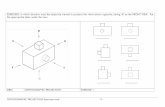
Orthographic Projection
-
Upload
srimanthula-srikanth -
Category
Documents
-
view
94 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Orthographic Projection

TOPICS OF “ENGINEERING GRAPHICS” (Mechanical Portion)Teacher : H. N. Soni
( C ) ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS FROM GIVEN ISOMETRIC VIEW
( D ) ISOMETRIC VIEW/PROJECTIONS FROM GIVEN ORTHOGRPHIC VIEWS
Without Sections ( For First Int. Test)
With Sections ( For Second Int. Test)
View i.e. drawing Projections
For Third Internal Test
Topic no. Topic Content No. of Lectures
07
05

TYPES OF LINES USED IN
ENGINEERING DRAWING
APPLICATIONS OF LINES ON DRAWING
G2CUTTING PLANE
LINE (IN T.V)
CONTINUOUS THICK
A
A
G1CUTTING PLANE
LINE (IN F.V)G1
B CONTINUOUS THIN (WAVY)
B
C SHORT ZIGZAG THIN
C
DDD CONTINUOUS
THIN
D
ESHORT DASH
MEDIUM (DOTED LINE )
E
F LONG CHAIN THIN (CENTER
LINE)
F
40 30
2515
0
60

Trimmed and untrimmed drawing sheet sizes are commercially designated as A0 (Maximum size), A1, A2, A3, A4 & A5 (Least size).
In Engineering Graphics’ term work, all the 4 sheets will be of A2 (approximately ½ Imperial) size
The following two systems are adopted for dimensioning purposes on orthographic views as well as on pictorial view.
Dimensioning Techniques

20
35
ALIGNED SYSTEM
(FOR A2 TO A5 SHEET SIZE)
UNIDIRECTIONAL SYSTEM
(FOR LARGE SIZED SHEETS)
35
20
ARROW HEADS
(H x 3H) 3H
H

ORTHOGRAPHIC PREOJECTIONS
(MULTI VIEW REPRESENTATIONS i.e.
F.V., T.V. & S.V. – L.H.S.V OR R.H.S.V)
FROM ISOMETRIC VIEW
PLANES OF PROJECTIONS
QUADRANTS
VISION
DIRECTIONS

SCALING OF A DRAWING (Full Size
1:1, Reduced 1:2 or Enlarged 5:1 )
VIEWES
METHODS OF PROJECTIONS WITH
THEIR SYMBOLS

(AS PER BUREAU OF INDIAN STANDARDS FOR ENGINEERING DRAWING.)
SCALING OF A DRAWING
RECOMMENDED SCALES
1. FULL SCALE e.g. 1: 1
In certain cases the engineering components may be very large or very small for drawing purposes, hence the corresponding scale may be preferred from the following

3. ENLARGED SCALE e.g. 50:1, 20:1, 10:1, 5:1, 2:1
2. REDUCED
SCALE e.g.
1:2, 1:2.5, 1:5,
1:10, 1:20,
1:15, 1:100,
1:200, 1:500,
1:1000, 1:2000,
1:5000,
1:10000

PICTORIAL VIEWS OF PLANES OF ORTHO. PROJEC.
SKETCH – 1
FOR L.H.S.V. (Z1)
SKETCH – 2
FOR R.H.S.V.(Z2)
7
Y
4
82
Y
Z2
3
1
X
X
15
26
43
X
Y
Z1
Y
X

Lines, perpendicular to “Planes of projections (i.e.View planes)” called projectors
3
71
4
82
15
26
43
Y
X
X
Y
Vision directions :
XY is the line of intersection of V.P. (1 &2) and H.P. (3&4).

