Lipids Worksheet
-
Upload
natalies-twin -
Category
Documents
-
view
36 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Lipids Worksheet
CHEM 121 Lipids Worksheet
Natalie Pemberton-Parris00027917
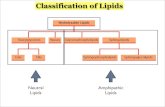
CHEM 121 Lipids Worksheet (53 marks)1. Some lipids are considered to be amphipathic because they have a polar and non-polar part.2. For a 12 carbon fatty acid, what is the value of n? 103. Is the fatty acid in figure 1 a saturated or unsaturated fatty acid?Saturated
Figure 14. Is a cis fatty acid saturated or unsaturated?Unsaturated 5. Is a Trans fatty acid saturated or unsaturated?Unsaturated
6. Listed below are three fatty acids:
18:2 cis 9, 12
18:0
18:2 Trans 9, 12
Write them in order of increasing melting point (Lowest ( Highest)
18:2 cis 9, 12-----> 18:2 Trans 9, 12 ----> 18:07. Listed below are three fatty acids:
18:1 cis 9 oleic acid
18:2 cis 9, 12 linoleic acid
18:3 cis 9, 12, 15 (-linolenic acid
Write them in order of decreasing melting point (Highest ( Lowest)
18:1 cis 9 oleic acid ---> 18:2 cis 9, 12 linoleic acid ---> 18:3 cis 9, 12, 15 a-linolenic acid
8. (a) Draw the structure of the fatty acid 18:3 cis 9,12,15(b) Rename the above fatty acid using the ( symbol
18: 3 cis (3, 6, 9
9. A glyceride is a molecule made from a linkage(s) between two other molecules. State the names of those two molecules.
1. Glycerol
2. Fatty Acid10. Name the important linkage which is present within a glyceride.
Esther Linkage11. A diglyceride contains how many of the linkages mentioned in question 9 and 10.
1 glycerol, 2 fatty acids and 2 Esther linkages
12. A Glycerophospholipids is made up of a one glycerol backbone, two fatty acids and a phosphate group which is linked to a variable group.13. Name two important linkages present within a Glycerophospholipids
1. Ester Linkage
2. Phosphate Ester Linkage14. The Sphingolipids ceramide is formed between a sphingosine molecule and an N-linked fatty acid molecule.15. The linkage formed from the reaction of the amino group on sphingosine and a carboxylic group from another molecule is called an amide bond linkage. 16. A cholesterol ester molecule is formed from a carboxylic group of the fatty acid molecule and a hydroxyl group of a cholesterol.17. Describe the structure of a lipoprotein.The core of these spherical particles contains primarily cholesteryl ester and triglyceride. These insoluble molecules are surrounded by a coating of proteins and phospholipids that are amphipathic; that is, they have both polar and nonpolar regions.18. What is the function of a lipoprotein?
Lipoproteins transport triglycerides, cholesterol and cholesteryl esters through the bloodstream.19. Lipoproteins are found traveling mainly through the bloodstream20. Chylomicrons transport mainly the lipid triglycerides21. Chylomicrons are produced in the small intestine22. What Apo lipoprotein does a nascent (newly-formed) chylomicron need to obtain in order for it to be able to get rid of its main lipid content? Apo c-II 23. From which other lipoprotein does the nascent chylomicron obtain the Apo lipoprotein in question 22? HDLs24. What is the function of the Apo lipoprotein Apo C-II?(1mark)
Activates an enzyme Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL) and return to HDLs25. What is the function of the Apo lipoprotein Apo E?(1mark)Apo E acts as a navigator to direct chylomicrons to the liver cells.26. Where is the Apo E receptor located?(1 mark)On the cell membrane of the Liver cell27. Where are VLDLs produced?(1 mark)In the Liver28. VLDLs obtain Apo-C-II and Apo E from which other lipoprotein?HDLs29. How are VLDLs converted into IDLs?(1 MARK)Apo C-II activates the enzyme Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL). It then hydrolyzes triacylglycerol into fatty acids and glycerol, thereby converting VLDLs into IDLs30. How are IDLs converted into LDLs?(1 mark)
Apo C-II and some Apo E return to HDLs, thereby converting IDLs into LDLs31. Cholesterol is produced naturally in cells and so there is no need for LDLs to be too high.a. Cholesterol is stored as cholesterol esters in cells(1 mark)b. Cholesterol is converted into its storage product in cells by the enzyme ACAT) (1mark)c. High levels of LDLs can lead to which condition?Atherosclerosis (1 mark)32. HDLs are released from the liver and small intestine.(2 marks)33. HDLs take up excess cholesterol from peripheral tissues, other lipoproteins and cell membranes.(3 marks)34. The Apo lipoprotein Apo A1 is responsible for activating the enzyme PCAT present on HDLs. What is the function of PCAT? To esterify cholesterol to cholesteryl esters. (1 mark)35. LDL lipoproteins can be modified by chemical reactions such as oxidations. Such modified LDLs lead to the formation of what medical condition?(1mark) Atherosclerosis 36. Lipoprotein (a) is associated with what medical condition? Coronary artery disease (1 mark)37. Two factors that increase levels of Lipoprotein (a) are:(2 marks)1. A diet high in trans-fatty acids2. Genetics