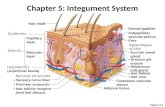
THE SKIN HAIR, SCALP & CONSULTATION. THE SKIN EPIDERMIS DERMIS HYPODERMIS.
IV. Dermis A. Layer of skin between epidermis and subQ (Hypodermis) layer B. Composed of connective...
-
Upload
anis-stephens -
Category
Documents
-
view
311 -
download
2
Transcript of IV. Dermis A. Layer of skin between epidermis and subQ (Hypodermis) layer B. Composed of connective...


IV. DermisA. Layer of skin between epidermis and subQ (Hypodermis) layerB. Composed of connective tissue containing collagen and elastic
fibersC. Dermal papillae
1. Superficial layer of dermis (top 1/5 of dermis)2. Papillae (nipple-shaped) structure
a). Contains capillary loops – capillariesb). Corpuscles of touch – tactile receptorc). Meissner corpuscles - nerve endings that are
sensitive to touchd). Free nerve endings – receive sensations of warmth,
coolness, pain, tickling, and itching.


D. The deeper part of the dermis1. Attached to the subQ (Hypodermis) layer 2. Consists of dense irregular connective tissue containing: a). Collagen, coarse elastic fibers b). Adipose cells, hair follicles, nerves, oil glands, and
sweat glands are found in-between the elastic fibers. c). Function of collagen and elastic fibers:
i). Extensibility – ability to stretchii). Elasticity – ability to return to original shape
after stretching iii). Striae – Stretch marks (cause by extreme stretching pregnancy and obesity


V. Skin ColorA. Three pigments that give color to skin
1. Melanin – Causes skin color: pale yellow, red, tan, and black. a). Melanocytes – cells that produce melanin and transfer it to keratinocytes b). Most plentiful in epidermis of penis, nipples, area around nipples, face, and limbs. c). Number of melanocytes is about the same in all people groups d). Differences in skin color are due to amount of melanin produced by cells. e). Age (liver) spots – Freckle-like blemish; light brown to black in color
i. Age spots are areas of skin where melanin accumulateii. Nevus (Mole) – round, flat, or raised area of overgrown
melanocytes -Moles are usually non-cancerous (Benign)

2. Hemoglobina). Oxygen carrying protein that gives albinos’ skin color range from pink to red.
3. Carotene a). Yellow-orange pigment that fives egg yolk and
carrots color. b). Associated with vitamin A (pigments for
vision) c). Meals high in carotene can cause the skin to turn orange.


VI. Accessory Structures of the SkinA. Hair1. Called pili - a thread of fused, dead keratinized
cells that consist of a shaft and root2. Present on most skin surfaces except on palms, fingers, soles, and toes3. High growth areas are: scalp, eyebrows, and around external genitalia4. Genetic traits and hormone levels determine thickness and pattern of hair distribution.


5. Structures of the Haira). Shaft – Superficial portion, which extends above the skinb). Root - Deeper portion, which extends below epidermis and
into the dermisc). Hair follicle – Surrounds the root
Follicle - a small secretory cavity, sac, or glandd). Hair root plexuses – Nerve endings that are sensitive to touche). Papilla of the hair – contain blood vessels that provide
nourishment f). Matrix – produces new hairs by cell division when old hairs are
shedg). Arrector pili – smooth muscle associated with hair
i. Extends from the upper dermis to the hair follicleii. Arrector pili contracts raising hair perpendicular to skiniii. This action causes “goose bumps”



6. Color of Haira). Melanin is secreted by melanocytes located in
the matrix of the hair bulbi. Dark hair contains true melaninii. Blond and red hair are caused by variants of melaniniii. Gray hair is caused by a decline in melanin
productioniv. White hair results from trapped air bubbles in the hair shaft

B. Glands of the Skin1. Sebaceous Glands or oil glands
a). Connected to hair follicles b). Oil gland opens into the hair follicle or opens directly on skin’s surface. c). No sebaceous glands on the palms of hands or soles of feet d). Sebum – Oily substance secreted by sebaceous glands
i). Keeps hair from drying outii). Slows evaporation of water from skiniii). Softens skiniv). Inhibits bacterial growth
e). Blackheads – blocked sebaceous glands with accumulated sebum
i). Sebum is nutritive to certain bacteria causing pimples or boils form
ii). The color of blackheads is due to melanin and oxidized oil not dirt

2. Sudoriferous Glands or Sweat Glandsa). Three to four million in the skinb). Two kinds
i.) Eccrine Sweat Glands-more common than apocrine gland -Most numerous in the skin of forehead, palms, and soles- Gland is deep in dermis and opens by pores in the skin-Glands produce 600mL day (over ½ a liter of sweat)-Sweat contains water, ions, Na+, Cl-, urea, uric acid, ammonia, amino acids, glucose, and lactic acid. -Sweat helps cool the body through evaporation

ii. Apocrine Sweat Glands-Sweat glands located in axilla (armpit), groin, areolae areas, and bearded regions of the face in males.-Glands mostly located in the subQ (hypodermis)
layer -Secreted fluid has oils and proteins that make it more viscous -Secreted during emotional stress (cold sweats)

3. Ceruminous Glands
a). Located in the skin of external auditory canal of ear
b). Cerumen (Earwax) – made up of ceruminous and sebaceous fluid
c). Prevents foreign debris from entering the ear canal

C. Nails
1. Made of tightly packed, hard, dead, keratinized cells of the epidermis.
2. Components of nailsa). Nail body – visible part of the nailb). Free edge – Part of nail that is clipped – part extends past end of finger or toe c). Nail root – Part of nail not visible, covered by cuticle d). Lunula – whitish crescent next to cuticlee). Nail Matrix – Where the nail grows (1mm per week) f). Cuticle – composed of stratum corneumg). Function – Helps grasp object, protects ends of
fingers, allows scratching