Indirect Damage: Host Response · –Herpes simplex 1 & 2, varicella zoster, papillmavirus...
Transcript of Indirect Damage: Host Response · –Herpes simplex 1 & 2, varicella zoster, papillmavirus...

1
Current Concepts in Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy May 2019
Leah MacPherson RDHBS MHP
Current Concepts in Non-surgical Periodontal Therapy
This is a course for oral health-care providers interested in an update in non-surgical periodontal therapy This course will review the literature concerning periodontal risk factors and how to use the information to assess patients for risk verses treating disease The host response and the cascade of events which occur in periodontitis will be reviewed and some of the periodontal and systemic connections will be highlighted
Learning Objectivesbull Assess a patientrsquos periodontal condition using clinical attachment levels bone loss and health historybull Review the various types of periodontal conditions microbiology and their treatment
bull Determine a patientrsquos level of periodontal risk
bull Biofilm grow amp provide a protective environment
bull Protective matrixslime layer
ndash Protective amp stick to surfaces
bull Micros behave differently when in a biofilm than outside
ndash These microorganisms are more resistant within the biofilm than individually
bull Biofilm can be good amp protective
ndash probiotics to add ldquohealthy associatedrdquo bacteria to promote health
BiofilmBiofilm
bull Biofilms contain aqueous channels
ndash channels provide nutrients amp waste
bull Quorum sensing
bull Bacterial micro colonies
bull Protected by the slime layer
bull Fluid channels provide nutrients pH levels oxygenenzymes metabolites amp waste products
bull pH disease similar to caries
Scientific America 2001
Theories
bull The polymicrobial synergy and dysbiosis (PSD) entire colony of multiple different bacteria (polymicrobial) working together (synergy) to initiate periodontal disease (dysbiosis)leading to inflammation
ndashKeystone pathogens- Porphyromonasgingivalis elevates the virulence of the entire bacterial colony by altering their gene expression rendering them more aggressive
Indirect Damage Host Response
bull Host cells respond to the microorganisms amp produce a variety of inflammatory mediators
ndash Mediators can cause inflammatory responses
bull capillary permeability
bull Smooth muscle contraction
bull Vasodilation
bull Migration amp attraction of leukocytes
bull Some mediators play an important role in health others are important to defend the host
bull Many of the destructive mediators breakdown CT (bone collagen)
2
Key Mediators of the HostCollagenase
ndash powerful digestive enzymes that can kill bacteria amp host tissues
ndash released by PMNs
ndash damages CT
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)
ndash group of Zinc- dependent enzymes
ndash produced by PMNs
ndash in health facilitates normal tissue turnover
ndash degrades connective tissue matrix
Prostoglandins (PGE2)
bull Lipid compounds (technically hormones)
bull Produced from macrophages and PMNs
bull Inhibits bone amp collagen formation
bull PGE2 is found in levels in aggressive perio
Mediators Conrsquot Cytokines
bull proteins that affect the function of other cells
bull produced by t-cells Natural Killer cells amp macrophages
bull can cause tissue destruction amp promote repair ndash L-1 promotes bone resorption stimulates PGE2releases
mmps levels in active disease amp inflammation
ndash IL-2 promotes T-cells levels in aggressive perio disease
ndash IL-6 stimulates osteoclastic activity levels in perio amp refractory
ndash IL-8 produce mainly by macrophagesstimulate MMP collagen destruction
Key Mediators of the Host C ndash Reactive Protein (CRP)
bull CRP is considered the ldquoMarker of systemic inflammationrdquobull Acute phase proteins triggered by PGE2
bull These proteins are found in patients w inflammation or infectionndash High CRP serum levels have been linked w chronic systemic
diseases (periodontitis cardiovascular disease diabetes LBW miscarriages)
bull CRP increases clotting amp enhances uptake of cholesterol
CRP Testingbull Testing pts- CRP over 3 is considered at risk (may be at risk for 20 years after)bull High CRP levels w high lipids have more riskbull High CRP levels are treated w statins
Periodontal Risk Factors
bull Smoking pipe cigar marijuana
bull Diabetes
bull Immune amp PMNs related diseases
bull Rheumatoidosteoarthritis
bull Alcohol
bull Hormones
bull Genetic
bull Osteoporosis
bull Viruses cytomegalovirus Epstein- Barr
virus herpes papilloma
bull Medications
bull Stress distress amp Fatigue
bull Nutritional deficiencies K
C B9 calcium protein CoQQ10
bull Obesity
bull Previous periodontitis
Risk Based Care
bull Inform patient
bull Asses Risk
bull Intervention with the appropriate level of preventionndash High-risk patients needed more than two visits (recare)
per year (Giannobile Wet al 2013)
ndash Personalized medicine approach based on risk factors for disease may be useful in determining recall intervals for patients and would be more cost effective (GiannobileWet al 2013)
The Systemic Connection
Periodontal Medicine
The science to support an association between periodontal disease and
systemic consequences
3
Systemic Link
bull Cardiovascular Diseases amp Stroke
ndash perio appears to be a mildmoderate risk for coronary heart disease Perio is a stronger risk factor for stroke
ndash 2 -7 fold increased risk of stroke in those w perio
bull Diabetes
ndash bi-directional relationship
Systemic Linkbull Respiratory diseases
ndash Microrsquos from the oral nasal amp pharyngeal frequently contaminate the upper airway
ndash Increased risk due to poor OH
bull May increase risk in lung cancer
ndash periodontal disease pts have a 124-fold increased risk of developing lung cancer
bull MiscarriagesPre-term DeliveryLow Birth Weight Babies
ndash Women w perio may be 7-8X more predisposed to deliver premature infants w LBW
ndash CRP amp PGE2 trigger early uterine contractions amp PTD
ndash microbiome Project found the microbiome of the placenta most resembles the subgingival environment
Systemic Link
bull Alzheimers Diseasendash Early exposure to periodontitis and inflammatory
conditions may increase one for Alzheimers disease later in life
bull theories
ndashInflammation allows bacteria to enter the brain
ndashPeriodontal spirochetes disrupt the normal defenses and may lead to neuronal degeneration
ndashPg
Periodontal MedicineSystemic Connection
bull Non- dental professionals appreciate the impact of oral health
bull As patient awareness of perio amp systemic implications increases more seek preventive care (Williams amp Offenbacher periodontol200023(1)9-12)
bull Some strong links have been observed
bull Further studies are needed
Diagnosis
bull A periodontal diagnosis must be made to facilitate good decision-making for both the clinician amp pt for proper treatment planning
bull It can be very effective amp powerful
2017 Periodontal Classification
bull Proceedings of the World (American Academy of
Periodontology and the European Federation of
Periodontology) Workshop on the Classification of
Periodontal and Peri‐Implant Diseases and
Conditions
Caton J Armitage G Berglundh T Et al A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri‐implant diseases and conditions ndashIntroduction and key changes from the 1999 classification Journal of Periodontology 89 S1 (S1-S8) (2018)
httpsonlinelibrarywileycomtoc19433670201889S1
4
Key Points
bull Created by incredible researchers in the field of perio
bull Case definitions for research vs clinicaltreatment
ndashResearch guidelines were needed
bull Includes a holistic approach to periodontology
ndash Included risk factors modifiers and overall perio systemic connection
bull Creating space for future research
bull Addressing the borderline between gingivitis and periodontitis
Key Points
bull Excessive occlusal force- Traumatic occlusal force
bull Biologic width- Supracrestal tissue attachment
bull 3 disease of perio- perio systemic necrotizing
bull Necrotizing periodontal disease- dropped ulcerative
bull Linear gingivitis removed is new term is Candidosis
bull Added implant
bull Periodontal abscesses (PA) classified according to the etiological factors involved
bull added gingival pigmentation due to medication
Key Pointsbull Must probe implants lightly to monitor depth changes
and bleeding progression of perio is faster on implants
bull CAL-lack of training affects DX initial periodontitis in regards to CAL
-Interdental CAL is detectable at ge2 non‐adjacent teeth or Buccal CAL ge3 mm with pocketing gt3 mm is detectable at ge2 teeth
bull Proposal for staging and grading framework which would allow for complexity and risk
ndash 3 sets of parameters
bull RATE RISK RISK
bull The intention was to liken to cancer
httpswwwperioorg2017wwdc
5
Types of Periodontal diseasesGingival
Dental biofilm Induced Gingivitis Most commonbull Typically biofilm is proportionate
to the amount of inflammation
bull No bone loss no LOA
Types- New
bull Localized = BOPgt 10 amp lt30
bull Generalized plaque induced gingivitis gt 30 BOP
Microorganisms
bull Non-specific includes both Gram - amp Gram +
Treatment
bull self care deplaquingdebridementscaling
bull eliminate local contributory factors
Modifying Factors of Biofilm induced Gingivitis hormonalPregnancy Gingivitis
Etiologybull biofilm amp hormone changes
bull degree of inflammation parallels OH
ndash good OH can prevent pregnancy gingivitis
bull will exacerbate any previous periodontal disease
Pregnancy Gingivitis
Microorganism
bull Prevotella intermedia
Treatment
bull subsides after giving birth
bull exaggerated response can be prevented w excellent OH
bull frequent recalls Oral self care
bull Deplaquingdebridementscaling
Pyogenic Granuloma
Treatment
bull may resolve on own after debridement
bull may need surgical removal
6
Drug-influenced gingivitis
bull Gingival enlargement
ndashAnticonvulsants
bull Phenytoin
ndashCalcium channel blockers
bull Nifedipine 6-43
ndash Immunosuppressants
bull Cyclosporin 25
ndashAnabolic Androgenic Steroid
ndash Prostate cancer treatment
Gingival enlargement
bull Level of biofilm amp drug dosage accumulation can affect the severity of overgrowth
bull Consult w MD for drug substitution
bull Some cases of hypertrophic gingival tissue have been reported as Kaposirsquos sarcoma amp squamous cell carcinoma
Non-biofilm induced related to bull Specific bacteria
ndash Neissera gonorrhea treponema pallidum streptococci
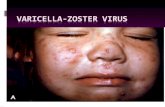
bull Viralndash Herpes simplex 1 amp 2 varicella zoster papillmavirus
bull Fungal
bull Cultured for true diagnosis amp treat appropriately antibiotics antiviral amp or antifungal
bull Not common amp usually not known
Non-plaque induced gingival diseases of fungal origin
Candidosisformally Linear gingivitis
bull Generally fungalcandiasis
bull Linear amp very distinctive band of severe erythema on gingival margin
bull Disproportion of inflammatory intensity for the amount of biofilm present
Candidosis Treatment
ndash OHE consider chlorhexidine
ndash Does not respond well to improved OH or scaling
ndash Biofilm removal debridementscaling
ndash May need additional physician consult
Lichen Planus
Etiologybull Unknownbull Cell mediated Immune pathogenesis bull Systemic Diseases
ndash Diabetes hypertension hepatitis B amp C chronic graft-versus-host disease amp lupus
bull Medicationsndash antimalarial drugs antihypertensives amp non-steroidal anti
inflammatory (NSAIDS)
Signsbull Affects skin and mucous membranesbull Lesions may be mild to moderately painful amp burning
7
Lichen PlanusTypes
Reticular-plaque papular
Erosive Bullous Atrophic ulcerative
bull Erosive- gingival
ndash bulbous forms ulcerative amp painful
ndash red and raw
bull Reticular
ndash asymptomatic keratontic lines called stria
ndash lacy white lines
Lichen Planus
bull severity may relate to stressConsiderationsbull Higher risk for non- reticular types for malignant transformation
ndash LP pts have a 10 fold increased risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma
Treatmentbull Look for triggers allergies sensitivity bull Aloe Vera rinses amp gelbull Corticosteriods
