentesis usually done between 16 to 20
weeks, which is during second trimester.
• Risk of miscarriage


Chorionic Villus Sampling
• Take a piece of the chorionic villus from the
placenta – it is made of baby cells – and test
as in amniocentesis It is done during
early pregnancy, most often between the
10th and 12th weeks.
– Risk of miscarriage
– Has been linked to deformed fingers

Bioethical Dilemma
• Once a prenatal diagnosis of a genetic disorder
is made, what are the parents going to do?
– Do nothing and give birth to child with disorder
– Abort embryo/fetus
• Who should make the decision?
• What should enter into making the decision?

Genetic Counseling
• Genetic counselor:
– educates the parents about the disorder,
– tells them of their options without
influencing their decision,
– and tells them of the consequences of
each option .

DNA Fingerprints
• The pattern of DNA formed during gel
electrophoresis. Used by law enforcement.


“DNA in the Courtroom”
1. Use of VNTRs (variable number of tandem
repeats; different individuals have different
numbers of repetitive stretches of DNA, for
example, GGAGG). One individual might
have 6, another 12.
2. VNTRs can be analyzed by gel
electrophoresis, creating a banding
pattern specific to each individual—like a
bar code .

END
Part II