MultiviewOrthographic Projection Based onportal.unimap.edu.my/portal/page/portal30/Lecture... ·...
Transcript of MultiviewOrthographic Projection Based onportal.unimap.edu.my/portal/page/portal30/Lecture... ·...

11/11/2015
1
MultiviewMultiview Orthographic ProjectionOrthographic Projection
CHAPTER 3 Projection Theory
To represent 3D objects on 2D media.
Based on two variables:1. Line of sight – Imaginary ray of light between an observer’s eye
and an object.2. Plane of projection – Imaginary flat plane upon which the image is
created by the lines of sight is projected.
Two projection methods primarily used; i) perspective and ii) parallel.
Parallel projection – Object is positioned at infinity and viewed from multiple points on an imaginary line, parallel to the object.
Perspective projection – Object is positioned at a finite distance and viewed from a single point.
Projection Theory (cont.)
Parallel Projection Perspective Projection
Multiview Projection Planes
Multiview projection – An orthographic projection for which the object is behind the projection plane, and the object is oriented such that only two of its dimensions are shown.
Multiview Projection Planes (cont.)
Multiview drawings – Three views of object are drawn. Each view is a 2D flat image. The views are defined according to the positions of the planes of projection with respect to the object.
Front View – Shows the width and height. Frontal plane is the plane onto which the front view of a multiview drawing is projected.
Front View
Top View – Shows the width and depth. The top view is projected onto the horizontal plane of projection.
Multiview Projection Planes (cont.)

11/11/2015
2
Side View – Shows the depth and height dimensions. The right side view is projected onto the right profile plane of projection.
Multiview Projection Planes (cont.) Orientation of Views
Always positioned above & aligned with the front view.
Always positioned to the right of and aligned with the front view.
The Six Principal Views
Principal views -the six mutually perpendicular views that are produced by six mutually perpendicular planes of projection.
The six principal views are front, top, left side, right side,bottom and rear.
Front View Right Side View
Top View
The Six Principal Views (cont.)
Bottom View
Left Side View
Rear View
The Six Principal Views (cont.) The Six Principal Views (cont.)
Unfolding the glass box to produce a six-view drawing.

11/11/2015
3
Conventional View Placement
What is the standard views used in engineering & technology?
Three-view multiview drawing – the other three views are mirror images and do not add to the knowledge about the object.
The standard views used in a three-view drawing are the top, front and right sideviews.
Conventional View Placement (cont.)
Scale Divider Miter Line
Because of the relative positioning of the three views, the depth dimension cannot be aligned using projection lines.
Instead, the depth dimension is measured in either the top or right side view and transferred to the other view using the following methods;
First- and Third-Angle Projection
There are two ways of drawing in orthographic – First Angle and Third Angle.
They differ only in the position of the principle views.
First Angle Projection – The object is imagined to be in first quadrant.
Third Angle Projection – The object is imagined to be in third quadrant.
Third-angle projection is used in the US, Canada, and many other countries throughout the world.
First-angle projection is used mainly in European and Asiancountries.
First Quadrant
ThirdQuadrant
First- and Third-Angle Projection (cont.)
1st Angle Projection 3rd Angle Projection
First- and Third-Angle Projection (cont.)
1st Angle Projection 3rd Angle Projection
Foldingline
Foldingline
Foldingline
Foldingline
First- and Third-Angle Projection (cont.)

11/11/2015
4
Front View
Front View
Right Side View
Right Side View
Top View
Top View
First- and Third-Angle Projection (cont.)
1st Angle Projection 3rd Angle Projection
Third-Angle Projection First-Angle Projection
First- and Third-Angle Projection (cont.)
First- and Third-Angle Projection (cont.)
Third-Angle Projection First-Angle Projection
Symbol: Symbol:
d 1.7d
2.2d
Suggested Proportion:
First- and Third-Angle Projection (cont.)
Creating a Three-View Multiview Drawing Line Conventions
The alphabet of lines is a set of standard linetypes established by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) for technical drawing.
Two line weights are sufficient to follow the standard – 0.6 mm (thick) and 0.3 mm (thin). Thick lines – drawn using soft lead, such as F or HB. Thin lines – drawn using hard lead, such H or 2H.
The alphabet of lines

11/11/2015
5
Line Conventions (cont.)
The alphabet of lines
Line Conventions (cont.)
Identification of the alphabet of lines
Line Conventions (cont.)
Drawing conventions for hidden lines
Line Conventions (cont.)
A visible line has precedence over all other types of lines, and a hidden and a cutting plane line have precedence over a center line.
Line Conventions (cont.)
An engineering drawing showing how the
precedence of line is applied.
Line Conventions (cont.)
An engineering drawing of a cylinder, showing the
application of center lines.

