Intimate Partner Violence and Rural Older Women
description
Transcript of Intimate Partner Violence and Rural Older Women

Intimate Partner Violence and
Rural Older Women
Center for Gerontology at Virginia TechCenter for Gerontology at Virginia Tech
Women’s Resource Center of the New River ValleyWomen’s Resource Center of the New River Valley
Funded by grant # R03HD059478 from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver NICHD Funded by grant # R03HD059478 from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver NICHD and the NIH Office of the Director (OD)and the NIH Office of the Director (OD)

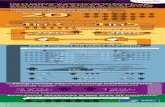
IPV StatisticsIPV Statistics

IPV in Late Life: United StatesIPV in Late Life: United States
National data indicates that
• 69% of IPV is committed by a spouse• 65% of IPV acts included simple assault• 41% of victims report IPV to the police
• 33% of perpetrators ages 50+ used alcohol and drugs prior to abusing their partners

Why Victims of IPV Why Victims of IPV Do Not Contact PoliceDo Not Contact Police
Source: 2000 US Department of Justice, Bureau of Justice Statistics

IPV in Late Life: VirginiaIPV in Late Life: Virginia1999-20071999-2007
Source: Office of Chief Medical Examiner, 2009
110 homicides against persons ages 50+were committed by their intimate partner.
Within 7 days of the homicide, 34% of theperpetrators committed suicide.

IPV in Late Life: VirginiaIPV in Late Life: Virginia1999-20071999-2007
Characteristics of 110 homicide victims:• Female (71%)
• Ages: 50 – 89 (Average age 62)
• Married (66%)
• White (73%) , Black (24%) , Asian (3%) Hispanic (<1%)
• 29% had a positive blood alcohol level between .01 and .38 at time of death
Source: Office of Chief Medical Examiner, 2009

Characteristics of victim-perpetrator relationship
• Relationship ended or was ending (55%)
• History of physical assault (52%)
• Abuser threatened harm to victim or family member(s) (30%)
• Previous calls to 9-1-1 about violence (28%)
Source: Office of Chief Medical Examiner, 2009
IPV in Late Life: VirginiaIPV in Late Life: Virginia1999-20071999-2007

IPV in Late Life: IPV in Late Life: New River ValleyNew River Valley
1999 – 2007• OCME – 1 homicide victim age 50+
2009• Police IBRs (6 depts. in NRV)
• 6% of responses to female victims aged 50+• WRC Emergency shelter
• 15% of occupants aged 50+• WRC Crisis hotline
• 11% of calls from women aged 50+