ndash topical- fluocinonide dexamethadone dipropionate spray topical steroids may help- can cause candida
bull Periodic biopsies are necessary for areas that do not respond to treatment
bull Regular recalls
Inflammatory And Immune Conditions And Lesions
Hypersensitivity ReactionsAllergic gingivitis
Other names desquamative Plasma cell gingivitis idiopathic
gingivostomatitis atypical gingivostomatitis allergic gingivostomatitis hypersensitivity and plasmacytosis
Plasma cell gingivitis is an uncommon inflammatory condition usually affecting the anterior maxillary gingiva and of uncertain etiology While some authors have associated plasma cell gingivitis with a hypersensitivity response to antigens in various substances others have raised doubt whether plasma cell gingivitis is a distinct clinicopathologic entity
Allergic gingivitis
Etiology
bull auto immune
bull Allergy
bull Signs
bull sloughing of the epithelium which leaves raw red surface
bull The edematous tissue often extends to the mucogingival junction with a deep red appearance
Allergic gingivitis
Symptoms
painful
Treatment
topicalsystemic steroid therapy
remove etiological factor if possible
-spices toothpaste flavorings peppermint wintergreen menthol cinnamon preservatives mints gum candy
Possible Offending Products to Gingival Tissue
bull Commercially available toothpaste (tartar-control additives and flavoring agents [possibly
cinnamon] that mask the tartar control additives)
bull Mouth rinses
bull Cinnamon aldehyde
bull Sodium benzoate and methyl paraben
bull Food substances such as wheat dairy chocolate eggs peanuts and monosodium glutamate
bull Red wine (sulfides and tartrazine additives)
bull Preservatives
bull Essential oils such as peppermint spearmint and wintergreen found in gums candy and mouth rinses
bull Dark cola drinks
bull Strong spices
bull Chili peppers
bull Clove
bull Cardamom Burkhart NW Toothpaste allergy RDH 2007 27(6) 86107-108
8
Types of Periodontal diseasesPeriodontitis
Periodontitis
bull Chronic
bull Disease will progress unless treated
bull Typical age of onset is 35 yrs of age
bull Bone loss
- slow
ndash rate may vary depending on the modifiers
bull Severity is determined by bone loss and LOA
bull Can become inactive (stable) active (recurrent) refractory
Periodontitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram ndash
bull P gingivalis
bull P intermedia
bull Tannerella forsythensis (B forsythus)
Treatmentbull Self carebull Scrt
pldebridement bull Depending type of
defects amp severity ndashpossibly surgery
amp perio referral
Not includedAggressive
This category includes formally called diseases
bull Juvenile
bullEarly onset
bullPrepubertal
bullRapidly progressive
Localized Aggressive Localized Juvenile Periodontitis
bull More significant bone loss surrounding 1st molars amp incisors ndash typically angular type bone loss amp mirror image bilaterally
bull Rate of bone loss is rapid
bull OH can be good
9
Localized Aggressive LJP
bull Defects in PMNs or macrophagesbull respond slowly
bull chemotaxis defect
bull impaired phagocytosis
bull Onset typically during teenage years
bull Hereditary componentgenetic
bull more common in females amp blacks
Localized Aggressive Localized Juvenile Periodontitis
Microorganisms
Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans
P gingivalis
Treatmentbull scrt pldebridement but typically unresponsivebull Antibiotics to be administered with or just after debridement
ndash combo metronidazole wamoxicillin or metro w augmentinndash Clindamycin Azithromycin
bull possibly surgerybull prompt perio referralbull suggest family be evaluated (siblings children etc)bull sea salt being used as prevention of AA amp Tx
Generalized Aggressive Formally Generalized Juvenile Periodontitis
bull More rare than LJPbull Can affect most teeth but more severe on 1st molar
amp incisorsndash must involve gt 3 other teeth
bull Onset usually under 30 years oldbull Associated with neutrophil disorderbull Generally significant inflammation amp heavy
plaquecalculusbull Children w Gagp seem more prone to ear skin amp
upper respiratory tract infections
Generalized Aggressive Generalized Juvenile Periodontitis
MicroorganismsA actinomycetemcomitansPorphyromas gingivalis Eikenella corrodens
Treatmentscrt pldebridementantibiotics
ndash combo metronidazole wamoxicillin or metro w augmentin
possibly surgeryprompt perio referralbull Suggest family be evaluated (siblings children etc)
Periodontitis as a Manifestation of Systemic Disease
bull Systemic diseases that severely impair host response should be considered a periodontal manifestation of the systemic disease amp primary diagnosis should be the systemic disease according to International Statistical Classification of Disease (ICD)
ndash Excludes diabetes
bull Hematologicacquired neutropenias leukemias
bull Genetic disorderfamilial neutopenias down syndrome leukocyte adhesion deficiency syndrome papillon-lefreve syndrome chediak-higshi histocytosis syndromes Glycogen storage disease genetic agranulcytosis cohen syndrome Ehlers-Danlossyndrome hypophosphatsis
Necrotizing Periodontal Diseases NG amp NP
Etiologybull Unknown
bull Risk factorsexcessive stress lack of rest poor oral hygiene smoking HIV poor immune response
bull More common in underdeveloped countries
bull Less common now in the US
bull Susceptible to reoccurrence
Symptomsbull SUDDEN onset of burning
mouth inability to eat metallic taste excessive salvia amp PAINFUL
Microorganisms
spirochetes
Prevotella intermedia
Fusiform bacillus
Fusobacterium nucleatum
Ulcerative has been eliminated
10
NGSigns
bull 3 key features papilla necrosis bleeding and pain
bull Punched out papillae cratered like depressions covered by a white necrotic pseudomembrane(collection of PMNS) bright red margins spontenousbleeding may occur
bull Distinctive foul odor
bull May have systemic involvement
ndash lymphadenopathy fever
bull May be a systemic
manifestations
ndash HIV
NG Treatmentbull Advise to avoid smoking amp etoh get rest and proper nutrition (rec
multi vitamin soft nutritious diet)+ self care
bull Rinses with frac12 glass warm water amp 1 tbsp hydrogen peroxide w half glass or chlorhexidine
bull Pain medication
bull Antibiotics can be used especially if systemic involvement
ndash metronidazole tetracycline pen vk
bull Initial supragingival debridement then complete
bull Consider complete laboratory work ndashup amp medical consult
ndash (NUG may be the first sign of HIV)
bull May progress to NUP
bull Follow ndashup phone call or visit within 24 hrsndash Re-eval surgery referral debridement wlocal= recurrent nature
NP
bull Progression of NUG
bull May be related to systemic disease
bull HIV nutrition deficiency
bull NUG superimposed on a previous periodontal disease
NP
Signs amp symptoms
bull Intensely red necrosis white pseudomembrane
bull Painful odor punched-out papillae
bull Reports of deep aching pain or jaw pain
bull Extensive bone loss
bull Spontaneous bleeding
Treatment
bull Same as NUG
Peridex culture antibiotics (metronidazole) or antifungals
Refractory
bull Not included in the new guidelines
bull Unresponsive to treatmentndash surgery frequent scrt pl antibiotics
bull Can be localized or generalized
bull Usually smokers
bull Treatment clindamycin metronidazole metriwamoxicillin or Augmentin
Periodontal Phenotype (Biotypes)
bull The term describes the thickness of the gingiva in a bucco-lingual dimension
bull 3 types
Thick flat
Thick scalloped
Thin
bull Thick (85) is more prevalent than thin (15)
11
Thin Gingival Phenotype
bull Triangle shaped teeth vs square
bull Thin tissue
bull Susceptible to recession
bull Dehiscence present
bull Instrumentation must be done
Carefully due to thin biotype
bull Reacts to insult by recession
Thick amp Flat Gingival Phenotype
bull Square shaped
bull Thick tissue
bull Susceptible to pocketing
bull Reacts to insult by pocketing
Thick Scalloped
bull Thick fibrotic gingiva
bull Slender teeth
bull Narrow zone of KT
bull Gingival scalloping
Recession
Type 1 Type 2
Interproximal CEJ
is clinically not
detectable
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is lt to buccal
Type 3
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is gt
buccal
attachment loss
Implants
bull Treat perio prior to implantsbull It takes 2 weeks for the implants to
become colonized by the surrounding teeth
bull No horizontal fibers like a tooth so infection goes straight to bone and perio happens very quickly
bull This perimucosal seal is delicate ndashBe careful during instrumentation
12
Implants
bull The implant coatingsrough surfaces may create more risk for implantitis but better for osteointergration
ndash The calculus is more embedded on these surfaces than the previous smoother surfaces
Stages of Peri-implant DiseasePeri-implant mucositis
bull Reversible inflammation of the soft tissues
bull Occurs in about 50 of implants placed within 9 - 14 years
Peri-implantitis
bull Bone Loss
bull Occurs in 12- 47 of implants 5 years after placement
bull Risk factors-Hx of severe perio poor self care amp lack of maintenance care
bull Cement Implantitis
bull Some evidence linking cement and titanium particles bio corrosion
Peri-implantitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram - Fusobacterium species Prevotella intermedia
bull Implant failure is usually due to the microbial challenge occlusal load or excessive cementndash Cement has been found in the tissues
bull Failure is evidenced by gt2 mm MOBILITY
bull Bone loss buccal and lingual results in dehiscence
Cement Implantitis
New AAP Case definitionPeri-implantitis
bull BOP
bull Probing depth gt 6 mm
bull Bone levels gt 3 mm apical of the most coronal portion of the intraosseous part of the implant
Caton J Armitage G Berglundh T Et al A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri‐implant diseases and conditions ndash Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification Journal of Periodontology 89 S1 (S1-S8) (2018)
Failing Criteria
bull Ailing (Peri-implant mucositis) inflammation present but no mobility
ndash bone appears normal or there may be an incipient lesion
bull Failing Peri-implantitis without mobility
ndash Inflammation has progressed to the bone as evidenced by radiographic lesion
bull Failed Peri-implantitis with mobility
ndash Implant has pronounced bone loss
Probing amp BOP
bull Metal probes on prosthetic part of the crown is fine
bull Some are concerned with metal probes on the threads
bull Must probe implants
bull Probe depths are generally deeper than natural tooth
bull BOP is not normal
threads
13
Treatment
bull Be aggressive amp prevent bone loss because very difficult to treat once initiated
bull Treatment
ndash Debride thoroughly
ndash Chlorhexidine
ndash Systemic antibiotics
ndash Bone grafts
ndash Arestin- local drug delivery
ndash Air flow polishing with glycine
Diagnosis Severity
bull Determining severity is based on CAL and bone loss
bull Clinical attachment level (CAL)
ndashdistance from the junctional epithelium to the CEJ
bull Probe depths alone are lacking because it does not take in account the gingival margin
ndashusing probe depths alone can result in over estimating or underestimating disease
Three possible relationships for gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ
GM
bull Where should the GM be normallyndash 1-2 mm coronal to the CEJ
bull What is the pattern of CEJs interproximallyacross the mouthndash More Flat on the Posteriors
ndash More Curvature on the Anteriors
ndash For interproximal space look at the papillae does it fill the embrasure space
ndash A normal GM on the anteriors could be +1mm
ndash A normal GM on the posteriors could be +2 mm
Clinical attachment level
Depends on position of the gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ (-)
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ (same)
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ (+)
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is coronal to CEJ
1 Measure probe depth
2 Measure from gingival margin to CEJ
3 Subtract second measurement from overall probe depth
FYI-This is a color
coded probe w
markings at 36912
14
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is levelwith CEJ
bull Probe depth is Clinical attachment level
