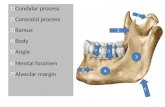
Mandible
-
Upload
rishi-pokhrel -
Category
Documents
-
view
401 -
download
3
Transcript of Mandible

CAPT RISHI POKHREL
COL RAJAN BHATNAGAR
COL SUSHIL KUMAR
“A Study of Sexual Dimorphism
in
Human Mandibles
using
Multivariate Discriminant Functional Analysis”

INTRODUCTION
Determination of sex from skeletal remains – initial step in determination of identity
Human mandible - among the strongest bones
- significant sexual dimorphism
Multivariate Discriminant Functional Analysis (MDFA)
– best among metric methods.
Population: Marathwada region of Maharashtra.

AIMS & OBJECTIVES
To test sexual dimorphism in mandibles of population under
study.
To identify parameters of mandible that show maximum sexual
dimorphism
To determine population specific cut off point and constants for
MDFA.
To test the accuracy of MDFA.

MATERIALS & METHODS
Cross sectional, observational study
Adult mandibles of known sex from Anatomy department, GMC,
Aurangabad.
Sample size : 103
Males: 77
Females : 26
Exclusion criteria
Incomplete
Gross asymmetry
Extreme of ages
Male; 77
Female; 26



MATERIALS USED

MATERIALS USED

PARAMETERS USED
Parameter (Midline) Abbn. Parameter (Bilateral) Abbn.
Symphyseal height ID GN Height of mandibular body HT
Bicondylar breadth CDL CDL Mandibular thickness at mental foramen
MB
Bigonial breadth GO GO Minimum ramus breadth MnRb
Mandibular length ML Maximum ramus breadth MxRB
Intermolar distance IMD Mandibular or gonial angle A
Intercanine distance ICD
Arch perimeter AP Units mm, degree, cms




STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
MDFA (multivariate discriminant function analysis)
Stepwise MDFA
Analysis : SPSS 19

OBSERVATIONS&
RESULTS

ID GN HT LT MB LT GO GO CDL CDL Mn RB Mx RB Mx RH ML A IMD ICD AP 0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
MALES
FEMALES
MEAN VALUES

DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS
Variable TOTAL (N = 103) MALE (N = 77) FEMALE (N = 26) Pvalue
MEAN SD MEAN SD MEAN SD
ID GN 27.06 4.27 27.55 4.25 25.62 4.070.0456
HT 26.48 3.48 26.77 3.46 25.60 3.430.138
MB 10.60 1.33 10.74 1.39 10.17 1.050.059
GO GO 100.20 9.86 101.90 8.99 95.15 10.740.002
CDL CDL 115.63 9.40 116.86 7.76 111.96 12.60.021
Mn RB 33.61 5.69 35.35 5.38 28.47 2.74<0.001
Mx RB 43.03 6.27 44.83 5.85 37.69 4.09<0.001
Mx RH 63.17 7.25 64.13 6.64 60.32 8.320.020
ML 66.62 7.00 68.22 6.31 61.89 6.91<0.001
A 118.79 6.87 117.84 6.67 121.58 6.810.016
IMD 36.55 5.87 36.80 5.88 35.80 5.900.456
ICD 23.10 7.01 23.91 7.26 20.68 5.650.042
AP 7.011 1.00 7.08 1.06 6.80 0.810.228

STEP 1: MDFAMultivariate discriminant function
f (x) = b0 + b1x1 + b2x2 + b3x3 + --------- + b13x13.
Where, f (x) : MDFA score
b0 : constant (-7.704)
b1 to b1 : raw coefficients
x1 to x13 : variables values
Parameter b
ID GN -0.037
HT 0.076
MB 0.267
GO GO -0.050
CDL CDL 0.041
Mn RB -0.185
Mx RB -0109
Mx RH 0.053
ML -0.015
A 0.101
IMD 0.053
ICD 0.033
AP -0.301
f(x) at group centroid for males = - 0. 556
f(x) value at group centroids for females = 1.648
Demarcation point = 1.09

STEP 2: STEPWISE MDFA A combination of MnRB and A was found to be best among
all.
The function
f (y) = b0 + b1 (MnRB) + b2 (A)
b0 = 3.755
b1 = 0.202
b2 = - 0.089
f(x) at group centroid for males = 0.435
f(x) value at group centroids for females = -1.288
Demarcation point = - 0.9628

METHOD Male Female Male % Female % Overall %
MDFA 72/77 21/26 93.5 80.8 90.3
S- MDFA 76/77 12/26 98.7 46.2 85.4
RESULTS
Male Female Overall0
102030405060708090
100
MDFA S-MDFAP
erce
ntag
e

FUNCTION FOR MDFA
f(x) = (- 0.704) + (-0.037) ID GN + (0.076) HT + MB (0.267) +GO GO (-
0.050) + CDL CDL (0.041) + MnRB (-0.185) + MxRB( -0109) + MxRH (0.053)
+ ML (-0.015) + A (0.101) + IMD (0.053) + ICD (0.033) + AP (-0.301)
f(x) > 1.09, the mandible belongs to female
f(x) < 1.09, the mandible belongs to male
Accuracy : 90.3%

FUNCTION FOR S - MDFA
f(y) = 3.744 + (0.202) MnRB + (-0.089) A
If, f(y) > - 0.9628 the mandible belongs to male and if
f(y) < - 0.9628, the mandible belongs to female
Accuracy: 85.4%

DISCUSSIONAuthor (s) with population No of Parameters
used
Accuracy %
(Hanihara, 1959), Japan 4 88.6
(Giles, 1964), USA 3 – 8 82.0 – 88.0
(Potsch-Schneider et al., 1985), Germany 17 71.6 - 81.7
(Steyn & Iscan, 1998), South Africa 5 81.5
(Barthélémy et al., 1999), France 2 - 7 87.3
(Muñoz et al., 2001), Spain 1 - 14 78.3 - 88.7
(Vodanović et al., 2006), Croatia 1-9 74.12 – 92.06
(Simona et al., 2007), Romania 5 - 7 86.0
(Saini et al., 2011), Varanasi, India 1 - 5 60.3 - 80.2
Current study, 2012, Maharashtra,
India
2 - 13 85.4 – 90.3

Saini et al, 2011, Indian Population (Varanasi)
Functions and Variables Avg. Acc. %
Max. ramus br. + min. Ramus. br. + condylar ht. + projective ht. +
coronoid ht.
80.2
Max. ramus br. + min. ramus br. + coronoid ht. 80.2
Condylar ht + projective ht + coronoid ht. 76.7
Coronoid ht. 74.1
Condylar ht. 72.4
Projective ht. 68.1
Max ramus br. 62.1
Min ramus br. 60.3
Our study Maximum 90.3% Minimum 85.4%
Sample size : Total 116, Male 92, Female 24

CONCLUSIONS
Mandibles of population under study show sexual
dimorphism.
MnRB and A show maximum sexual dimorphism.
Population specific coefficients, constants and
demarcation points for MDFA are derived.
Accuracy of sexing is comparable to other
populations.

Acknowledgement
HOD and Department of Anatomy,
Government Medical College,
Aurangabad

DISCUSSION