Spheres of the Earth Atmosphere Hydrosphere Lithosphere Weather Dynamics Unit Science 10.
Maps Pg. 21. Overview of Earth Science Formation of Earth- nebular hypothesis; formed from a...
-
Upload
gerald-bradley -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
1
Transcript of Maps Pg. 21. Overview of Earth Science Formation of Earth- nebular hypothesis; formed from a...

Maps
Pg. 21

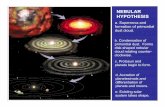
Overview of Earth Science• Formation of Earth- nebular hypothesis;
formed from a rotating cloud made of H and He
• 4 major spheres- – Hydrosphere: all water on Earth – Atmosphere- gasses surrounding Earth– Geosphere- Rocks, minerals, the interior– Biosphere- all life on Earth

Determining location
• Use two measurements to measure location: latitude and longitude
• Measured in degrees• Latitude is position north or south of the
equator (lines run horizontally)– 0-90 degrees N & S
• Longitude is position east or west of the prime meridian (lines run vertically)– 0 and 180 degrees W & E

Global Grid
• Equator marks 0o latitude– Divide northern and southern hemispheres
• Prime meridian marks 0o longitude– Divides eastern and western hemispheres– Runs through Greenwich, England
• Can mark absolute location of something– Latitude then longitude (32o N, 81o W)


Globes
• Accurate way to map Earth in the way it truly is, just scaled down
• Problem: not specific enough to be useful for everyday

The Mercator Projection• Gerardus Mercator created the map to help
sailors navigate around Earth• Lines of longitude are parallel• Sizes and distances distorted, but directions
accurate

Robinson Projection map• Show most distances, sizes, and shapes
accurately.• Distortions around the edges• Shows whole globe as a flat map

Conic Projection Maps• Made by wrapping a cone of paper around a
certain latitude• Almost no distortion along line of latitude,
but much away• Used to make road and weather maps

Gnomonic Projections• Place a piece of paper on a globe so it touches
one point• Points and lines are then projected on the paper• Shows with accuracy the shortest distance
between two points

Topographic maps
• Represents Earth’s 3D surface in 2D• Shows elevation using contour lines• Also show water, roads, buildings, political
boundaries, etc.• Very useful


Contour lines
• Every position along a single line represents the same elevation
• Every 5th line is bold and has the elevation labeled called index contour
• Contour interval tells you difference between adjacent lines
• Form a V when crossing a stream– Apex of the V points up stream



Steepness• Can be determined by examining closeness
of lines• Closer the lines, steeper the slope• Contour lines that form a circle represent a
hill• A depression is represented by circles with
hash marks that point to the center• Lines never intersect unless there is a
vertical cliff


Scale• Need to represent large areas• Scale them down• Use ratios to represent scale (1:24,000)• Bar scales are represented on maps so you ca
measure distance

Geologic Maps
• Shows the type and age of exposed rocks• Each rock formation is assigned a color and
sometimes a pattern