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is apical to CEJ
bull Measure probe depthbull Measure recessionbull Add recession to probe depth
Grading
Bone Loss
Stage 1
Coronal 13
lt 15
Coronal 13
Mid 13
Last 13
15 Normal bone Height
33 stage 2
Stage 3Extends to mid third of root amp beyondStage 4Extends to mid third of root amp beyond
Stage 1
stage 3 amp 4
Predicting Activity
bull BOP
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will not break down
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will breakdown
ndash Sites that do not bleed will not breakdown
ndash The absence of bleeding provides more information than whether bleeding exists
ndash Therefore when sites bleed we say it is active
bull Inflammation
bull Nutrient canals
bull Rough looking crestal bone vs smooth amp well demarcated may indicate activity
15
Predicting Activity
bull Nutrient canals
ndash Highly visible canals may indicate active or rapid destruction
ndash canals are thought to be engorged large blood vessels
Crestal Bone
Rough looking crestal boneSmoother more demarcated crestal bone
Planningbull Systematic Informed consent
bull Diagnosis prognosis options risks benefits
ndashPatients must have all the information
bull Studies indicate slight reductions in PD s gt 6 mm after full-mouth scaling and root planingperformed in one appointment vs over longer intervals
bull These protocols particularly effective in patients with aggressive periodontitis andor pts w systemic conditions
Eberhard J et al J Clin Periodontol 200835591ndash604 amp Fang et al J Periodont Res October 19 2015)
ImplementationTreatment
bull Goals are to eliminate infection and risk factorsbull The objective is to remove all clinically detectable
calculus without excessive root planingndash bacterial endotoxins are weakly adherent to the root
surface (Nakib 1982)
bull The term debridement vs root planing
ImplementationTreatment
bull Treat patientrsquos significant otherbull 40 of the time spouses have the
same microbiotabull Donrsquot kiss dogs amp cats- they may have
periobull Avoid gross scaling
bull risk of abscessbull educationbull more difficult to re-insert
instruments
16
Air Polishing with glycine
ndashGlycine has anti inflammatory ampimmune modulation effectsbull Glycine receptor gingival tissue
ndashPerpulsionndashFDA approval for lt5 mmndashRemoval biofilm amp stainndashPerio maintenance ndashImplantsndashDecontaminate prior to grafts
Host-Modulating Treatmentbull Treating periodontitis by trying to resolve
inflammation
bull Resolvins
ndash Omega 3 Fatty acids correlated with less bone loss
ndash may be due to their ability to generate mediators that fight inflammation and aid in inflammation resolution
bull Low-dose doxycycline 20 mg 2x daily
ndash Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor is the only FDA-approved
ndash Reduction of PD amp CAL gain over 3 months to 9 monthsGolub LM et al Doxycycline i hibits neutrophil (PMN)-type matrix metalloproteinases in human adult periodontitis gingiva J Clin Periodontol 199522100ndash109 amp
Golub LM et al Adjunctive treatment with subantimicrobial doses of doxycycline effects on gingival fluid collagenase activity and attachment loss in adult periodontitis J Clin Periodontol 200128146ndash156
Host-Modulating Treatment
bull NSAIDsndash Reduces PGE 2 which can reduce bone loss
ndash Flurbiprofen and topical (ketorolac)
ndash Case controls demonstrate decrease risk
bull Bisphosphonates ndash Used for treating Pagetrsquos bone pain amp osteoporosis
ndash Alendronate sodium (Fosamax) risedronate (Actonel)
ndash Investigating for its ability to modulate the host
bull Used experimentally in animals to inhibit bone resorption amp bone mineral content amp to interfere w breakdown of collagen in the periodontium
ndash WARNING case reports of bone necrosis after extractions
bull questions scrtpl w pts on drug
Treatment
bull Statins have an anti-inflammatory and immune effects reducing levels of C-Reactive Protein MMP Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
ndash Statins reduce bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclast formation
ndash Some results show lower alveolar bone loss and reduction of clinical signs of inflammation
(meta anyalsis Estanislau etal J Clin Pharmacol 2014 Dec)
ndash Topical gels (simvastatin atorvastatin)
Treatment
bull Probioticsndash Improved biofilm index and probe depths (Shimauchi 2008)
bull Valtrexbull Photodynamic therapy
ndash Light-sensitive drug is applied then a light laser directly on the area treated with the drug
ndash When the light is combined with the drug phototoxic reactions are induced which destroy bacterial cells
ndash Shows short term benefits (Sgolastra 2012)bull Periowave
bull Emdogainndash Enamel matrix derivative for periodontal tissue regeneration in
infrabony defects amp used w SRP to enhance resultsbull Derived from developing pig teethbull Stimulate adherence attachment to cementum
Treatmentbull Topical antioxidants
ndash Antioxidant gel and rinse
ndash Periosciences ndash toothpaste rinse gel
ndash Topical coenzyme COQ10
bull Due to correlation w perio oxidative stress markers amp low level of natural occurring salivary antioxidants looking at polyphenolsantioxidants in the mouth locally delivered
ndash needs more research
bull Hyaluronic acid (HA) gel and mouth rinsendash hyaluronic acid plays a large role in the collagen building 02
hyaluronan gel topically amp subgingivally
ndash Studies have been done to evaluate on wound healing amp improving perio outcomes
ndash Further evidence is needed
17
LasersNeodymium lasersbull Ex NdYAG NdYAP lasers
bull FDA approved-PerioLase (FRNdYAG) patented procedure LANAPshown to regenerate cementum bone amp PDL
bull No histological studies LANAP with regeneration ( Linden E Laser Basics Dimensions of dental hygiene april 2016)
Diode Lasersbull Most commonly used by RDHs
bull Wide range of wavelengths
bull Used to reduce bacteria amp remove inflammatory byproducts
bull Absorbed by pigmented structures hemoglobin amp melanin
bull Warming amp ablation
bull There is insufficient evidence
Evaluation
bull Evaluating the host response
1 week acute or painful conditions
4-6 weeks changes in attachment level
12 weeks microbiota returns to pre TX levels
bull Complete final diagnosis
bull Many lawsuits exist due to lack of follow-up where as before it was due to failure to diagnose
Evaluation
bull Responded well
ndashDetermine appropriate PMP interval
bull Unresponsive
ndashProblem solve
bull Try to determine whyndashVirulent microorganisms Inadequate host
response Ineffective initial therapy or contributory amp risk factors
ndashFormulate new plan
Possible Solutions
bull Improve initial therapyndash re-scale root plan re-root plan
ndash self care
ndash adjunctive chemotherapeutics necessary
bull Reduce risk amp contributory factors
ndash smoking restorative
bull ex Overhangs
bull Medical consult periodontal referral Advanced diagnostic
Advanced Diagnostics
bull A test to determine active disease or predict an active episode of disease
bull currently we are not able to do this well
bull Many new tests are being developed still under investigation and still being assessed for usefulness
bull Many are not available yet or very expensive
bull Provide information that adds to the clinical exam
bull If it would be nice to know but not change anything we need to ask the questionhellip
bull Is the benefit worth the cost
Testing
OralDNA Labs Inc- httpwwworaldnacom
bull Genetic risk bacterial profile HPV-related oral cancers Herpes Candida Chlamydia trachomatis(CT) Neisseria gonorrhea(NG) gene markers related to inflammatory response DNA DrugMaptrade
micro-Ident- DNA probes
bull httpswwwhain-lifesciencecom
Oravital-Toronto based company uses biofilm testing the use of prescribed antibiotic antimicrobial rinses httpswwworavitalcom
Temple Oral Microbiology testing service 800-788-6687
USC Oral microbiology testing Lab 213-740-3163
UNC Oral microbiology Lab oralmicrodentistryuncedu

2
Key Mediators of the HostCollagenase
ndash powerful digestive enzymes that can kill bacteria amp host tissues
ndash released by PMNs
ndash damages CT
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)
ndash group of Zinc- dependent enzymes
ndash produced by PMNs
ndash in health facilitates normal tissue turnover
ndash degrades connective tissue matrix
Prostoglandins (PGE2)
bull Lipid compounds (technically hormones)
bull Produced from macrophages and PMNs
bull Inhibits bone amp collagen formation
bull PGE2 is found in levels in aggressive perio
Mediators Conrsquot Cytokines
bull proteins that affect the function of other cells
bull produced by t-cells Natural Killer cells amp macrophages
bull can cause tissue destruction amp promote repair ndash L-1 promotes bone resorption stimulates PGE2releases
mmps levels in active disease amp inflammation
ndash IL-2 promotes T-cells levels in aggressive perio disease
ndash IL-6 stimulates osteoclastic activity levels in perio amp refractory
ndash IL-8 produce mainly by macrophagesstimulate MMP collagen destruction
Key Mediators of the Host C ndash Reactive Protein (CRP)
bull CRP is considered the ldquoMarker of systemic inflammationrdquobull Acute phase proteins triggered by PGE2
bull These proteins are found in patients w inflammation or infectionndash High CRP serum levels have been linked w chronic systemic
diseases (periodontitis cardiovascular disease diabetes LBW miscarriages)
bull CRP increases clotting amp enhances uptake of cholesterol
CRP Testingbull Testing pts- CRP over 3 is considered at risk (may be at risk for 20 years after)bull High CRP levels w high lipids have more riskbull High CRP levels are treated w statins
Periodontal Risk Factors
bull Smoking pipe cigar marijuana
bull Diabetes
bull Immune amp PMNs related diseases
bull Rheumatoidosteoarthritis
bull Alcohol
bull Hormones
bull Genetic
bull Osteoporosis
bull Viruses cytomegalovirus Epstein- Barr
virus herpes papilloma
bull Medications
bull Stress distress amp Fatigue
bull Nutritional deficiencies K
C B9 calcium protein CoQQ10
bull Obesity
bull Previous periodontitis
Risk Based Care
bull Inform patient
bull Asses Risk
bull Intervention with the appropriate level of preventionndash High-risk patients needed more than two visits (recare)
per year (Giannobile Wet al 2013)
ndash Personalized medicine approach based on risk factors for disease may be useful in determining recall intervals for patients and would be more cost effective (GiannobileWet al 2013)
The Systemic Connection
Periodontal Medicine
The science to support an association between periodontal disease and
systemic consequences
3
Systemic Link
bull Cardiovascular Diseases amp Stroke
ndash perio appears to be a mildmoderate risk for coronary heart disease Perio is a stronger risk factor for stroke
ndash 2 -7 fold increased risk of stroke in those w perio
bull Diabetes
ndash bi-directional relationship
Systemic Linkbull Respiratory diseases
ndash Microrsquos from the oral nasal amp pharyngeal frequently contaminate the upper airway
ndash Increased risk due to poor OH
bull May increase risk in lung cancer
ndash periodontal disease pts have a 124-fold increased risk of developing lung cancer
bull MiscarriagesPre-term DeliveryLow Birth Weight Babies
ndash Women w perio may be 7-8X more predisposed to deliver premature infants w LBW
ndash CRP amp PGE2 trigger early uterine contractions amp PTD
ndash microbiome Project found the microbiome of the placenta most resembles the subgingival environment
Systemic Link
bull Alzheimers Diseasendash Early exposure to periodontitis and inflammatory
conditions may increase one for Alzheimers disease later in life
bull theories
ndashInflammation allows bacteria to enter the brain
ndashPeriodontal spirochetes disrupt the normal defenses and may lead to neuronal degeneration
ndashPg
Periodontal MedicineSystemic Connection
bull Non- dental professionals appreciate the impact of oral health
bull As patient awareness of perio amp systemic implications increases more seek preventive care (Williams amp Offenbacher periodontol200023(1)9-12)
bull Some strong links have been observed
bull Further studies are needed
Diagnosis
