Lipids. Lipids = fats that are mostly energy storing molecules Hydrophobic Two “Monomers” =...
-
Upload
collin-horn -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of Lipids. Lipids = fats that are mostly energy storing molecules Hydrophobic Two “Monomers” =...

Lipids

Lipids = fats that are mostly energy storing molecules
Hydrophobic
Two “Monomers” = glycerol and fatty acids
Lipids

Monomers
Glycerol contains the hydroxyl (OH) group.
Fatty acids contain the carboxyl (COOH) group.

Structure of a Lipid
Dissolves in water (hydrophilic)
Does not dissolve in water (hydrophobic)

Saturated vs. Unsaturated Fatty Acids

Saturated Fats have a strong link to arthrosclerosis (hardening of the arteries due
to plaque buildup). Take a look at the structure of these two fats, and explain why.

Clogged Arteries

Steroids• Lipids where carbon skeleton contain four rings

Review Guide!!!!
2. Lipids

Lipids (Fats/Oils) – Section 3.8 pg. 40
• A.K.A. ______________________• Structure:
– Glycerol “head” and 3 fatty acid tail
• _________________________________________________
• __________________________________________________
• __________________________________________________
CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2
CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2
CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2

• Function: _________________________– 9 calories / gram of triglyceride– Now make a Venn diagram
• Saturated vs. Unsaturated

Saturated Fats
• Saturated:– Straight tails– Not healthy– No double bonds in the fatty acid tail – Solid at room temperature– Dense, compact, can pack together easily. (EW!)
• Ex - Butter

Unsaturated Fats
• Contain C=C double bonds in one or more of the fatty acid tails
• Liquid at room temperature• Better for you
– Ex – Olive Oil• Bent Tails

Both
• Glycerol head with three fatty acid tails• 9 calories/gram• Energy storage• Contain Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), & Oxygen (O)• Triglycerides

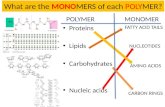
Proteins

Proteins Monomers: Amino AcidsStructure of Amino
Acids: Amino Group, Carboxyl Group, and an
R GroupR Group: chemical group that varies between the 20 different amino acids
(everything else stays the same)

Protein FunctionMost important role = Enzymes!
An enzyme is a chemical catalyst that speed up and regulate almost all
chemical reactions in cells.
Structure = Function

Globular Proteins Fibrous Proteins
• Found in enzymes, some hormones, and hemoglobin
• Can dissolve in water (hydrophilic)
• Found in skin, tendons, bones, and muscles
• Do not dissolve in water (hydrophobic)

Linking Amino Acids!

Review Guide!!!!
3. Proteins

PROTEINS
• Always contain nitrogen.• Amino Acids are the building blocks.
Amino group Carboxyl group

proteins
• Amino acids are connected through: Dehydration synthesis
• Dipeptides are made from _2_ amino acids
• Polypeptides are made from _3+_ amino acids
• The long chains “scrunch up” through chemical bonds and form a ribbon structure. The shape of a protein determines its function.

Functions of proteins
1. Enzymes!!!! MOST important function
2. Structural proteins (hair, ligaments, etc.)
3. Contractile proteins (muscles)
4. Defensive proteins (antibodies)
5. Signal proteins (hormones / messengers)
6. Receptor proteins (signal transmitters)
7. Transport proteins (deliver O2 around the body)
8. Storage proteins (egg yolk, milk, plant seeds, etc.)

Nucleic Acids

Nucleic Acids: 3.14 PG 46Two Types: ● DNA = Deoxyribonucleic acid● RNA = Ribonucleic acidMonomers: Nucleotides Key Functional Group: Phosphate Group

More information to come in our DNA unit!
- Complimentary bases
- Transcription
- Translation

Review / Studying
• Please use the following materials to review for this unit test:
– PowerPoint Presentation Notes!– Organic Molecules Review Guide!– Organic Molecules Worksheet!– Biochemistry Study Guide!