11/11/2015
6
Fundamental Views of Edges & Planes
Normal line – An edge line that is parallel to a plane of projection and thus perpendicular to the line of sight. Example; Line 1 – 2.
Inclined line – A line that is parallel to a plane of projection but inclined to the adjacent planes, and it appears foreshorten in the adjacent planes. Example; Line 3 – 4.
1) Edge Line
Fundamental Views of Edges & Planes (cont.)
Oblique line – A line that is not parallel to any principal plane of projection; therefore, it neverappears as a point or in true length in any of the six principal views. Example; Line 1 – 2.
1) Edge Line (cont.)
2) Planes
Fundamental Views of Edges & Planes (cont.)
Principal Planes:i. Frontal plane – A plane that is parallel to the front plane of projection and is
true size and shape in the front view.ii. Horizontal plane – A plane that is parallel to the horizontal plane of projection
and is true size and shape in the top/bottom view.iii. Profile plane – A plane that is parallel to the profile planes of projection and is
true size and shape in the profile views.
Inclined Planes – A plane that is perpendicular to one plane of projection and inclined to adjacent planes and cannot be viewed in true size and shape in any of the principal views.
Oblique Planes – A plane that is not parallel to any of the principal planes of projection.
Fundamental Views of Edges & Planes (cont.)
Plane A = Frontal plane; Plane B = Horizontal plane; Plane C = Profile plane. Plane D = Inclined plane Plane E = Oblique plane
Multiview Representation
Being able to identify 2D primitives and the 3D primitive solids they represent is important in visualizing and creating multiview drawings.
The next figure showing multiview drawings of common geometric solids.
Angles on Planes
An angle is represented in true size when it is in a normal plane.
If an angle is not in a normal plane, then the angle will appear either larger or smaller than true size.

11/11/2015
7
Holes
Through hole – a hole that goes all the way through an object.
Blind hole – a hole that is not drilled all the way through the material.
Counterbored hole – to allow the heads of bolts to be flush with or below the surface of the part.
Countersunk hole – for flathead fasteners. It is represented by drawing 45º lines.
Spotfaced hole – a place for the heads of fasteners to rest.
No line
No line
Tangent
Tangent
Intersect
Intersect
Tangent and Intersections
No line is formed when curved surface tangent to a plane surface.
Line is formed when curved surface intersects a plane surface.
Intersect
TangentTangent
Tangent
Plane
Limiting Element
Tangent and Intersections (cont.)
Intersect
No line
Tangent
Tangent
Tangent
Tangent
Tangent
No line
TangentNo line
Tangent and Intersections (cont.)
Example 1
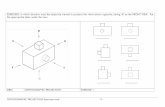
Draw a third-angle projection of the object below, showing the front view (indicated by thearrow F), top view and right-side view of the object. All dimensions are shown in millimetres(mm). Dimensioning is not required. You may show the construction lines but must be thin (0.3mm).
Example 2
Draw a third-angle projection of the object below, showing the front view (indicated by thearrow F), top view and right-side view of the object. All dimensions are shown in millimetres(mm). Dimensioning is not required. You may show the construction lines but must be thin (0.3mm).

11/11/2015
8
Example 3
Draw a third-angle projection of the object below, showing the front view (indicated by thearrow F), top view and right-side view of the object. All dimensions are shown in millimetres(mm). Dimensioning is not required. You may show the construction lines but must be thin (0.3mm).
Examples of the standard representations of various geometric forms.
Exercises Exercises (cont.)
Make freehand sketches in Third Angle Projection for the following objects showing the front view, top view and right-side view of the object. You are not required to make full scale accurate drawings, but sketches must be clean, showing all lines (visible, hidden and centre lines), and aligned in the correct positions.
Frontview
Frontview
Exercises (cont.)
1 2
Exercises (cont.)
3 4

11/11/2015
9
Exercises (cont.)
5 6