bull A periodontal diagnosis must be made to facilitate good decision-making for both the clinician amp pt for proper treatment planning
bull It can be very effective amp powerful
2017 Periodontal Classification
bull Proceedings of the World (American Academy of
Periodontology and the European Federation of
Periodontology) Workshop on the Classification of
Periodontal and Peri‐Implant Diseases and
Conditions
Caton J Armitage G Berglundh T Et al A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri‐implant diseases and conditions ndashIntroduction and key changes from the 1999 classification Journal of Periodontology 89 S1 (S1-S8) (2018)
httpsonlinelibrarywileycomtoc19433670201889S1
4
Key Points
bull Created by incredible researchers in the field of perio
bull Case definitions for research vs clinicaltreatment
ndashResearch guidelines were needed
bull Includes a holistic approach to periodontology
ndash Included risk factors modifiers and overall perio systemic connection
bull Creating space for future research
bull Addressing the borderline between gingivitis and periodontitis
Key Points
bull Excessive occlusal force- Traumatic occlusal force
bull Biologic width- Supracrestal tissue attachment
bull 3 disease of perio- perio systemic necrotizing
bull Necrotizing periodontal disease- dropped ulcerative
bull Linear gingivitis removed is new term is Candidosis
bull Added implant
bull Periodontal abscesses (PA) classified according to the etiological factors involved
bull added gingival pigmentation due to medication
Key Pointsbull Must probe implants lightly to monitor depth changes
and bleeding progression of perio is faster on implants
bull CAL-lack of training affects DX initial periodontitis in regards to CAL
-Interdental CAL is detectable at ge2 non‐adjacent teeth or Buccal CAL ge3 mm with pocketing gt3 mm is detectable at ge2 teeth
bull Proposal for staging and grading framework which would allow for complexity and risk
ndash 3 sets of parameters
bull RATE RISK RISK
bull The intention was to liken to cancer
httpswwwperioorg2017wwdc
5
Types of Periodontal diseasesGingival
Dental biofilm Induced Gingivitis Most commonbull Typically biofilm is proportionate
to the amount of inflammation
bull No bone loss no LOA
Types- New
bull Localized = BOPgt 10 amp lt30
bull Generalized plaque induced gingivitis gt 30 BOP
Microorganisms
bull Non-specific includes both Gram - amp Gram +
Treatment
bull self care deplaquingdebridementscaling
bull eliminate local contributory factors
Modifying Factors of Biofilm induced Gingivitis hormonalPregnancy Gingivitis
Etiologybull biofilm amp hormone changes
bull degree of inflammation parallels OH
ndash good OH can prevent pregnancy gingivitis
bull will exacerbate any previous periodontal disease
Pregnancy Gingivitis
Microorganism
bull Prevotella intermedia
Treatment
bull subsides after giving birth
bull exaggerated response can be prevented w excellent OH
bull frequent recalls Oral self care
bull Deplaquingdebridementscaling
Pyogenic Granuloma
Treatment
bull may resolve on own after debridement
bull may need surgical removal
6
Drug-influenced gingivitis
bull Gingival enlargement
ndashAnticonvulsants
bull Phenytoin
ndashCalcium channel blockers
bull Nifedipine 6-43
ndash Immunosuppressants
bull Cyclosporin 25
ndashAnabolic Androgenic Steroid
ndash Prostate cancer treatment
Gingival enlargement
bull Level of biofilm amp drug dosage accumulation can affect the severity of overgrowth
bull Consult w MD for drug substitution
bull Some cases of hypertrophic gingival tissue have been reported as Kaposirsquos sarcoma amp squamous cell carcinoma
Non-biofilm induced related to bull Specific bacteria
ndash Neissera gonorrhea treponema pallidum streptococci
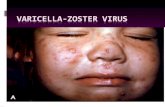
bull Viralndash Herpes simplex 1 amp 2 varicella zoster papillmavirus
bull Fungal
bull Cultured for true diagnosis amp treat appropriately antibiotics antiviral amp or antifungal
bull Not common amp usually not known
Non-plaque induced gingival diseases of fungal origin
Candidosisformally Linear gingivitis
bull Generally fungalcandiasis
bull Linear amp very distinctive band of severe erythema on gingival margin
bull Disproportion of inflammatory intensity for the amount of biofilm present
Candidosis Treatment
ndash OHE consider chlorhexidine
ndash Does not respond well to improved OH or scaling
ndash Biofilm removal debridementscaling
ndash May need additional physician consult
Lichen Planus
Etiologybull Unknownbull Cell mediated Immune pathogenesis bull Systemic Diseases
ndash Diabetes hypertension hepatitis B amp C chronic graft-versus-host disease amp lupus
bull Medicationsndash antimalarial drugs antihypertensives amp non-steroidal anti
inflammatory (NSAIDS)
Signsbull Affects skin and mucous membranesbull Lesions may be mild to moderately painful amp burning
7
Lichen PlanusTypes
Reticular-plaque papular
Erosive Bullous Atrophic ulcerative
bull Erosive- gingival
ndash bulbous forms ulcerative amp painful
ndash red and raw
bull Reticular
ndash asymptomatic keratontic lines called stria
ndash lacy white lines
Lichen Planus
bull severity may relate to stressConsiderationsbull Higher risk for non- reticular types for malignant transformation
ndash LP pts have a 10 fold increased risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma
Treatmentbull Look for triggers allergies sensitivity bull Aloe Vera rinses amp gelbull Corticosteriods
ndash topical- fluocinonide dexamethadone dipropionate spray topical steroids may help- can cause candida
bull Periodic biopsies are necessary for areas that do not respond to treatment
bull Regular recalls
Inflammatory And Immune Conditions And Lesions
Hypersensitivity ReactionsAllergic gingivitis
Other names desquamative Plasma cell gingivitis idiopathic
gingivostomatitis atypical gingivostomatitis allergic gingivostomatitis hypersensitivity and plasmacytosis
Plasma cell gingivitis is an uncommon inflammatory condition usually affecting the anterior maxillary gingiva and of uncertain etiology While some authors have associated plasma cell gingivitis with a hypersensitivity response to antigens in various substances others have raised doubt whether plasma cell gingivitis is a distinct clinicopathologic entity
Allergic gingivitis
Etiology
bull auto immune
bull Allergy
bull Signs
bull sloughing of the epithelium which leaves raw red surface
bull The edematous tissue often extends to the mucogingival junction with a deep red appearance
Allergic gingivitis
Symptoms
painful
Treatment
topicalsystemic steroid therapy
remove etiological factor if possible
-spices toothpaste flavorings peppermint wintergreen menthol cinnamon preservatives mints gum candy
Possible Offending Products to Gingival Tissue
bull Commercially available toothpaste (tartar-control additives and flavoring agents [possibly
cinnamon] that mask the tartar control additives)
bull Mouth rinses
bull Cinnamon aldehyde
bull Sodium benzoate and methyl paraben
bull Food substances such as wheat dairy chocolate eggs peanuts and monosodium glutamate
bull Red wine (sulfides and tartrazine additives)
bull Preservatives
bull Essential oils such as peppermint spearmint and wintergreen found in gums candy and mouth rinses
bull Dark cola drinks
bull Strong spices
bull Chili peppers
bull Clove
bull Cardamom Burkhart NW Toothpaste allergy RDH 2007 27(6) 86107-108
8
Types of Periodontal diseasesPeriodontitis
Periodontitis
bull Chronic
bull Disease will progress unless treated
bull Typical age of onset is 35 yrs of age
bull Bone loss
- slow
ndash rate may vary depending on the modifiers
bull Severity is determined by bone loss and LOA
bull Can become inactive (stable) active (recurrent) refractory
Periodontitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram ndash
bull P gingivalis
bull P intermedia
bull Tannerella forsythensis (B forsythus)
Treatmentbull Self carebull Scrt
pldebridement bull Depending type of
defects amp severity ndashpossibly surgery
amp perio referral
Not includedAggressive
This category includes formally called diseases
bull Juvenile
bullEarly onset
bullPrepubertal
bullRapidly progressive
Localized Aggressive Localized Juvenile Periodontitis
bull More significant bone loss surrounding 1st molars amp incisors ndash typically angular type bone loss amp mirror image bilaterally
bull Rate of bone loss is rapid
bull OH can be good
9
Localized Aggressive LJP
bull Defects in PMNs or macrophagesbull respond slowly
bull chemotaxis defect
bull impaired phagocytosis
bull Onset typically during teenage years
bull Hereditary componentgenetic
bull more common in females amp blacks
Localized Aggressive Localized Juvenile Periodontitis
Microorganisms
Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans
P gingivalis
Treatmentbull scrt pldebridement but typically unresponsivebull Antibiotics to be administered with or just after debridement
ndash combo metronidazole wamoxicillin or metro w augmentinndash Clindamycin Azithromycin
bull possibly surgerybull prompt perio referralbull suggest family be evaluated (siblings children etc)bull sea salt being used as prevention of AA amp Tx
Generalized Aggressive Formally Generalized Juvenile Periodontitis
bull More rare than LJPbull Can affect most teeth but more severe on 1st molar
amp incisorsndash must involve gt 3 other teeth
bull Onset usually under 30 years oldbull Associated with neutrophil disorderbull Generally significant inflammation amp heavy
plaquecalculusbull Children w Gagp seem more prone to ear skin amp
upper respiratory tract infections
Generalized Aggressive Generalized Juvenile Periodontitis
MicroorganismsA actinomycetemcomitansPorphyromas gingivalis Eikenella corrodens
Treatmentscrt pldebridementantibiotics
ndash combo metronidazole wamoxicillin or metro w augmentin
possibly surgeryprompt perio referralbull Suggest family be evaluated (siblings children etc)
Periodontitis as a Manifestation of Systemic Disease
bull Systemic diseases that severely impair host response should be considered a periodontal manifestation of the systemic disease amp primary diagnosis should be the systemic disease according to International Statistical Classification of Disease (ICD)
ndash Excludes diabetes
bull Hematologicacquired neutropenias leukemias
bull Genetic disorderfamilial neutopenias down syndrome leukocyte adhesion deficiency syndrome papillon-lefreve syndrome chediak-higshi histocytosis syndromes Glycogen storage disease genetic agranulcytosis cohen syndrome Ehlers-Danlossyndrome hypophosphatsis
Necrotizing Periodontal Diseases NG amp NP
Etiologybull Unknown
bull Risk factorsexcessive stress lack of rest poor oral hygiene smoking HIV poor immune response
bull More common in underdeveloped countries
bull Less common now in the US
bull Susceptible to reoccurrence
Symptomsbull SUDDEN onset of burning
mouth inability to eat metallic taste excessive salvia amp PAINFUL
Microorganisms
spirochetes
Prevotella intermedia
Fusiform bacillus
Fusobacterium nucleatum
Ulcerative has been eliminated
10
NGSigns
bull 3 key features papilla necrosis bleeding and pain
bull Punched out papillae cratered like depressions covered by a white necrotic pseudomembrane(collection of PMNS) bright red margins spontenousbleeding may occur
bull Distinctive foul odor
bull May have systemic involvement
ndash lymphadenopathy fever
bull May be a systemic
manifestations
ndash HIV
NG Treatmentbull Advise to avoid smoking amp etoh get rest and proper nutrition (rec
multi vitamin soft nutritious diet)+ self care
bull Rinses with frac12 glass warm water amp 1 tbsp hydrogen peroxide w half glass or chlorhexidine
bull Pain medication
bull Antibiotics can be used especially if systemic involvement
ndash metronidazole tetracycline pen vk
bull Initial supragingival debridement then complete
bull Consider complete laboratory work ndashup amp medical consult
ndash (NUG may be the first sign of HIV)
bull May progress to NUP
bull Follow ndashup phone call or visit within 24 hrsndash Re-eval surgery referral debridement wlocal= recurrent nature
NP
bull Progression of NUG
bull May be related to systemic disease
bull HIV nutrition deficiency
bull NUG superimposed on a previous periodontal disease
NP
Signs amp symptoms
bull Intensely red necrosis white pseudomembrane
bull Painful odor punched-out papillae