3
71
4
82
15
26
4 3Y
X
X
Y
Y Y
Y :- Vertically (downward) direction, for T.V. (i.e.Plan){on Pl.3 for I angle & on 4 for III angle)}
x x
X :- Horizontal direction, for F.V.(i.e.Elevation) {on Pl.1(for I angle) & on 2 (for III angle)}

Z1:- Horizontal (Perpendicular to pl.
5 & 6), for L.H.S. View, for I angle & III angle Z2:- Horizontal (Perpendicular to pl.
7 & 8), for R.H.S. View, for I angle & III angle
3
71
4
82
Z2
15
26
43
Y
X
X
Y
Z1
Y Y
x x

11
Plane Code
Plane, Called
View Projected on this
Of Proj. Method
Fixed or
Turned
1 Vertical Plane (V.P.) Above
H.P.
Front View (F.V.)
Ist AngleFixed Plane (Above XY)
XY
X Y
X X
X –FRONT VIEW DIRECTION
3D
(1,3 & 5/7)

Z2 – R.H.S.V. DIRE.X –FRONT VIEW
DIRECTION
7511
33
57
Horizontal Plane (H.P.) In front of V.P.
3 Top View (T.V.) Ist Angle
Turned Down(Below X Y)
L.H.S./R.H.S. View
Ist Angle Turned on R.H.S./L.H.S. Of 1
Profile Plane (P.P.)(On R.H.S./L.H.S of 1)
XY
X Y
Z1
Y Y
Z2X X
3D
(1,3 & 5/7)
Y – TOP VIEW DIRECTION
Z1 – L.H.S.V. DIRE.
Plane Code
Plane, Called
View Projected on this
Of Proj. Method
Fixed or
Turned

22
44
2 Vertical Plane (V.P.)Below H.P.
Front View (F.V.)
IIIrd
AngleFixed Plane (Below XY)
Horizontal Plane (H.P.) Behind V.P.
4 Top View (T.V.)
IIIrd Angle
Turned Up(Above XY)
Plane Code
Plane, Called
View Projected on this
Of Proj. Method
Fixed or
Turned
Y
X
X
Y
YY
XX
3D
(2, 4 & 6/8)
X –FRONT VIEW DIRECTION
Y – TOP VIEW DIRECTION

86
3D
(2, 4 & 6/8)
X –FRONT VIEW DIRECTION Z2 – R.H.S.V. DIRE.
Y – TOP VIEW DIRECTION
Z1 – L.H.S.V. DIRE.
Plane Code
Plane, Called
View Projected on this
Of Proj. Method
Fixed or
Turned
Z1Z2
6/8L.H.S./R.H.S.
ViewIIIrd
Angle
Turned on L.H.S./R.H.S.
Of 2
Profile Plane (P.P.) (On
L.H.S./R.H.S of 2)
22
44Y
X
X
Y
YY
XX

1
2
3
4
X Y
V.P. above H.P.F.V. Plane
For Ist Angle
V.P. below H.P.F.V. Plane
For IIIrd Angle
H.P. In
front of V.P.
T.V.Plane for Ist Angle
H.P. Behind V.P.
T.V. Plane for IIIrd Angle
T.V. of
V.P. (1&2)
F.V. of H.P. (3&4)
F.V. of Pl. 5
F.V. Of PL.8
F.V. Of PL.6
F.V. of Pl. 7
Pl. 5 & 7 are infront of Pl. 1& Pl. 6 & 8 are behind Pl. 2

H.P. In
front of V.P.
H.P. Behind V.P.
T.V.Plane for Ist Angle
1
2
3
4
V.P. above H.P.F.V. Plane
For Ist Angle
V.P. below H.P.F.V. Plane
For IIIrd Angle
T.V. Plane for IIIrd Angle
IIIIII IV
5
6
L.H.S.V. Plane for IIIrd
Angle
Plane 1
Plane 2
Plane 3
Plane 4
L.H.S.V. of sketch – 1Showing Quadrants (I to IV)
Xx y
L.H.S.V. Plane for Ist Angle
5
8 6
7
Pl. 6 & 8 are behind Pl. 2Pl. 5 & 7 are infront of Pl. 1

I IIIIIIV
7
8
R.H.S.V. Plane for
IIIrd Angle
Plane 3
Plane 4
R.H.S.V. of sketchShowing Quadrants (I to IV)
X
R.H.S.V. Plane for Ist Angle
Plane 2
Plane 1
H.P. In
front of V.P.
H.P. Behind V.P.
T.V.Plane for Ist Angle
1
2
3
4
V.P. above H.P.F.V. Plane
For Ist Angle
V.P. below H.P.F.V. Plane
For IIIrd Angle
T.V. Plane for IIIrd Angle
x y7 5
8 6
Pl. 6 & 8 are behind Pl. 2Pl. 5 & 7 are infront of Pl. 1

SYMBOLS USED ON ENGINEERING DRAWING SHEET
FIRST ANGLE METHOD OF
ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS
THIRD ANGLE METHOD OF
ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS
M/c. PARTS ARE NEVER ASSUMED IN SECOND OR IN FOURTH QUADRANT, AS THE VIEWS MAY OVERLAP ON ONE ANOTHER ABOVE XY OR BELOW XY RESPECTIVELY.

