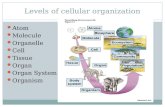
Levels of Organization Cells Levels of Organization Cells: microscopic units of living matter.
Invitation to Biology Chapter 1. Life’s Levels of Organization The world of life shows levels of...
-
Upload
arline-walton -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of Invitation to Biology Chapter 1. Life’s Levels of Organization The world of life shows levels of...

Invitation to Biology
Chapter 1

Life’s Levels of Organization
• The world of life shows levels of organization, from the simple to the complex, which extend through:– cells– populations– communities– ecosystems– the biosphere

Molecules of Life• All things are made up of the same units of
matter: – atoms, molecules
• Living things are made of up of a certain subset of molecules:– nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, lipids

DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
• The signature
molecule of life
• Molecule of
inheritance
• Directs assembly
of amino acids

Heritability of DNA
Inheritance– Acquisition of traits by way of
transmission of DNA from parent to offspring
Reproduction – Mechanisms by which an organism
produces offspring – Governed by instructions in DNA

DNA Guides Development
Development
– Transformation from fertilized egg to adult
– Series of stages
– Instructions for each stage in DNA

Energy Is the Basis of Metabolism
Energy = Capacity to do work
Metabolism = Reactions by which cells acquire and use energy to
grow, survive, and reproduce

Interdependencies among Organisms
ProducersMake their own food
ConsumersDepend on energy stored in
tissues of producers
DecomposersBreak down remains and wastes

Energy Flow
• Usually starts with energy from sun
• Transfer from one organism to another
• Energy flows in one direction• Eventually, all energy flows
back to the environment

energy input (mainly sunlight)
producers(plants and other self-feeding organisms;
they make their own food from simple raw materials)
nutrientcycling
consumers, decomposers(animals, most fungi, many protists,
many bacteria that can’t make their own food)
energy output (mainly metabolic heat)

Sensing and Responding
• Organisms sense changes in their environment and make responses to them
• Receptors detect specific forms of energy
• The form of energy detected by a receptor is a stimulus

Homeostasis
• Maintenance of internal environment within range suitable for cell activities
• Pancreas maintains level of sugar in blood by secreting hormones

Unity of Life
All organisms:
– Are composed of the same substances
– Engage in metabolism
– Sense and respond to the environment
– Have the capacity to reproduce based
on instructions in DNA

Diversity of Life
• Millions of living species
• Additional millions of species now
extinct
• Classification scheme attempts to
organize this diversity

Scientific Names
• Two-part naming system devised by
Carolus Linnaeus
• First name is genus (plural, genera)
– Homo sapiens - genus is Homo
• Second name is species within genus

• Bacteria
• Archaea
• Eukarya (includes protists, plants, fungi,
and animals)
Three-Domain Classification
Bacteria(EUBACTERIA)
Archaea(ARCHAEBACTERIA)
Eukarya(EUKARYOTES)

Life’s Diversity

Prokaryotes
Archaea and Bacteria
• Single-celled
• No nucleus or organelles
• Include producers, consumers,
decomposers

Eukaryotes
Eukarya (plants, fungi, animals, protists)
• DNA is inside a nucleus
• Most are larger and more complex than the prokaryotes

Plants
• All are multicelled
• Most are photosynthetic
producers
• Make up the food base for
communities, especially on
land

Fungi
• Most are multicelled
• Consumers and decomposers
• Extracellular digestion and
absorption

Animals
• Multicelled consumers– Herbivores
– Carnivores
– Parasites
– Scavengers
• Move about during at least some stage of their life

Mutation: Source of Variation
• Mutation = change in structure of DNA
• Basis for the variation in heritable traits
• Most are harmful

Adaptive Trait
A trait that gives the individual an advantage in survival or reproduction,
under a given set of circumstances

Evolution
• Genetically based change in a line of descent over time
• Population changes, not individuals

Natural Selection
• The outcome of differences in survival and reproduction among individuals that vary in details of heritable traits
• This process helps explain evolution - changes in a line of descent over generations

Artificial Selection
• Breeders favor some form of traits over others
• Individuals exhibiting favored traits are bred
• Favored traits increase in the population

Observations, Hypotheses, and Tests
• Observe phenomenon
• Develop hypotheses
• Make predictions
• Devise test of predictions
• Carry out test and analyze results

Scientific Theory
• A hypothesis that has been tested for its predictive power many times and has not yet been found incorrect
• Has wide-ranging explanatory power– Darwin’s Theory of Evolution by Natural
Selection

Role of Experiments
• Procedures used to study a phenomenon under known conditions
• Allows you to predict what will happen if a hypothesis is not wrong
• Can never prove a hypothesis 100% correct

Experimental Design
• Control group
– A standard for comparison
– Identical to experimental group except for
variable being studied
• Sampling error
– Non-representative sample skews results
– Minimize by using large samples

CONTROL GROUPGets regularpotato chips
EXPERIMENTAL GROUPGets Olestra potato chips
Make Prediction
Eat potato chips Eat potato chips
Analyze Results
Draw ConclusionEating Olestra potato chips
does not cause intestinal distress
If Olestra® potato chips cause intestinal distress then people who eat them will get cramps
Perform Experiment
93 of 529 people (17.6%)suffer from cramps later
89 of 563 people (15.8%)suffer from cramps later
About the same number of people in each group get cramps

Field Experiment
Control Group 34 H. cydnoindividuals
with yellow markings
Experimental Group
46 H. cydno individuals
with white markings
ExperimentBoth yellow and white formsof H. cydno butterflies areintroduced into isolatedrain forest habitat of yellowH. eleuchia butterflies.Numbers of individualsresighted recorded on adaily basis for two weeks.
ResultsExperimental group (H. cydno individuals without yellow wing markings) is selected against. 37 of the original group of 46white butterflies disappear (80%), compared with 20 of the 34 yellow controls (58%).
• Study of Heliconius butterflies

Limits of Science
• Scientific approach cannot provide answers to subjective questions
• Cannot provide moral, aesthetic, or philosophical standards

Science and the Supernatural
• Science has run up against religious
belief systems
– Copernicus suggested that sun, not the
Earth, was center of universe
– Darwin suggested that life was shaped by
evolution, not a single creation event

Asking Questions
• Scientists still ask questions that
challenge widely held beliefs
• The external world, not internal
conviction, is the testing ground for
scientific beliefs