bull Reports of deep aching pain or jaw pain
bull Extensive bone loss
bull Spontaneous bleeding
Treatment
bull Same as NUG
Peridex culture antibiotics (metronidazole) or antifungals
Refractory
bull Not included in the new guidelines
bull Unresponsive to treatmentndash surgery frequent scrt pl antibiotics
bull Can be localized or generalized
bull Usually smokers
bull Treatment clindamycin metronidazole metriwamoxicillin or Augmentin
Periodontal Phenotype (Biotypes)
bull The term describes the thickness of the gingiva in a bucco-lingual dimension
bull 3 types
Thick flat
Thick scalloped
Thin
bull Thick (85) is more prevalent than thin (15)
11
Thin Gingival Phenotype
bull Triangle shaped teeth vs square
bull Thin tissue
bull Susceptible to recession
bull Dehiscence present
bull Instrumentation must be done
Carefully due to thin biotype
bull Reacts to insult by recession
Thick amp Flat Gingival Phenotype
bull Square shaped
bull Thick tissue
bull Susceptible to pocketing
bull Reacts to insult by pocketing
Thick Scalloped
bull Thick fibrotic gingiva
bull Slender teeth
bull Narrow zone of KT
bull Gingival scalloping
Recession
Type 1 Type 2
Interproximal CEJ
is clinically not
detectable
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is lt to buccal
Type 3
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is gt
buccal
attachment loss
Implants
bull Treat perio prior to implantsbull It takes 2 weeks for the implants to
become colonized by the surrounding teeth
bull No horizontal fibers like a tooth so infection goes straight to bone and perio happens very quickly
bull This perimucosal seal is delicate ndashBe careful during instrumentation
12
Implants
bull The implant coatingsrough surfaces may create more risk for implantitis but better for osteointergration
ndash The calculus is more embedded on these surfaces than the previous smoother surfaces
Stages of Peri-implant DiseasePeri-implant mucositis
bull Reversible inflammation of the soft tissues
bull Occurs in about 50 of implants placed within 9 - 14 years
Peri-implantitis
bull Bone Loss
bull Occurs in 12- 47 of implants 5 years after placement
bull Risk factors-Hx of severe perio poor self care amp lack of maintenance care
bull Cement Implantitis
bull Some evidence linking cement and titanium particles bio corrosion
Peri-implantitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram - Fusobacterium species Prevotella intermedia
bull Implant failure is usually due to the microbial challenge occlusal load or excessive cementndash Cement has been found in the tissues
bull Failure is evidenced by gt2 mm MOBILITY
bull Bone loss buccal and lingual results in dehiscence
Cement Implantitis
New AAP Case definitionPeri-implantitis
bull BOP
bull Probing depth gt 6 mm
bull Bone levels gt 3 mm apical of the most coronal portion of the intraosseous part of the implant
Caton J Armitage G Berglundh T Et al A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri‐implant diseases and conditions ndash Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification Journal of Periodontology 89 S1 (S1-S8) (2018)
Failing Criteria
bull Ailing (Peri-implant mucositis) inflammation present but no mobility
ndash bone appears normal or there may be an incipient lesion
bull Failing Peri-implantitis without mobility
ndash Inflammation has progressed to the bone as evidenced by radiographic lesion
bull Failed Peri-implantitis with mobility
ndash Implant has pronounced bone loss
Probing amp BOP
bull Metal probes on prosthetic part of the crown is fine
bull Some are concerned with metal probes on the threads
bull Must probe implants
bull Probe depths are generally deeper than natural tooth
bull BOP is not normal
threads
13
Treatment
bull Be aggressive amp prevent bone loss because very difficult to treat once initiated
bull Treatment
ndash Debride thoroughly
ndash Chlorhexidine
ndash Systemic antibiotics
ndash Bone grafts
ndash Arestin- local drug delivery
ndash Air flow polishing with glycine
Diagnosis Severity
bull Determining severity is based on CAL and bone loss
bull Clinical attachment level (CAL)
ndashdistance from the junctional epithelium to the CEJ
bull Probe depths alone are lacking because it does not take in account the gingival margin
ndashusing probe depths alone can result in over estimating or underestimating disease
Three possible relationships for gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ
GM
bull Where should the GM be normallyndash 1-2 mm coronal to the CEJ
bull What is the pattern of CEJs interproximallyacross the mouthndash More Flat on the Posteriors
ndash More Curvature on the Anteriors
ndash For interproximal space look at the papillae does it fill the embrasure space
ndash A normal GM on the anteriors could be +1mm
ndash A normal GM on the posteriors could be +2 mm
Clinical attachment level
Depends on position of the gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ (-)
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ (same)
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ (+)
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is coronal to CEJ
1 Measure probe depth
2 Measure from gingival margin to CEJ
3 Subtract second measurement from overall probe depth
FYI-This is a color
coded probe w
markings at 36912
14
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is levelwith CEJ
bull Probe depth is Clinical attachment level
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is apical to CEJ
bull Measure probe depthbull Measure recessionbull Add recession to probe depth
Grading
Bone Loss
Stage 1
Coronal 13
lt 15
Coronal 13
Mid 13
Last 13
15 Normal bone Height
33 stage 2
Stage 3Extends to mid third of root amp beyondStage 4Extends to mid third of root amp beyond
Stage 1
stage 3 amp 4
Predicting Activity
bull BOP
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will not break down
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will breakdown
ndash Sites that do not bleed will not breakdown
ndash The absence of bleeding provides more information than whether bleeding exists
ndash Therefore when sites bleed we say it is active
bull Inflammation
bull Nutrient canals
bull Rough looking crestal bone vs smooth amp well demarcated may indicate activity
15
Predicting Activity
bull Nutrient canals
ndash Highly visible canals may indicate active or rapid destruction
ndash canals are thought to be engorged large blood vessels
Crestal Bone
Rough looking crestal boneSmoother more demarcated crestal bone
Planningbull Systematic Informed consent
bull Diagnosis prognosis options risks benefits
ndashPatients must have all the information
bull Studies indicate slight reductions in PD s gt 6 mm after full-mouth scaling and root planingperformed in one appointment vs over longer intervals
bull These protocols particularly effective in patients with aggressive periodontitis andor pts w systemic conditions
Eberhard J et al J Clin Periodontol 200835591ndash604 amp Fang et al J Periodont Res October 19 2015)
ImplementationTreatment
bull Goals are to eliminate infection and risk factorsbull The objective is to remove all clinically detectable
calculus without excessive root planingndash bacterial endotoxins are weakly adherent to the root
surface (Nakib 1982)
bull The term debridement vs root planing
ImplementationTreatment
bull Treat patientrsquos significant otherbull 40 of the time spouses have the
same microbiotabull Donrsquot kiss dogs amp cats- they may have
periobull Avoid gross scaling
bull risk of abscessbull educationbull more difficult to re-insert
instruments
16
Air Polishing with glycine
ndashGlycine has anti inflammatory ampimmune modulation effectsbull Glycine receptor gingival tissue
ndashPerpulsionndashFDA approval for lt5 mmndashRemoval biofilm amp stainndashPerio maintenance ndashImplantsndashDecontaminate prior to grafts
Host-Modulating Treatmentbull Treating periodontitis by trying to resolve
inflammation
bull Resolvins
ndash Omega 3 Fatty acids correlated with less bone loss
ndash may be due to their ability to generate mediators that fight inflammation and aid in inflammation resolution
bull Low-dose doxycycline 20 mg 2x daily
ndash Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor is the only FDA-approved
ndash Reduction of PD amp CAL gain over 3 months to 9 monthsGolub LM et al Doxycycline i hibits neutrophil (PMN)-type matrix metalloproteinases in human adult periodontitis gingiva J Clin Periodontol 199522100ndash109 amp
Golub LM et al Adjunctive treatment with subantimicrobial doses of doxycycline effects on gingival fluid collagenase activity and attachment loss in adult periodontitis J Clin Periodontol 200128146ndash156
Host-Modulating Treatment
bull NSAIDsndash Reduces PGE 2 which can reduce bone loss
ndash Flurbiprofen and topical (ketorolac)
ndash Case controls demonstrate decrease risk
bull Bisphosphonates ndash Used for treating Pagetrsquos bone pain amp osteoporosis
ndash Alendronate sodium (Fosamax) risedronate (Actonel)
ndash Investigating for its ability to modulate the host
bull Used experimentally in animals to inhibit bone resorption amp bone mineral content amp to interfere w breakdown of collagen in the periodontium
ndash WARNING case reports of bone necrosis after extractions
bull questions scrtpl w pts on drug
Treatment
bull Statins have an anti-inflammatory and immune effects reducing levels of C-Reactive Protein MMP Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
ndash Statins reduce bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclast formation
ndash Some results show lower alveolar bone loss and reduction of clinical signs of inflammation
(meta anyalsis Estanislau etal J Clin Pharmacol 2014 Dec)
ndash Topical gels (simvastatin atorvastatin)
Treatment
bull Probioticsndash Improved biofilm index and probe depths (Shimauchi 2008)
bull Valtrexbull Photodynamic therapy
ndash Light-sensitive drug is applied then a light laser directly on the area treated with the drug
ndash When the light is combined with the drug phototoxic reactions are induced which destroy bacterial cells
ndash Shows short term benefits (Sgolastra 2012)bull Periowave
bull Emdogainndash Enamel matrix derivative for periodontal tissue regeneration in
infrabony defects amp used w SRP to enhance resultsbull Derived from developing pig teethbull Stimulate adherence attachment to cementum
Treatmentbull Topical antioxidants
ndash Antioxidant gel and rinse
ndash Periosciences ndash toothpaste rinse gel
ndash Topical coenzyme COQ10
bull Due to correlation w perio oxidative stress markers amp low level of natural occurring salivary antioxidants looking at polyphenolsantioxidants in the mouth locally delivered
ndash needs more research
bull Hyaluronic acid (HA) gel and mouth rinsendash hyaluronic acid plays a large role in the collagen building 02
hyaluronan gel topically amp subgingivally
ndash Studies have been done to evaluate on wound healing amp improving perio outcomes
ndash Further evidence is needed
17
LasersNeodymium lasersbull Ex NdYAG NdYAP lasers
bull FDA approved-PerioLase (FRNdYAG) patented procedure LANAPshown to regenerate cementum bone amp PDL
bull No histological studies LANAP with regeneration ( Linden E Laser Basics Dimensions of dental hygiene april 2016)
Diode Lasersbull Most commonly used by RDHs
bull Wide range of wavelengths
bull Used to reduce bacteria amp remove inflammatory byproducts
bull Absorbed by pigmented structures hemoglobin amp melanin
bull Warming amp ablation
bull There is insufficient evidence
Evaluation
bull Evaluating the host response
1 week acute or painful conditions
4-6 weeks changes in attachment level
12 weeks microbiota returns to pre TX levels
bull Complete final diagnosis
bull Many lawsuits exist due to lack of follow-up where as before it was due to failure to diagnose
Evaluation
bull Responded well
ndashDetermine appropriate PMP interval
bull Unresponsive
ndashProblem solve
bull Try to determine whyndashVirulent microorganisms Inadequate host
response Ineffective initial therapy or contributory amp risk factors
ndashFormulate new plan
Possible Solutions
bull Improve initial therapyndash re-scale root plan re-root plan
ndash self care
ndash adjunctive chemotherapeutics necessary
bull Reduce risk amp contributory factors
ndash smoking restorative