ISOMETRIC VIEW
OFL
F.V.T.V.
HS.V.F.V.
D S.V.T.V.
LHF.V.
LD
T.V.
HD
S.V.
FIRST ANGLE METHOD OF PROJECTIONS (FOR L.H.S.V.)
Z1
1 L.H.S.V.
T.V.
L
F.V.
L
X
F.V. Plane
T.V. Plane
L.H.S.V. Plane
Y
D
H
Y
XH
D
5
3
OBJECT IN FIRST
QUADRANT (FOR L.H.S.V.)
(i.e. within planes 1,3 &5)

Fig. 2(c) shows turning of the planes 3 & 5 with their respective hinges, considering plane 1 as fixed plane.
b) F.V is within L & H, T.V is within L & D, While L.H.S.V is within H & D.
It may be noted that :-(a) F.V. (X directional view) is on 1, T.V. (Y
directional view) is on 3, while L.H.S.V (Z1 directional view) is on 5
c) The symbol for Ist angle method of projections
is placed as shown on fig. 2(c)

Fig. 2(c)
X Y3
T.V.
L
1
F.V.
L.H.S.V.D
5
H
Note :-
XY line, boundary of planes 1,3,5 & hinges are not drawn, in actual otho. practice
Symbol here

AIM: Fig. 2(a) shows the Pictorial
(ISOMETRIC) view of a cut
block. Draw its following
orthographic views using Ist angle
method of projections.
I. Front View
II. Top View
III.R. H. S.View

X
Fig 2(b)
7
H
D
R.H.S.V.
Z2
Y
X
1
L
F.V.
3 T.V.
Z2
LD
H
Fig 2(a)
X
Y
YY

Note : Ist angle means, the block is assumed in
front of 1, above 3 and inside 7, as in
fig. 2(b) where the F.V. is projected on
1, seen in X direction, T.V. is projected
on 3, seen in Y direction & R.H.S.V. is
projected on 7, seen in Z2 direction

It may be noted that :-
a) F.V. (X directional view) is on 1, T.V. (Y directional view) is on 3, while R.H.S.V (Z2 directional view) is on 7
Fig. 2(c) shows turning of the planes 3 & 7 with their respective hinges, considering plane 1 as fixed plane.
b) F.V is within L & H, T.V is within L & D, While R.H.S.V is within H & D.
c) The symbol for Ist angle method of projections is
placed as shown on fig. 2(c)

Fig. 2(c)
3
T.V.
L
F.V.
1
X YR.H.S.V.
D
7
H
Note :-
XY line, boundary of planes 1,3,7 & hinges are not drawn, in actual otho. practice
Symbol here

AIM: Fig. 3(a) shows the Pictorial
(ISOMETRIC) view of a cut block.
Draw its following orthographic views
using IIIrd angle method of projections.
I. Front View
II. Top View
III. Left Hand Side View

T.V.
4HL.H.S.V.
6
D
X
Y
Z1
X
Y
2
F.V.
L
Fig 3(b)
Y
Z1X
D
H
L
Fig 3(a)
Plane 4 turned up(above plane 2)
Plane 6 turned side way(towards left side of plane 2)

Note : IIIrd angle means, the block is
assumed behind 2, below 4 and inside
6, as in fig. 3(b) where the F.V. is
projected on 2, seen in X direction,
T.V. is projected on 4, seen in Y
direction & L.H.S.V. is projected on 6,
seen in Z1 direction

c) The symbol for IIIrd angle method of projections is placed as shown on fig. 3(c)
b) F.V is within L & H, T.V is within L & D, While L.H.S.V is within H & D.
Fig. 3(c) shows turning of the planes 4 & 6 with their respective hinges, considering plane 2 as fixed plane.
It may be noted that :-
a) F.V. (X directional view) is on 2, T.V. (Y directional view) is on 4, while L.H.S.V (Z1 directional view) is on 6

