Age Changes in Mandible
-
Upload
arsalan-r-khan -
Category
Documents
-
view
1.300 -
download
19
Transcript of Age Changes in Mandible

AGE CHANGES IN AGE CHANGES IN MANDIBLEMANDIBLE
SADAF KAZMISADAF KAZMI
BDS – 1BDS – 1stst year year ROLL NO : 01ROLL NO : 01

The mandible, from Latin mandibula,"jawbone" or inferior maxillary bone is, together with the maxilla, the largest and strongest bone of the face
INTRODUCTION TO MANDIBLEINTRODUCTION TO MANDIBLE

INTRODUCTIONINTRODUCTION
This U-shaped bone forms the skeleton of the This U-shaped bone forms the skeleton of the lower jaw.lower jaw.
The mandibular teeth project superiorly from The mandibular teeth project superiorly from their sockets in the alveolar processes of the their sockets in the alveolar processes of the mandible.mandible.
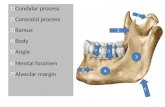
It develops from the first pharangeal arch.It develops from the first pharangeal arch. Mandible has 2 parts , a horizontal Mandible has 2 parts , a horizontal bodybody and 2 and 2
vertical vertical rami.rami.

Introduction(contd.)Introduction(contd.)
The superior border of the ramus has 2 The superior border of the ramus has 2 processes : a posterior processes : a posterior condylar processcondylar process with a with a condyl and a neck , and a sharp anterior condyl and a neck , and a sharp anterior CoronoidCoronoid process. process.
Both the processes are separated from each Both the processes are separated from each other by other by mandibular notchmandibular notch..
Mandible articulates only with temporal bone Mandible articulates only with temporal bone on either sides by the condylar head.on either sides by the condylar head.


AT BIRTHAT BIRTH
At birth, the body of the At birth, the body of the mandible is a mere mandible is a mere shell, containing the shell, containing the sockets for the two sockets for the two incisors, the canine and incisors, the canine and the two deciduous molar the two deciduous molar teeth.teeth.
Only composed of Only composed of alveolar part.alveolar part.

AN ADULT MANDIBLEAN ADULT MANDIBLE

AT BIRTH (cont.)AT BIRTH (cont.)
The mental foramen The mental foramen opens beneath the opens beneath the socket of the first socket of the first deciduous molar tooth. deciduous molar tooth. It is present near the It is present near the lower border of the lower border of the body of mandible.body of mandible.
The mandibular canal is The mandibular canal is of large size and also of large size and also runs near the lower runs near the lower border of the mandible.border of the mandible.

AT BIRTH (cont.)AT BIRTH (cont.)
The angle of mandible The angle of mandible is obtuse is obtuse (140°-175°).(140°-175°).
The condylar process is The condylar process is nearly inline with the nearly inline with the body .The coronoid body .The coronoid process is of process is of comparatively larger comparatively larger size and projects above size and projects above the level of the condyl.the level of the condyl.

GROWTH OF MANDIBLEGROWTH OF MANDIBLE
FORMATION OF SYMPHYSIS MENTI :-FORMATION OF SYMPHYSIS MENTI :-
The two segments of the bone become The two segments of the bone become joined at the symphysis, from below upward, joined at the symphysis, from below upward, in the first year; but a trace of separation may in the first year; but a trace of separation may be visible in the beginning of the second year, be visible in the beginning of the second year, near the alveolar margin. near the alveolar margin.

GROWTH CHANGESGROWTH CHANGES
ELONGATION :-ELONGATION :- BODY :-BODY :- The body becomes elongated in its whole length, but The body becomes elongated in its whole length, but
more especially behind the mental foramen, to more especially behind the mental foramen, to provide space for the three additional teeth developed provide space for the three additional teeth developed in this partin this part..
RAMUS:-RAMUS:- The elongation of ramus is also required ,for the jaws The elongation of ramus is also required ,for the jaws
must separate to allow room for the eruption of the must separate to allow room for the eruption of the teeth.teeth.

GROWTH CHANGESGROWTH CHANGES

GROWTH CHANGESGROWTH CHANGES
DEPTH:-DEPTH:- owing to increased growth of the owing to increased growth of the alveolar partalveolar part, ,
to make room for the roots of the teeth.to make room for the roots of the teeth. by thickening of the by thickening of the subalveolar portionsubalveolar portion which which
enables the jaw to withstand the powerful enables the jaw to withstand the powerful action of the masticatory muscles.action of the masticatory muscles.
The alveolar portion is the deeper of the two, The alveolar portion is the deeper of the two, and, consequently, the chief part of the body and, consequently, the chief part of the body lies above the oblique line.lies above the oblique line.

GROWTH CHANGESGROWTH CHANGES
WIDTH:-WIDTH:-With the growth in the width of the With the growth in the width of the face , the mandible widens correspondingly. face , the mandible widens correspondingly. It It is suggested that during postnatal growth, an is suggested that during postnatal growth, an increasing load from the masticatory occlusal increasing load from the masticatory occlusal forces might influence the alveolar bone forces might influence the alveolar bone remodeling in the mandibular body, thus remodeling in the mandibular body, thus producing or allowing a gradual permanent producing or allowing a gradual permanent outward bending of the right and left outward bending of the right and left mandibular halves.mandibular halves.

An epiphysis at the neck of the mandible allows moulding according to the changing size of the articular cartilage.
The mandibular canal and the mental foramen gradually start shifting upwards from the inferior border of the body of mandible.
The angle becomes less obtuse, owing to the separation of the jaws by the teeth; about the fourth year it is 140°.

IN ADULT :-IN ADULT :-
In the adult , the In the adult , the alveolar and the sub-alveolar and the sub-alveolar portions of the alveolar portions of the body are of equal depth.body are of equal depth.
The mental foramen The mental foramen opens midway between opens midway between the upper and the lower the upper and the lower borders of the body. borders of the body.

AN ADULT MANDIBLEAN ADULT MANDIBLE The mandibular canal The mandibular canal
runs nearly parallel to the runs nearly parallel to the mylohyoid line.mylohyoid line.
The ramus is almost The ramus is almost vertical in direction, the vertical in direction, the angle measuring from angle measuring from 110° to 120°.110° to 120°.
Due to the upward Due to the upward projection or growth of projection or growth of the condyle, it comes to the condyle, it comes to lie at a level superior to lie at a level superior to the coronoid process.the coronoid process.

AN EDENTULOUS MANDIBLEAN EDENTULOUS MANDIBLE
Mandible becomes Mandible becomes greatly reduced in greatly reduced in size.With the loss of the size.With the loss of the teeth, the alveolar teeth, the alveolar process is absorbed, process is absorbed, and, consequently, the and, consequently, the chief part of the bone is chief part of the bone is below the oblique line below the oblique line i.e., sub-alveolar part. i.e., sub-alveolar part.

AN EDENTULOUS MANDIBLEAN EDENTULOUS MANDIBLE
The mandibular canal, The mandibular canal, with the mental foramen with the mental foramen opening from it, is close opening from it, is close to the alveolar border. to the alveolar border.
The ramus is oblique in The ramus is oblique in direction, the angle direction, the angle measures about 140°, measures about 140°, and the neck of the and the neck of the condyle is more or less condyle is more or less bent backward.bent backward.

THANK YOUTHANK YOU