bull ex Overhangs
bull Medical consult periodontal referral Advanced diagnostic
Advanced Diagnostics
bull A test to determine active disease or predict an active episode of disease
bull currently we are not able to do this well
bull Many new tests are being developed still under investigation and still being assessed for usefulness
bull Many are not available yet or very expensive
bull Provide information that adds to the clinical exam
bull If it would be nice to know but not change anything we need to ask the questionhellip
bull Is the benefit worth the cost
Testing
OralDNA Labs Inc- httpwwworaldnacom
bull Genetic risk bacterial profile HPV-related oral cancers Herpes Candida Chlamydia trachomatis(CT) Neisseria gonorrhea(NG) gene markers related to inflammatory response DNA DrugMaptrade
micro-Ident- DNA probes
bull httpswwwhain-lifesciencecom
Oravital-Toronto based company uses biofilm testing the use of prescribed antibiotic antimicrobial rinses httpswwworavitalcom
Temple Oral Microbiology testing service 800-788-6687
USC Oral microbiology testing Lab 213-740-3163
UNC Oral microbiology Lab oralmicrodentistryuncedu

3
Systemic Link
bull Cardiovascular Diseases amp Stroke
ndash perio appears to be a mildmoderate risk for coronary heart disease Perio is a stronger risk factor for stroke
ndash 2 -7 fold increased risk of stroke in those w perio
bull Diabetes
ndash bi-directional relationship
Systemic Linkbull Respiratory diseases
ndash Microrsquos from the oral nasal amp pharyngeal frequently contaminate the upper airway
ndash Increased risk due to poor OH
bull May increase risk in lung cancer
ndash periodontal disease pts have a 124-fold increased risk of developing lung cancer
bull MiscarriagesPre-term DeliveryLow Birth Weight Babies
ndash Women w perio may be 7-8X more predisposed to deliver premature infants w LBW
ndash CRP amp PGE2 trigger early uterine contractions amp PTD
ndash microbiome Project found the microbiome of the placenta most resembles the subgingival environment
Systemic Link
bull Alzheimers Diseasendash Early exposure to periodontitis and inflammatory
conditions may increase one for Alzheimers disease later in life
bull theories
ndashInflammation allows bacteria to enter the brain
ndashPeriodontal spirochetes disrupt the normal defenses and may lead to neuronal degeneration
ndashPg
Periodontal MedicineSystemic Connection
bull Non- dental professionals appreciate the impact of oral health
bull As patient awareness of perio amp systemic implications increases more seek preventive care (Williams amp Offenbacher periodontol200023(1)9-12)
bull Some strong links have been observed
bull Further studies are needed
Diagnosis
bull A periodontal diagnosis must be made to facilitate good decision-making for both the clinician amp pt for proper treatment planning
bull It can be very effective amp powerful
2017 Periodontal Classification
bull Proceedings of the World (American Academy of
Periodontology and the European Federation of
Periodontology) Workshop on the Classification of
Periodontal and Peri‐Implant Diseases and
Conditions
Caton J Armitage G Berglundh T Et al A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri‐implant diseases and conditions ndashIntroduction and key changes from the 1999 classification Journal of Periodontology 89 S1 (S1-S8) (2018)
httpsonlinelibrarywileycomtoc19433670201889S1
4
Key Points
bull Created by incredible researchers in the field of perio
bull Case definitions for research vs clinicaltreatment
ndashResearch guidelines were needed
bull Includes a holistic approach to periodontology
ndash Included risk factors modifiers and overall perio systemic connection
bull Creating space for future research
bull Addressing the borderline between gingivitis and periodontitis
Key Points
bull Excessive occlusal force- Traumatic occlusal force
bull Biologic width- Supracrestal tissue attachment
bull 3 disease of perio- perio systemic necrotizing
bull Necrotizing periodontal disease- dropped ulcerative
bull Linear gingivitis removed is new term is Candidosis
bull Added implant
bull Periodontal abscesses (PA) classified according to the etiological factors involved
bull added gingival pigmentation due to medication
Key Pointsbull Must probe implants lightly to monitor depth changes
and bleeding progression of perio is faster on implants
bull CAL-lack of training affects DX initial periodontitis in regards to CAL
-Interdental CAL is detectable at ge2 non‐adjacent teeth or Buccal CAL ge3 mm with pocketing gt3 mm is detectable at ge2 teeth
bull Proposal for staging and grading framework which would allow for complexity and risk
ndash 3 sets of parameters
bull RATE RISK RISK
bull The intention was to liken to cancer
httpswwwperioorg2017wwdc
5
Types of Periodontal diseasesGingival
Dental biofilm Induced Gingivitis Most commonbull Typically biofilm is proportionate
to the amount of inflammation
bull No bone loss no LOA
Types- New
bull Localized = BOPgt 10 amp lt30
bull Generalized plaque induced gingivitis gt 30 BOP
Microorganisms
bull Non-specific includes both Gram - amp Gram +
Treatment
bull self care deplaquingdebridementscaling
bull eliminate local contributory factors
Modifying Factors of Biofilm induced Gingivitis hormonalPregnancy Gingivitis
Etiologybull biofilm amp hormone changes
bull degree of inflammation parallels OH
ndash good OH can prevent pregnancy gingivitis
bull will exacerbate any previous periodontal disease
Pregnancy Gingivitis
Microorganism
bull Prevotella intermedia
Treatment
bull subsides after giving birth
bull exaggerated response can be prevented w excellent OH
bull frequent recalls Oral self care
bull Deplaquingdebridementscaling
Pyogenic Granuloma
Treatment
bull may resolve on own after debridement
bull may need surgical removal
6
Drug-influenced gingivitis
bull Gingival enlargement
ndashAnticonvulsants
bull Phenytoin
ndashCalcium channel blockers
bull Nifedipine 6-43
ndash Immunosuppressants
bull Cyclosporin 25
ndashAnabolic Androgenic Steroid
ndash Prostate cancer treatment
Gingival enlargement
bull Level of biofilm amp drug dosage accumulation can affect the severity of overgrowth
bull Consult w MD for drug substitution
bull Some cases of hypertrophic gingival tissue have been reported as Kaposirsquos sarcoma amp squamous cell carcinoma
Non-biofilm induced related to bull Specific bacteria
ndash Neissera gonorrhea treponema pallidum streptococci
bull Viralndash Herpes simplex 1 amp 2 varicella zoster papillmavirus
bull Fungal
bull Cultured for true diagnosis amp treat appropriately antibiotics antiviral amp or antifungal
bull Not common amp usually not known
Non-plaque induced gingival diseases of fungal origin
Candidosisformally Linear gingivitis
bull Generally fungalcandiasis
bull Linear amp very distinctive band of severe erythema on gingival margin
bull Disproportion of inflammatory intensity for the amount of biofilm present
Candidosis Treatment
ndash OHE consider chlorhexidine
ndash Does not respond well to improved OH or scaling
ndash Biofilm removal debridementscaling
ndash May need additional physician consult
Lichen Planus
Etiologybull Unknownbull Cell mediated Immune pathogenesis bull Systemic Diseases
ndash Diabetes hypertension hepatitis B amp C chronic graft-versus-host disease amp lupus
bull Medicationsndash antimalarial drugs antihypertensives amp non-steroidal anti
inflammatory (NSAIDS)
Signsbull Affects skin and mucous membranesbull Lesions may be mild to moderately painful amp burning
7
Lichen PlanusTypes
Reticular-plaque papular
Erosive Bullous Atrophic ulcerative
bull Erosive- gingival
ndash bulbous forms ulcerative amp painful
ndash red and raw
bull Reticular
ndash asymptomatic keratontic lines called stria
ndash lacy white lines
Lichen Planus
bull severity may relate to stressConsiderationsbull Higher risk for non- reticular types for malignant transformation
ndash LP pts have a 10 fold increased risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma
Treatmentbull Look for triggers allergies sensitivity bull Aloe Vera rinses amp gelbull Corticosteriods
ndash topical- fluocinonide dexamethadone dipropionate spray topical steroids may help- can cause candida
bull Periodic biopsies are necessary for areas that do not respond to treatment
bull Regular recalls
Inflammatory And Immune Conditions And Lesions
Hypersensitivity ReactionsAllergic gingivitis
Other names desquamative Plasma cell gingivitis idiopathic
gingivostomatitis atypical gingivostomatitis allergic gingivostomatitis hypersensitivity and plasmacytosis
Plasma cell gingivitis is an uncommon inflammatory condition usually affecting the anterior maxillary gingiva and of uncertain etiology While some authors have associated plasma cell gingivitis with a hypersensitivity response to antigens in various substances others have raised doubt whether plasma cell gingivitis is a distinct clinicopathologic entity
Allergic gingivitis
Etiology
bull auto immune
bull Allergy
bull Signs
bull sloughing of the epithelium which leaves raw red surface
bull The edematous tissue often extends to the mucogingival junction with a deep red appearance
Allergic gingivitis
Symptoms
painful
Treatment
topicalsystemic steroid therapy
remove etiological factor if possible
-spices toothpaste flavorings peppermint wintergreen menthol cinnamon preservatives mints gum candy
Possible Offending Products to Gingival Tissue
bull Commercially available toothpaste (tartar-control additives and flavoring agents [possibly
cinnamon] that mask the tartar control additives)
bull Mouth rinses
bull Cinnamon aldehyde
bull Sodium benzoate and methyl paraben
bull Food substances such as wheat dairy chocolate eggs peanuts and monosodium glutamate
bull Red wine (sulfides and tartrazine additives)
bull Preservatives
bull Essential oils such as peppermint spearmint and wintergreen found in gums candy and mouth rinses
bull Dark cola drinks
bull Strong spices
bull Chili peppers
bull Clove
bull Cardamom Burkhart NW Toothpaste allergy RDH 2007 27(6) 86107-108
8
Types of Periodontal diseasesPeriodontitis
Periodontitis
bull Chronic
bull Disease will progress unless treated
bull Typical age of onset is 35 yrs of age
bull Bone loss
- slow
ndash rate may vary depending on the modifiers
bull Severity is determined by bone loss and LOA
bull Can become inactive (stable) active (recurrent) refractory
Periodontitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram ndash
bull P gingivalis
bull P intermedia
bull Tannerella forsythensis (B forsythus)
Treatmentbull Self carebull Scrt
pldebridement bull Depending type of
defects amp severity ndashpossibly surgery
amp perio referral
Not includedAggressive
This category includes formally called diseases
bull Juvenile
bullEarly onset
bullPrepubertal
bullRapidly progressive
Localized Aggressive Localized Juvenile Periodontitis
bull More significant bone loss surrounding 1st molars amp incisors ndash typically angular type bone loss amp mirror image bilaterally
bull Rate of bone loss is rapid
bull OH can be good
9
Localized Aggressive LJP
bull Defects in PMNs or macrophagesbull respond slowly
bull chemotaxis defect
bull impaired phagocytosis
bull Onset typically during teenage years
bull Hereditary componentgenetic
bull more common in females amp blacks
Localized Aggressive Localized Juvenile Periodontitis
Microorganisms
Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans
P gingivalis
Treatmentbull scrt pldebridement but typically unresponsivebull Antibiotics to be administered with or just after debridement
ndash combo metronidazole wamoxicillin or metro w augmentinndash Clindamycin Azithromycin
bull possibly surgerybull prompt perio referralbull suggest family be evaluated (siblings children etc)bull sea salt being used as prevention of AA amp Tx
Generalized Aggressive Formally Generalized Juvenile Periodontitis
bull More rare than LJPbull Can affect most teeth but more severe on 1st molar
amp incisorsndash must involve gt 3 other teeth
bull Onset usually under 30 years oldbull Associated with neutrophil disorderbull Generally significant inflammation amp heavy
plaquecalculusbull Children w Gagp seem more prone to ear skin amp
upper respiratory tract infections
Generalized Aggressive Generalized Juvenile Periodontitis