T.V.
4
D6
L.H.S.VH
2
F.V.
L
X Y
Fig. 3(c)
Note :-
XY line, boundary of planes 2,4,6 & hinges are not drawn, in actual otho. practice
Symbol here

AIM: Fig. 4(a) shows the Pictorial
(ISOMETRIC) view of a cut block.
Draw its following orthographic
views using IIIrd angle method of
projections.
I. Front View
II. Top View
III.Right Hand Side View

X
Y
X
Y
R.H.S.V.H
8
D
Z2
Fig. 4(b)
Planes 2, 4 & 8 are assumed as transparent
Y
Z2
Fig. 4(a)
X
4
DLT.V.
2 HL
F.V.

Note : IIIrd angle means, the block is assumed
behind 2, below 4 and inside 8, as in fig.
4(b) where the F.V. is projected on 2,
seen in X direction, T.V. is projected on
4, seen in Y direction & R.H.S.V. is
projected on 8, seen in Z2 direction.

b) F.V is within L & H, T.V is within L & D, While R.H.S.V is within H & D.
c) The symbol for IIIrd angle method of projections is placed as shown on fig. 4(c)
Fig. 4(c) shows turning of the planes 4 & 8 with their respective hinges, considering plane 2 as fixed plane.
It may be noted that :-
a) F.V. (X directional view) is on 2, T.V. (Y directional view) is on 4, while R.H.S.V (Z2 directional view) is on 8
XY line & boundary of planes 2,4 & 8 are not drawn, in actual otho. practice

YX
4
T.V.
D
2
F.V.
L
Fig. 4(c)Note :-
XY line, boundary of planes 2,4,8 & hinges are not drawn, in actual otho. practice.
8
R.H.S.V.
H
Symbol here

Step by step procedure
Suggested to prepare
Orthographic views (First angle
method) for The simple
component Shown pictorially in
figure

100
20
80
20
20
40
20
60
R40Ø40
ISOMETRIC ISOMETRIC VIEWVIEW XX

R40
20
100
80ø40
80
20
TOP VIEWTOP VIEW
FRONT VIEWFRONT VIEWR.H.S.VR.H.S.V
SCALE: 1:1SCALE: 1:1
SYMBOLSYMBOL IS IS NOT MARKEDNOT MARKED
20 20
R20

FIGURE SHOWS ISOMETRIC VIEW OF A SIMPLE OBJECT(WITHOUT DIMENSIONS) SHOW ITS THREE ORTHOGRAPHIC VIEWS
Use First Angle Method
1. Front View
2. Top View
3. L.H.S.ViewA
B
a
b
3
c
2
1

F.V
T.V
L.H.S.V.
B
a
bc
32
1
b
3
A

FIGURE SHOWS ISOMETRIC VIEW OF AN OBJECT(WITHOUT DIMENSIONS) SHOW ITS THREE ORTHO GRAPHIC VIEWS
Use Third Angle Method
1. Front View
2. Top View
3. L.H.S.View
1. Front View
2. Top View
3. L.H.S.ViewA
a
b
3 c
2
1

FRONT VIEWL.H.S VIEW
TOP VIEW
A
ab
3
c
2 1

Aim : Figure shows isometric view, of a simple machine component.
Draw its following Orthographic views, & dimension them.
1. Front View2. Top View3. R.H.S. View
Use First Angle Method of projection

10
10
Figure, is the isometric view
10
50
75
40
20
R25
30X
Figure
L = 75+25=100
H = 10+30=40
D=50

R2510
10
20
F.V.
5010
40
25 75
40
T.V.
R.H.S.V.
ORTHOGRAPHIC VIEWS
F.V L=100H=40
T.V L=100D=50
S.V D=50H=40

5
5
45
35
35
30
40
15
10
25 SQ
15 SQ
10
Ø30,Depth 1040 SQ
ISOMETRIC
ORTHO. VIEWS

25 Sq25 Sq
4040
1515
454535353535
15 Sq15 Sq
40 Sq40 Sq
Ø30Ø30
55
1010
3030
1010
551010
R.H.R.H.S.V.S.V.
F.V.F.V.
T.V.T.V.

