PITUITARY ADENOMA PITUITARY ADENOMA HORMONAL AND MEDICAL MANAGEMENT.
Next, the posterior pituitary Different anatomical structure Different hormones (VP, Oxy) Different...
-
Upload
zoe-hudson -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of Next, the posterior pituitary Different anatomical structure Different hormones (VP, Oxy) Different...

Next, the posterior pituitary
• Different anatomical structure
• Different hormones (VP, Oxy)
• Different functions
• Distinct pathophysiology

Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Secretion (a summary)
• Magnocellular neurons in SON and PVN synthesize precursor peptides for vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) or oxytocin)
• Products are packaged into neurosecretory vesicles and transported in axons forming the hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract
• Vesicles are stored in posterior pituitary.
• Release by exocytosis is controlled by neuroendocrine reflexes.

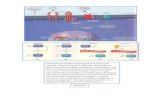
Neurohypophysial hormones:similar nonapeptides,
derived from different precursors

Figure 2. Prepro-oxytocin. Proteolytic maturation proceeds from top to bottom
Processing in rough ER (loss of signal peptide)
Pro-oxytocin
-lys-arg- -lys-arg- -COOHH2N-
Signal peptide
Prepro-oxytocin
-lys-arg- -lys-arg- -COOHH2N-
Oxytocin Neurophysin IOxytosin carrier protein
in axon
Processing in Golgi – hydrolysis of lys-arg bonds
H2N-
H2N-
H2N-

Processing in rough ER (loss of signal peptide)
Pro-vasopressin
-lys-arg- -lys-arg- -COOHH2N-
Signal peptide
Prepro-vasopressin
-lys-arg- -lys-arg- -COOHH2N-
Vasopressin Neurophysin IIADH carrier protein in
axon
Glycoprotein
Processing in Golgi – hydrolysis of lys-arg bonds
Figure 2. Processing of prepro-vasopressin.

Schema to represent steps in neuropeptide synthesis, transport and release

Neurohypophysis: histology

EM image of neurosecretory granules packed into
Herring bodies in neurohypophysial axon terminals

Hormone storage and release from neurohypophysial axon terminals

Immunocytochemical visualization of vasopressin- and oxytocin-synthesizing neurons
• Upper box, coronal section through the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN)
• Lower box, section through the hypothalamic supraoptic nucleus (SON)
• VP, dark, Oxy light brown
• NB: VP, Oxy in separate cells, applies to both male and female brain

Physiology of Oxytocin Secretion• In females, 2 unique
roles: • Milk ejection: sensory
stimulation of the nipple induces firing of oxytocin cells, release of oxytocin into the blood, activation of oxytocin receptors in breast myoepithelial cells and milk expulsion
• Delivery of the fetus: distention of the uterus at term triggers firing of oxytocin neurons, releasing oxytocin as a hormone into the blood; occupany of oxytocin receptors in uterine smooth muscle induces contractions that assist in expulsion of the fetus.

Lactation is a cooperation between anterior and posterior pituitary hormones.
Prolactin released from the anterior pituitary lactotrophs promotes milk production; oxytocin released from posterior pituitary storage sites
promotes contraction of myoepithelial cells and milk expulsion

Structure of the oxytocin receptor

In-vivo electrophysiology of oxytocin-secreting neurosecretory neurons
prerequisite:antidromic identification to verify axon target

Rat hypothalamus exposed for in-vivo electrophysiology
Under anesthesia, removal of the sphenoid bone and dura mater
exposes the ventral surface of the hypothalamus from the optic chiasm
to the posterior pituitary. A stimulating electrode positioned in
the posterior pituitary allows activation of axon terminals of
neurosecretory neurons. A recording micropipette positioned
near the junction of the middle and anterior cerebral arteries serves to
record extracellular activity from antidromically-identified supraoptic
nucleus neurons.