MicroorganismsA actinomycetemcomitansPorphyromas gingivalis Eikenella corrodens
Treatmentscrt pldebridementantibiotics
ndash combo metronidazole wamoxicillin or metro w augmentin
possibly surgeryprompt perio referralbull Suggest family be evaluated (siblings children etc)
Periodontitis as a Manifestation of Systemic Disease
bull Systemic diseases that severely impair host response should be considered a periodontal manifestation of the systemic disease amp primary diagnosis should be the systemic disease according to International Statistical Classification of Disease (ICD)
ndash Excludes diabetes
bull Hematologicacquired neutropenias leukemias
bull Genetic disorderfamilial neutopenias down syndrome leukocyte adhesion deficiency syndrome papillon-lefreve syndrome chediak-higshi histocytosis syndromes Glycogen storage disease genetic agranulcytosis cohen syndrome Ehlers-Danlossyndrome hypophosphatsis
Necrotizing Periodontal Diseases NG amp NP
Etiologybull Unknown
bull Risk factorsexcessive stress lack of rest poor oral hygiene smoking HIV poor immune response
bull More common in underdeveloped countries
bull Less common now in the US
bull Susceptible to reoccurrence
Symptomsbull SUDDEN onset of burning
mouth inability to eat metallic taste excessive salvia amp PAINFUL
Microorganisms
spirochetes
Prevotella intermedia
Fusiform bacillus
Fusobacterium nucleatum
Ulcerative has been eliminated
10
NGSigns
bull 3 key features papilla necrosis bleeding and pain
bull Punched out papillae cratered like depressions covered by a white necrotic pseudomembrane(collection of PMNS) bright red margins spontenousbleeding may occur
bull Distinctive foul odor
bull May have systemic involvement
ndash lymphadenopathy fever
bull May be a systemic
manifestations
ndash HIV
NG Treatmentbull Advise to avoid smoking amp etoh get rest and proper nutrition (rec
multi vitamin soft nutritious diet)+ self care
bull Rinses with frac12 glass warm water amp 1 tbsp hydrogen peroxide w half glass or chlorhexidine
bull Pain medication
bull Antibiotics can be used especially if systemic involvement
ndash metronidazole tetracycline pen vk
bull Initial supragingival debridement then complete
bull Consider complete laboratory work ndashup amp medical consult
ndash (NUG may be the first sign of HIV)
bull May progress to NUP
bull Follow ndashup phone call or visit within 24 hrsndash Re-eval surgery referral debridement wlocal= recurrent nature
NP
bull Progression of NUG
bull May be related to systemic disease
bull HIV nutrition deficiency
bull NUG superimposed on a previous periodontal disease
NP
Signs amp symptoms
bull Intensely red necrosis white pseudomembrane
bull Painful odor punched-out papillae
bull Reports of deep aching pain or jaw pain
bull Extensive bone loss
bull Spontaneous bleeding
Treatment
bull Same as NUG
Peridex culture antibiotics (metronidazole) or antifungals
Refractory
bull Not included in the new guidelines
bull Unresponsive to treatmentndash surgery frequent scrt pl antibiotics
bull Can be localized or generalized
bull Usually smokers
bull Treatment clindamycin metronidazole metriwamoxicillin or Augmentin
Periodontal Phenotype (Biotypes)
bull The term describes the thickness of the gingiva in a bucco-lingual dimension
bull 3 types
Thick flat
Thick scalloped
Thin
bull Thick (85) is more prevalent than thin (15)
11
Thin Gingival Phenotype
bull Triangle shaped teeth vs square
bull Thin tissue
bull Susceptible to recession
bull Dehiscence present
bull Instrumentation must be done
Carefully due to thin biotype
bull Reacts to insult by recession
Thick amp Flat Gingival Phenotype
bull Square shaped
bull Thick tissue
bull Susceptible to pocketing
bull Reacts to insult by pocketing
Thick Scalloped
bull Thick fibrotic gingiva
bull Slender teeth
bull Narrow zone of KT
bull Gingival scalloping
Recession
Type 1 Type 2
Interproximal CEJ
is clinically not
detectable
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is lt to buccal
Type 3
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is gt
buccal
attachment loss
Implants
bull Treat perio prior to implantsbull It takes 2 weeks for the implants to
become colonized by the surrounding teeth
bull No horizontal fibers like a tooth so infection goes straight to bone and perio happens very quickly
bull This perimucosal seal is delicate ndashBe careful during instrumentation
12
Implants
bull The implant coatingsrough surfaces may create more risk for implantitis but better for osteointergration
ndash The calculus is more embedded on these surfaces than the previous smoother surfaces
Stages of Peri-implant DiseasePeri-implant mucositis
bull Reversible inflammation of the soft tissues
bull Occurs in about 50 of implants placed within 9 - 14 years
Peri-implantitis
bull Bone Loss
bull Occurs in 12- 47 of implants 5 years after placement
bull Risk factors-Hx of severe perio poor self care amp lack of maintenance care
bull Cement Implantitis
bull Some evidence linking cement and titanium particles bio corrosion
Peri-implantitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram - Fusobacterium species Prevotella intermedia
bull Implant failure is usually due to the microbial challenge occlusal load or excessive cementndash Cement has been found in the tissues
bull Failure is evidenced by gt2 mm MOBILITY
bull Bone loss buccal and lingual results in dehiscence
Cement Implantitis
New AAP Case definitionPeri-implantitis
bull BOP
bull Probing depth gt 6 mm
bull Bone levels gt 3 mm apical of the most coronal portion of the intraosseous part of the implant
Caton J Armitage G Berglundh T Et al A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri‐implant diseases and conditions ndash Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification Journal of Periodontology 89 S1 (S1-S8) (2018)
Failing Criteria
bull Ailing (Peri-implant mucositis) inflammation present but no mobility
ndash bone appears normal or there may be an incipient lesion
bull Failing Peri-implantitis without mobility
ndash Inflammation has progressed to the bone as evidenced by radiographic lesion
bull Failed Peri-implantitis with mobility
ndash Implant has pronounced bone loss
Probing amp BOP
bull Metal probes on prosthetic part of the crown is fine
bull Some are concerned with metal probes on the threads
bull Must probe implants
bull Probe depths are generally deeper than natural tooth
bull BOP is not normal
threads
13
Treatment
bull Be aggressive amp prevent bone loss because very difficult to treat once initiated
bull Treatment
ndash Debride thoroughly
ndash Chlorhexidine
ndash Systemic antibiotics
ndash Bone grafts
ndash Arestin- local drug delivery
ndash Air flow polishing with glycine
Diagnosis Severity
bull Determining severity is based on CAL and bone loss
bull Clinical attachment level (CAL)
ndashdistance from the junctional epithelium to the CEJ
bull Probe depths alone are lacking because it does not take in account the gingival margin
ndashusing probe depths alone can result in over estimating or underestimating disease
Three possible relationships for gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ
GM
bull Where should the GM be normallyndash 1-2 mm coronal to the CEJ
bull What is the pattern of CEJs interproximallyacross the mouthndash More Flat on the Posteriors
ndash More Curvature on the Anteriors
ndash For interproximal space look at the papillae does it fill the embrasure space
ndash A normal GM on the anteriors could be +1mm
ndash A normal GM on the posteriors could be +2 mm
Clinical attachment level
Depends on position of the gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ (-)
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ (same)
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ (+)
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is coronal to CEJ
1 Measure probe depth
2 Measure from gingival margin to CEJ
3 Subtract second measurement from overall probe depth
FYI-This is a color
coded probe w
markings at 36912
14
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is levelwith CEJ
bull Probe depth is Clinical attachment level
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is apical to CEJ
bull Measure probe depthbull Measure recessionbull Add recession to probe depth
Grading
Bone Loss
Stage 1
Coronal 13
lt 15
Coronal 13
Mid 13
Last 13
15 Normal bone Height
33 stage 2
Stage 3Extends to mid third of root amp beyondStage 4Extends to mid third of root amp beyond
Stage 1
stage 3 amp 4
Predicting Activity
bull BOP
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will not break down
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will breakdown
ndash Sites that do not bleed will not breakdown
ndash The absence of bleeding provides more information than whether bleeding exists
ndash Therefore when sites bleed we say it is active
bull Inflammation
bull Nutrient canals
bull Rough looking crestal bone vs smooth amp well demarcated may indicate activity
15
Predicting Activity
bull Nutrient canals
ndash Highly visible canals may indicate active or rapid destruction
ndash canals are thought to be engorged large blood vessels
Crestal Bone
Rough looking crestal boneSmoother more demarcated crestal bone
Planningbull Systematic Informed consent
bull Diagnosis prognosis options risks benefits
ndashPatients must have all the information
bull Studies indicate slight reductions in PD s gt 6 mm after full-mouth scaling and root planingperformed in one appointment vs over longer intervals
bull These protocols particularly effective in patients with aggressive periodontitis andor pts w systemic conditions
Eberhard J et al J Clin Periodontol 200835591ndash604 amp Fang et al J Periodont Res October 19 2015)
ImplementationTreatment
bull Goals are to eliminate infection and risk factorsbull The objective is to remove all clinically detectable
calculus without excessive root planingndash bacterial endotoxins are weakly adherent to the root
surface (Nakib 1982)
bull The term debridement vs root planing
ImplementationTreatment
bull Treat patientrsquos significant otherbull 40 of the time spouses have the
same microbiotabull Donrsquot kiss dogs amp cats- they may have
periobull Avoid gross scaling
bull risk of abscessbull educationbull more difficult to re-insert
instruments
16
Air Polishing with glycine
ndashGlycine has anti inflammatory ampimmune modulation effectsbull Glycine receptor gingival tissue
ndashPerpulsionndashFDA approval for lt5 mmndashRemoval biofilm amp stainndashPerio maintenance ndashImplantsndashDecontaminate prior to grafts
Host-Modulating Treatmentbull Treating periodontitis by trying to resolve
inflammation
bull Resolvins
ndash Omega 3 Fatty acids correlated with less bone loss
ndash may be due to their ability to generate mediators that fight inflammation and aid in inflammation resolution
bull Low-dose doxycycline 20 mg 2x daily
ndash Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor is the only FDA-approved
ndash Reduction of PD amp CAL gain over 3 months to 9 monthsGolub LM et al Doxycycline i hibits neutrophil (PMN)-type matrix metalloproteinases in human adult periodontitis gingiva J Clin Periodontol 199522100ndash109 amp
Golub LM et al Adjunctive treatment with subantimicrobial doses of doxycycline effects on gingival fluid collagenase activity and attachment loss in adult periodontitis J Clin Periodontol 200128146ndash156
Host-Modulating Treatment
bull NSAIDsndash Reduces PGE 2 which can reduce bone loss
ndash Flurbiprofen and topical (ketorolac)
ndash Case controls demonstrate decrease risk
bull Bisphosphonates ndash Used for treating Pagetrsquos bone pain amp osteoporosis
ndash Alendronate sodium (Fosamax) risedronate (Actonel)
ndash Investigating for its ability to modulate the host
bull Used experimentally in animals to inhibit bone resorption amp bone mineral content amp to interfere w breakdown of collagen in the periodontium
ndash WARNING case reports of bone necrosis after extractions
bull questions scrtpl w pts on drug
Treatment
bull Statins have an anti-inflammatory and immune effects reducing levels of C-Reactive Protein MMP Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
ndash Statins reduce bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclast formation
ndash Some results show lower alveolar bone loss and reduction of clinical signs of inflammation