Figure shows the isometric view of a vertical shaft support.
Draw its all the three views, using first angle method of projections.
Give the necessary dimensions as per aligned system.
Exercise :-

ISOMETRIC ISOMETRIC VIEWVIEW
140
Ø40
Ø64
24
20
10
4850
25

1414
48
70
24
10
Ø40
50
Ø64
30
140
L.H.S.VL.H.S.VFRONT VIEWFRONT VIEW
TOP VIEWTOP VIEW

Isometric view of a rod support is
given.
Draw its all the three orthographic
views, using first angle method of
projections.
Give all the dimensions.
Exercise :-Exercise :-

ISOMETRIC VIEW
16
20
4020
20
20
Ø24
R22
140
40
80 60
30
X

TOP VIEW
R22
2040
10
FRONT VIEWRIGHT SIDE
VIEW
14020
80
SCALE: 1:1
303066
26
30

108
20R20
100
45
16
20
25R8
10
30
30
ISOMETRIC
ORTHO. VIEWS

4530 8
20 25
16
R8
R2030
20
10
100

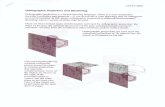
SECTIONING OF A
MACHINE COMPONENT
BY ANY ONE SECTION
PLA NE ,OUT OF THREE
FOLLOWING MENTIONED
SECTION PLANES

(1)BY A VERTICAL SECTION PLANE
(PARALLEL TO PRINCIPLE V.P.)
Hence ,
(a)The real or true shape of the section is
observed in its F.V.
(b)Section plane will be seen as a cutting
plane line (similar to center line ,thick at
ends) with corresponding horizontal vision
direction arrows at the center of thick ends in
its T.V. & S.V.

(2)BY A HORIZONTAL SECTION PLANE
Hence,
(a)The real or true shape of the section is observed in
its T.V.
(b) The cutting or section plane will be observed as a
cutting plane line (similar to center line ,thick at
ends) with the corresponding vertically downward
vision direction arrows at the center of the thick
ends in its F.V. and in S.V.

(3) BY A SECTION PLANE , NORMAL TO BOTH H.P. AND V.P.(i.e. parallel to profile plane or side view plane)
Hence,
(a)The real or true shape of the section is observed in
its S.V.
(b) The cutting or section plane will be observed as a
cutting plane line (similar to center line ,thick at
ends) with the corresponding vertically downward
vision direction arrows at the center of the thick
ends in its F.V. and in T.V.

50
50
50
10
3015
6040
30
15
R12.55
15
30
A
B
X
Figure shows isometric view of a machine component. Draw its
(1)Front view, Top view & L.H.S View, using 3rd angle method of projections.
(2)Sectional Front view, Top view & L.H.S.V., using 3rd angle method of projections.

10
50 50
604030
1525
5
30
50
15
Front View
Top View
L.H.S.View
1.
X
Ortho. Views (No sectioning)

A
B
A
B
X
Retained split of the machine parts
XIt will be nearer to V.P. in 1st angle method & against the vertical plane in 3rd angle method.

50 50
604030
1525
5
10
30
Top View
Sectional Front View -ABL.H.S. View
A B
A
B
B
A
2.(With sectioning)

120120
2828
2020
2020
28286060
Ø30Ø30Ø20
Ø20
1414
77AA
AA
XX
Figure shows the pictorial view of a machine component. Draw its following views as per First angle method of projections
(1) Front view from X direction.
(2) Sectional top view-AA(3) L.H.S. View

120120
2828
2020
Sketch shows the assumed cut model (retained part of the machine component / split against the observer) due to horizontal section plane passing through AB.
XX

120120
6060
2828
Ø30, 7deep Ø20Ø20
2020
2020
1414
F.V.F.V.
Sectional T.V.Sectional T.V.
L.H.S.V.L.H.S.V.
AA AAAA AA

6060
2020
9090
2020
4040
6060
10103030
R10R10
XXA
BFigure shows the pictorial view
of a machine components. Draw its following views, using 3rd angle method of projections.
(1) Front view from arrow X
(2) Top View
(3) Sectional R.H.S.V - AB

B
A
Retained split of the machine parts
Retained split, will be nearer to V.P. in 1st angle method & against the vertical plane in 3rd angle method.
No hatching in this area as not contained in the section plane

