Levels of Classification …But mostly Domains and Kingdoms…
-
Upload
felicity-reynolds -
Category
Documents
-
view
227 -
download
0
Transcript of Levels of Classification …But mostly Domains and Kingdoms…

Levels of Levels of ClassificationClassification
……But mostly Domains and But mostly Domains and Kingdoms…Kingdoms…

Levels of ClassificationLevels of Classification
Scientists use classification to help study Scientists use classification to help study and organize life on Earth.and organize life on Earth.
There are several levels of classification to There are several levels of classification to further break down how closely organisms further break down how closely organisms are related. The broadest level is at the are related. The broadest level is at the top of the list, the most specific at the top of the list, the most specific at the bottom.bottom.

Levels of ClassificationLevels of Classification
Levels of classification from broadest to Levels of classification from broadest to most specific:most specific:
DomainDomain KingdomKingdom PhylumPhylum ClassClass OrderOrder FamilyFamily GenusGenus SpeciesSpecies

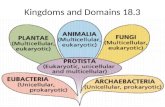
Domains and KingdomsDomains and Kingdoms
Today, a three domain system of Today, a three domain system of classification is commonly used.classification is commonly used.
The three domains are:The three domains are:BacteriaBacteriaArchaeaArchaeaEukaryaEukarya

How are Domains and How are Domains and Kingdoms determined?Kingdoms determined?
Organisms are placed into Organisms are placed into domains and kingdoms based on domains and kingdoms based on 3 things: 3 things:
Their cell type Their cell type How they obtain energyHow they obtain energy The number of cells in their The number of cells in their
bodiesbodies

Cell TypeCell Type
EukaryoteEukaryote: : Cells that have a Cells that have a nucleus.nucleus.
ProkaryoteProkaryote: : Cells that do not Cells that do not have a nucleus.have a nucleus.

How Organism’s Obtain How Organism’s Obtain EnergyEnergy
AutotrophAutotroph: : Organisms capable of Organisms capable of producing their own food from the Sunproducing their own food from the Sun’’s s energy, or from inorganic chemical energy, or from inorganic chemical material.material.
HeterotrophHeterotroph: : Organisms that cannot Organisms that cannot produce their own food and obtain their produce their own food and obtain their energy from eating others.energy from eating others.

Number of CellsNumber of Cells
UnicellularUnicellular: An organism made of just one : An organism made of just one cell.cell.
MulticellularMulticellular: A complex organism made : A complex organism made up of many cells.up of many cells.

The Domains: BacteriaThe Domains: Bacteria
Members of the domain bacteria are Members of the domain bacteria are prokaryotesprokaryotes. These cells do not have a . These cells do not have a nucleusnucleus
In prokaryotes, nucleic acids are not In prokaryotes, nucleic acids are not contained within a nucleus.contained within a nucleus.
Some bacteria are autotrophs while others Some bacteria are autotrophs while others are heterotrophs.are heterotrophs.
All bacteria are All bacteria are unicellularunicellular, meaning they , meaning they are made of just one cell.are made of just one cell.

Domains: ArchaeaDomains: Archaea
Comes from the Greek word meaning Comes from the Greek word meaning ““ancientancient””
Can be found in the most extreme Can be found in the most extreme environments on Earth:environments on Earth:
Hot SpringsHot Springs Very Salty WaterVery Salty Water Swamp landSwamp land Cow intestines!Cow intestines!

Domains: Archaea (cont.)Domains: Archaea (cont.)
Like bacteria, they are Like bacteria, they are unicellular unicellular prokaryotes. Some are autotrophs, some prokaryotes. Some are autotrophs, some heterotrophsheterotrophs
They are classified in a different domain They are classified in a different domain then bacteria because then bacteria because they have a they have a different structure and chemical makeup to different structure and chemical makeup to that of a bacterium.that of a bacterium.

Domains: EukaryaDomains: Eukarya
Eukaryotic cells are those which contain a Eukaryotic cells are those which contain a nucleusnucleus
The domain Eukarya is split into 4 The domain Eukarya is split into 4 kingdoms:kingdoms:
ProtistsProtists FungiFungi PlantsPlants AnimalsAnimals

Kingdom: ProtistsKingdom: Protists
ProtistsProtists: A : A eukaryotic eukaryotic organism that organism that cannot cannot be classified as an animal, plant or fungus.be classified as an animal, plant or fungus.
Members are very different from one another, Members are very different from one another, so it is often referred to as the so it is often referred to as the ““odds and odds and endsends”” kingdom. kingdom.
Can be either an autotroph or heterotroph or Can be either an autotroph or heterotroph or both!both!
Most are unicellular Most are unicellular but but somesome, such as , such as seaweeds, are large seaweeds, are large multicellularmulticellular organisms. organisms.

Kingdom: FungiKingdom: Fungi
Mushrooms, mold, and mildew Mushrooms, mold, and mildew are all are all members of the Fungi kingdom.members of the Fungi kingdom.
Most are multicellularMost are multicellular, but , but some, such as some, such as yeast, are unicellularyeast, are unicellular eukaryotes.eukaryotes.
All fungi are All fungi are heterotrophsheterotrophs. They live . They live almost anywhere on land but very few also almost anywhere on land but very few also live in fresh water.live in fresh water.
Most fungi feed from absorbing nutrients Most fungi feed from absorbing nutrients from dead or decaying organisms.from dead or decaying organisms.

Kingdom: PlantsKingdom: Plants
Dandelions, mosses and peas Dandelions, mosses and peas are all examples are all examples of the plant kingdom.of the plant kingdom.
Plants are all Plants are all multicellular eukaryotesmulticellular eukaryotes, most live , most live on land.on land.
They are They are ALWAYS autotrophsALWAYS autotrophs, and they provide , and they provide food for most heterotrophs on landfood for most heterotrophs on land
This kingdom is home to much diversity, This kingdom is home to much diversity, containing redwood trees that can be gigantic containing redwood trees that can be gigantic and mosses that never grow more than a few and mosses that never grow more than a few centimeters.centimeters.

Kingdom: AnimalsKingdom: Animals
A dog, a flea in a dogA dog, a flea in a dog’’s ear, or a cat that a dog s ear, or a cat that a dog chases chases are all part of the animal kingdom.are all part of the animal kingdom.
They are They are ALL multicellular ALL multicellular and and ALL ALL heterotrophsheterotrophs
Animals have different adaptations that allow Animals have different adaptations that allow them to locate, capture, eat, and digest foodthem to locate, capture, eat, and digest food
Animals can be found basically anywhere on Animals can be found basically anywhere on the planet, living in a wide variety of the planet, living in a wide variety of environmentsenvironments