Lipids
description
Transcript of Lipids

2005-2006
Lipids

5. lipids:1. have little or no affinity for water2. contain C, H, O sometimes P 3. H:O never 2:14. types – fats, oils, phospholipids, steroids,
and waxes
neutral lipids (a.k.a. triglycerides, fats, or oils) =
3 fatty acids + 1 glycerol molecule

2005-2006
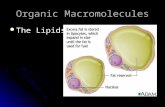
LIPIDS Lipids are composed of C, H, O (same elements
as carbs but very diff structure/proportions & therefore very different biological properties)long hydrocarbon chain
Diverse groupfatsphospholipidssteroids
Do not form polymersbig molecules made of
subunit smaller moleculesnot a continuing chain

FATS Structure: what makes them
hydrophobic?: carboxyl groupglycerol (3C alcohol) + fatty acid
dehydration synthesis
fatty acid = long HC “tail” with COOH group at “head”

FAT Triacylglycerol (big fat molecule!!)
3 fatty acids linked to glycerol ester linkage = between OH & COOH

DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS (PULLING THE WATER OUT TO FREE UP THE BOND)

FATS (Q: WHAT HAPPENS WHEN YOU ADD OIL TO WATER?)
Long HC chainpolar or non-polar?hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
Function:energy storage
very rich 2x carbohydrates
cushion organs insulates body
think whale blubber!
“Let’s go to the video tape!”(play movie here)

SATURATED FATS AND UNSATURATED FATSSaturated no double bonds found
between carbon atoms on the fatty acid chains
solid at room temperature at room temp., the
molecules are packed closely together
high melting point i.e. butter
Unsaturated one or more double bonds
present between carbon atoms on the fatty acid chains
liquid at room temperature at room temp., the
molecules cannot pack together closely enough to solidify because of the kinks caused by the double bonds
low melting point i.e. olive oil

SATURATED OR UNSATURATED?
a)b)
c)
d)

SATURATED FATS All C bonded to H No C=C double bonds
long, straight chainmost animal fats solid at room temp.(mostly animal fats)
contributes to cardiovascular disease (atherosclerosis) = plaque deposits

UNSATURATED FATS C=C double bonds in the fatty acids
plant & fish fats vegetable oilsliquid at room
temperaturethe kinks made by double bonded C prevent the molecules from packing tightlytogether

HYDROGENATED FATS (TRANS FATS)
i.e. peanut butter, margarine
unsaturated fats have been synthetically converted to saturated fats by adding hydrogen
prevent lipids from separating out in liquid (oil) form

2005-2006
STRUCTURE OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS glycerol + 2 fatty acids + PO4
PO4 negatively charged
other small molecules may also be attachedadenine (ATP)

THE ARRANGEMENT OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS IN CELL MEMBRANES
this arrangement occurs spontaneously when added to water
hydrophobic fatty acids meet “tail-to-tail”
hydrophilic head groups interact water
major components of all cell membranes

2005-2006
PHOSPHOLIPIDS Hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
fatty acid tails = hydrophobicPO4 = hydrophilic headdual “personality”
interaction with H2O is complex& very important!

2005-2006
PHOSPHOLIPIDS IN WATER Hydrophilic heads attracted to H2O Hydrophobic tails “hide” from H2O
self-assemble into aggregates micelleliposomeearly evolutionary stage of cell?

2005-2006
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? Phospholipids define outside vs. inside Where do we find phospholipids in cells?
cell membranes

2005-2006
PHOSPHOLIPIDS & CELLS Phospholipids of cell membrane
double layer = bilayerhydrophilic heads on outside
in contact with aqueous solutionhydrophobic tails on inside
form coreforms barrier between cell &
external environment

CHOLESTEROL, A STEROID a molecule from
which other steroids, including the sex hormones are synthesized
contains four fused (interlocking) rings
a common component of animal cell membranes
high levels of it in the blood may contribute to atherosclerosis

2005-2006
DIVERSITY IN STEROIDS

STEROIDS ex: cholesterol, sex hormones 4 fused C rings
different steroids created by attaching different functional groups to rings
cholesterol

FROM CHOLESTEROL SEX HORMONES What a big difference a little atom can make!

CHOLESTEROL Important cell component
animal cell membranes precursor of all other steroids
including vertebrate sex hormones high levels in blood may contribute to
cardiovascular disease

CHOLESTEROLhelps keep cell membranes fluid & flexible

Let’s build some Lipids!