8080
2020
2020 2020
6060
9090
4040
3030
AA
AA
AAF.V.
T.V.
SEC.R.H.S.V

Ø30,2 HOLES
7
26
7
15
13
70
15
15
30
Ø30
R20
26
45
A
A

Ø30,2 HOLES
13

1212
2626
1515 7070
1515 15151010
2626
1313
3030
R20R20
ø30
ø30
77
6565
8181
SCECTIONAL F.V.-AASCECTIONAL F.V.-AA
TOP VIEWTOP VIEW
L.H.S.V.L.H.S.V.
7070
1010
00
A A

Aim:-Sketch-1, shows Isometric View of a Aim:-Sketch-1, shows Isometric View of a machine part. Draw its following machine part. Draw its following orthographic views using third angle orthographic views using third angle method of projections, giving dimensions.method of projections, giving dimensions.
(1) Sectional F.V.-AA(1) Sectional F.V.-AA
(2) T.V.(2) T.V.
(3) L.H.S.V(3) L.H.S.V
AA
AA
1414
88
6565
Φ20Φ20R35
R35
Φ36Φ36
7070100100
AA
AALEFT HAND SIDE VIEWLEFT HAND SIDE VIEW SECTIONAL FRONT VIEW AASECTIONAL FRONT VIEW AA
TOP VIEWTOP VIEW
XX
SCALE:- 1:1SCALE:- 1:1SYMBOL OF PROJECTION METHOD, NOT SHOWNSYMBOL OF PROJECTION METHOD, NOT SHOWN
Sketch-1Sketch-1
1414
3030
1414
7070
3434
2 HOLES,Ö 2 HOLES,Ö 1414
Ö36Ö36
Ö20Ö20
R35R3588
101000
1414
6565
1414 `̀
100
100
App
rox.
25A
ppro
x.25
AAAA
SOLUTION`SOLUTION`
1414
14141414
88
3030

7070 1414
14141414
88
100100
AA
AALEFT HAND SIDE VIEWLEFT HAND SIDE VIEW SECTIONAL FRONT VIEW AASECTIONAL FRONT VIEW AA
TOP VIEWTOP VIEWSCALE:- 1:1SCALE:- 1:1
SYMBOL OF PROJECTION METHOD, NOT SHOWNSYMBOL OF PROJECTION METHOD, NOT SHOWN
SOLUTION`SOLUTION`
App
rox.
25A
ppro
x.25
AAAA
100
100
1414
88
6565
Φ20Φ20R35
R35
Φ36Φ36
2 HOLES,Ö 2 HOLES,Ö 1414
XX
3434
Φ36Φ36
Φ20Φ20
R35R35
AA
AA
Aim:-Sketch-1, shows Isometric View of a Aim:-Sketch-1, shows Isometric View of a machine part. Draw its following machine part. Draw its following orthographic views using third angle orthographic views using third angle method of projections, giving dimensions.method of projections, giving dimensions.(1) Sectional F.V.-AA(1) Sectional F.V.-AA
(2) T.V.(2) T.V.
(3) L.H.S.V(3) L.H.S.V
1414
3030
Hatch (section) lines, to be kept at 1 to 1.5 mm apart, Hatch (section) lines, to be kept at 1 to 1.5 mm apart, at 45° normally, but depends on areas to be hatched. at 45° normally, but depends on areas to be hatched.

PROBLEM
Sketch, shows isometric view of a machine part.Draw its (1) F.V. or SEC. F.V.
(2) T.V.
(3) R.H.S.V.Use third angle method of orthographic projection. Dimension the view as per the align system.

R30
ø30
40
12
302045
20
100100
A
B
15
20
R20
Given Given Isometric Isometric viewview
L=100, D=100 & H= 100L=100, D=100 & H= 100

ø30
2045
1520
20
100
100
40
R30
100
12
60
R.H.S. VIEWR.H.S. VIEW FRONT VIEW FRONT VIEW
TOP VIEWTOP VIEW30
R20

A
B
2045
1520
20
100
100
40
ø40
R30
R20
30
100
12
BBR.H.S. VIEWR.H.S. VIEWSEC. FRONT VIEWSEC. FRONT VIEW
AATOP VIEWTOP VIEW
BBAA
60

The following figure shows the isometric view of a machine componentDraw its
1)Front view (without section &with section)2)Top view3)L.H.S view
Use First angle method of projections and dimensioning using aligned system only
PROBLEM - 1

140
25
45
12.5
12.5
35
60
55
60°
R 25
25 ,10 deep 2
5
6Web 10 th
ick
15
10
A
B
X
20
15
Z1

R 25
TOP VIEW
55
140
20
70
80
25
4525 60
451
2.5
60
10
10
6
10
10
Ø25
FRONT VIEW L.H.S. VIEW

B
55
140
20
70
80
R 25
25
45
25 60
451
2.5
60
A
B
A10
10
6
10
10
Ø25
SECTIONAL FRONT VIEW -ABL.H.S. VIEW -AB
TOP VIEW

HALF SECTION
SPECIALSECTIONS

A
C
B
HALF SECTIONAL F.V.-AB HALF SECTIONALLEFT S.V.-BC
TOP VIEW
In half section the hidden line should be used only on Un sectioned side of the view, provided that they are necessary for dimensioning or for clarity.

REMOVED & REVOLVED SECTIONS
SPECIAL SECTIONS

REMOVEDSECTION
REVOLVEDSECTION
REMOVEDSECTION

REVOLVED SECTION

REMOVED SECTION

REMOVED SECTIONS

NOTE:- (As per Previous I S 696 – 1972 Page 38)
When the cutting plane passes (contains) the center line of such elements as, Shafts, bolts, nuts, rods, rivets, keys, pins, pulley arms, spokes, webs (ribs), screws, ball or roller bearings or similar shapes - no section lining or sectioning is needed for the objects , i.e. the hatching should be eliminated.(See the next demonstrating exercises following the above rule)

Vertical Collared Shaft (supported on webbed and drilled flange) in Conventional section in F.V., along withthe T.V.
Note:- As a rule, all the hidden lines should be omitted from a sectional view. The only exemption is where the hidden lines are absolutely Indispensable for clarification or for dimensioning.
Actual or true projections are not preferred to draw

Section lines are to be staggered as
shown at R
OFFSET SECTION: The path of the cutting plane is bent to pass through features not located in a straight line, i.e. it is offset to pass through both principle features of the object. Example is shown below in Ex. 1 & Ex. 2.
B
BEx. 1.
R

AA
P Q
F.V (SECTION –AA)
Section lines are to be staggered as shown at P,Q
Ex. 2.
Off set sectioning

pulley
Tap bolt(fastener)
shaft
Shaft and pulley partly broken out to show internal fastening
This is used to show only a desired features of the object . No cutting plane lines are necessary , shown by wavy line
Partial (broken, local or Zonal)
Section.
See Ex. A,B & C
Ex. A

Partial (broken, local or Zonal)
Section.
Ex. B

SPECIAL SECTION SECTION IN TWO INTERSECTING PLANES
A
B
SEC. F.V. - ABR.H.S.V.

SPECIAL SECTION
Cross hatching of adjacent parts See at (1) & (2)
(1)

Hatching more than two adjacent components at (2)
(2)
A
B
C
(hatchedat 60 )
D45
45
hatchedat 30on D
SPECIAL SECTION

A B
F.V.
SEC.T.V.Two vertical plates ,fastened by a horizontalrivet is shown in its F.V. & T.V., cut by horizontalsection plane. Note the rivet is shown in section inT.V.

CONVENTIONAL REPRESENTATIONOF CYLINDER IN WHICH CIRCULAR OR RECTANGULAR HOLE CUT IN ITS F.V.Note:- The actual shape of hole or slot may be understood fromits side view.
For circular hole
For rectangular slot
ACTUALPROJECTIONS

AUXILARY SECTION
A
SECTION AA
A

It is the sectional view not in principal planes. it may be full, half ,broken out , removed or revolved. The section should be shown in its normal auxiliary position and clearly identified with a cutting plane with letters
AUXILIARY SECTION (as specialsection)

A
A
BC D
DCB
SECTIONAA SECTION
BBSECTION
CC
SECTIONDD
SUCCESSIVE SECTIONS (REMOVED TYPE)

A
A
BC D
DCB
SUCCESSIVE SECTIONS (REMOVED TYPE)

SECTIONAA SECTION
BBSECTION
CCSECTION
DD
SUCCESSIVE SECTIONS (REMOVED TYPE)