(meta anyalsis Estanislau etal J Clin Pharmacol 2014 Dec)
ndash Topical gels (simvastatin atorvastatin)
Treatment
bull Probioticsndash Improved biofilm index and probe depths (Shimauchi 2008)
bull Valtrexbull Photodynamic therapy
ndash Light-sensitive drug is applied then a light laser directly on the area treated with the drug
ndash When the light is combined with the drug phototoxic reactions are induced which destroy bacterial cells
ndash Shows short term benefits (Sgolastra 2012)bull Periowave
bull Emdogainndash Enamel matrix derivative for periodontal tissue regeneration in
infrabony defects amp used w SRP to enhance resultsbull Derived from developing pig teethbull Stimulate adherence attachment to cementum
Treatmentbull Topical antioxidants
ndash Antioxidant gel and rinse
ndash Periosciences ndash toothpaste rinse gel
ndash Topical coenzyme COQ10
bull Due to correlation w perio oxidative stress markers amp low level of natural occurring salivary antioxidants looking at polyphenolsantioxidants in the mouth locally delivered
ndash needs more research
bull Hyaluronic acid (HA) gel and mouth rinsendash hyaluronic acid plays a large role in the collagen building 02
hyaluronan gel topically amp subgingivally
ndash Studies have been done to evaluate on wound healing amp improving perio outcomes
ndash Further evidence is needed
17
LasersNeodymium lasersbull Ex NdYAG NdYAP lasers
bull FDA approved-PerioLase (FRNdYAG) patented procedure LANAPshown to regenerate cementum bone amp PDL
bull No histological studies LANAP with regeneration ( Linden E Laser Basics Dimensions of dental hygiene april 2016)
Diode Lasersbull Most commonly used by RDHs
bull Wide range of wavelengths
bull Used to reduce bacteria amp remove inflammatory byproducts
bull Absorbed by pigmented structures hemoglobin amp melanin
bull Warming amp ablation
bull There is insufficient evidence
Evaluation
bull Evaluating the host response
1 week acute or painful conditions
4-6 weeks changes in attachment level
12 weeks microbiota returns to pre TX levels
bull Complete final diagnosis
bull Many lawsuits exist due to lack of follow-up where as before it was due to failure to diagnose
Evaluation
bull Responded well
ndashDetermine appropriate PMP interval
bull Unresponsive
ndashProblem solve
bull Try to determine whyndashVirulent microorganisms Inadequate host
response Ineffective initial therapy or contributory amp risk factors
ndashFormulate new plan
Possible Solutions
bull Improve initial therapyndash re-scale root plan re-root plan
ndash self care
ndash adjunctive chemotherapeutics necessary
bull Reduce risk amp contributory factors
ndash smoking restorative
bull ex Overhangs
bull Medical consult periodontal referral Advanced diagnostic
Advanced Diagnostics
bull A test to determine active disease or predict an active episode of disease
bull currently we are not able to do this well
bull Many new tests are being developed still under investigation and still being assessed for usefulness
bull Many are not available yet or very expensive
bull Provide information that adds to the clinical exam
bull If it would be nice to know but not change anything we need to ask the questionhellip
bull Is the benefit worth the cost
Testing
OralDNA Labs Inc- httpwwworaldnacom
bull Genetic risk bacterial profile HPV-related oral cancers Herpes Candida Chlamydia trachomatis(CT) Neisseria gonorrhea(NG) gene markers related to inflammatory response DNA DrugMaptrade
micro-Ident- DNA probes
bull httpswwwhain-lifesciencecom
Oravital-Toronto based company uses biofilm testing the use of prescribed antibiotic antimicrobial rinses httpswwworavitalcom
Temple Oral Microbiology testing service 800-788-6687
USC Oral microbiology testing Lab 213-740-3163
UNC Oral microbiology Lab oralmicrodentistryuncedu

4
Key Points
bull Created by incredible researchers in the field of perio
bull Case definitions for research vs clinicaltreatment
ndashResearch guidelines were needed
bull Includes a holistic approach to periodontology
ndash Included risk factors modifiers and overall perio systemic connection
bull Creating space for future research
bull Addressing the borderline between gingivitis and periodontitis
Key Points
bull Excessive occlusal force- Traumatic occlusal force
bull Biologic width- Supracrestal tissue attachment
bull 3 disease of perio- perio systemic necrotizing
bull Necrotizing periodontal disease- dropped ulcerative
bull Linear gingivitis removed is new term is Candidosis
bull Added implant
bull Periodontal abscesses (PA) classified according to the etiological factors involved
bull added gingival pigmentation due to medication
Key Pointsbull Must probe implants lightly to monitor depth changes
and bleeding progression of perio is faster on implants
bull CAL-lack of training affects DX initial periodontitis in regards to CAL
-Interdental CAL is detectable at ge2 non‐adjacent teeth or Buccal CAL ge3 mm with pocketing gt3 mm is detectable at ge2 teeth
bull Proposal for staging and grading framework which would allow for complexity and risk
ndash 3 sets of parameters
bull RATE RISK RISK
bull The intention was to liken to cancer
httpswwwperioorg2017wwdc
5
Types of Periodontal diseasesGingival
Dental biofilm Induced Gingivitis Most commonbull Typically biofilm is proportionate
to the amount of inflammation
bull No bone loss no LOA
Types- New
bull Localized = BOPgt 10 amp lt30
bull Generalized plaque induced gingivitis gt 30 BOP
Microorganisms
bull Non-specific includes both Gram - amp Gram +
Treatment
bull self care deplaquingdebridementscaling
bull eliminate local contributory factors
Modifying Factors of Biofilm induced Gingivitis hormonalPregnancy Gingivitis
Etiologybull biofilm amp hormone changes
bull degree of inflammation parallels OH
ndash good OH can prevent pregnancy gingivitis
bull will exacerbate any previous periodontal disease
Pregnancy Gingivitis
Microorganism
bull Prevotella intermedia
Treatment
bull subsides after giving birth
bull exaggerated response can be prevented w excellent OH
bull frequent recalls Oral self care
bull Deplaquingdebridementscaling
Pyogenic Granuloma
Treatment
bull may resolve on own after debridement
bull may need surgical removal
6
Drug-influenced gingivitis
bull Gingival enlargement
ndashAnticonvulsants
bull Phenytoin
ndashCalcium channel blockers
bull Nifedipine 6-43
ndash Immunosuppressants
bull Cyclosporin 25
ndashAnabolic Androgenic Steroid
ndash Prostate cancer treatment
Gingival enlargement
bull Level of biofilm amp drug dosage accumulation can affect the severity of overgrowth
bull Consult w MD for drug substitution
bull Some cases of hypertrophic gingival tissue have been reported as Kaposirsquos sarcoma amp squamous cell carcinoma
Non-biofilm induced related to bull Specific bacteria
ndash Neissera gonorrhea treponema pallidum streptococci
bull Viralndash Herpes simplex 1 amp 2 varicella zoster papillmavirus
bull Fungal
bull Cultured for true diagnosis amp treat appropriately antibiotics antiviral amp or antifungal
bull Not common amp usually not known
Non-plaque induced gingival diseases of fungal origin
Candidosisformally Linear gingivitis
bull Generally fungalcandiasis
bull Linear amp very distinctive band of severe erythema on gingival margin
bull Disproportion of inflammatory intensity for the amount of biofilm present
Candidosis Treatment
ndash OHE consider chlorhexidine
ndash Does not respond well to improved OH or scaling
ndash Biofilm removal debridementscaling
ndash May need additional physician consult
Lichen Planus
Etiologybull Unknownbull Cell mediated Immune pathogenesis bull Systemic Diseases
ndash Diabetes hypertension hepatitis B amp C chronic graft-versus-host disease amp lupus
bull Medicationsndash antimalarial drugs antihypertensives amp non-steroidal anti
inflammatory (NSAIDS)
Signsbull Affects skin and mucous membranesbull Lesions may be mild to moderately painful amp burning
7
Lichen PlanusTypes
Reticular-plaque papular
Erosive Bullous Atrophic ulcerative
bull Erosive- gingival
ndash bulbous forms ulcerative amp painful
ndash red and raw
bull Reticular
ndash asymptomatic keratontic lines called stria
ndash lacy white lines
Lichen Planus
bull severity may relate to stressConsiderationsbull Higher risk for non- reticular types for malignant transformation
ndash LP pts have a 10 fold increased risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma
Treatmentbull Look for triggers allergies sensitivity bull Aloe Vera rinses amp gelbull Corticosteriods
ndash topical- fluocinonide dexamethadone dipropionate spray topical steroids may help- can cause candida
bull Periodic biopsies are necessary for areas that do not respond to treatment
bull Regular recalls
Inflammatory And Immune Conditions And Lesions
Hypersensitivity ReactionsAllergic gingivitis
Other names desquamative Plasma cell gingivitis idiopathic
gingivostomatitis atypical gingivostomatitis allergic gingivostomatitis hypersensitivity and plasmacytosis
Plasma cell gingivitis is an uncommon inflammatory condition usually affecting the anterior maxillary gingiva and of uncertain etiology While some authors have associated plasma cell gingivitis with a hypersensitivity response to antigens in various substances others have raised doubt whether plasma cell gingivitis is a distinct clinicopathologic entity
Allergic gingivitis
Etiology
bull auto immune
bull Allergy
bull Signs
bull sloughing of the epithelium which leaves raw red surface
bull The edematous tissue often extends to the mucogingival junction with a deep red appearance
Allergic gingivitis
Symptoms
painful
Treatment
topicalsystemic steroid therapy
remove etiological factor if possible
-spices toothpaste flavorings peppermint wintergreen menthol cinnamon preservatives mints gum candy
Possible Offending Products to Gingival Tissue
bull Commercially available toothpaste (tartar-control additives and flavoring agents [possibly
cinnamon] that mask the tartar control additives)
bull Mouth rinses
bull Cinnamon aldehyde
bull Sodium benzoate and methyl paraben
bull Food substances such as wheat dairy chocolate eggs peanuts and monosodium glutamate
bull Red wine (sulfides and tartrazine additives)
bull Preservatives
bull Essential oils such as peppermint spearmint and wintergreen found in gums candy and mouth rinses
bull Dark cola drinks
bull Strong spices
bull Chili peppers
bull Clove
bull Cardamom Burkhart NW Toothpaste allergy RDH 2007 27(6) 86107-108
8
Types of Periodontal diseasesPeriodontitis
Periodontitis
bull Chronic
bull Disease will progress unless treated
bull Typical age of onset is 35 yrs of age
bull Bone loss
- slow
ndash rate may vary depending on the modifiers
bull Severity is determined by bone loss and LOA
bull Can become inactive (stable) active (recurrent) refractory
Periodontitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram ndash
bull P gingivalis
bull P intermedia
bull Tannerella forsythensis (B forsythus)
Treatmentbull Self carebull Scrt
pldebridement bull Depending type of
defects amp severity ndashpossibly surgery
amp perio referral
Not includedAggressive
This category includes formally called diseases
bull Juvenile
bullEarly onset
bullPrepubertal
bullRapidly progressive
Localized Aggressive Localized Juvenile Periodontitis
bull More significant bone loss surrounding 1st molars amp incisors ndash typically angular type bone loss amp mirror image bilaterally
bull Rate of bone loss is rapid
bull OH can be good
9
Localized Aggressive LJP
bull Defects in PMNs or macrophagesbull respond slowly
bull chemotaxis defect
bull impaired phagocytosis
bull Onset typically during teenage years
bull Hereditary componentgenetic
bull more common in females amp blacks
Localized Aggressive Localized Juvenile Periodontitis
Microorganisms
Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans
P gingivalis
Treatmentbull scrt pldebridement but typically unresponsivebull Antibiotics to be administered with or just after debridement
ndash combo metronidazole wamoxicillin or metro w augmentinndash Clindamycin Azithromycin
bull possibly surgerybull prompt perio referralbull suggest family be evaluated (siblings children etc)bull sea salt being used as prevention of AA amp Tx
Generalized Aggressive Formally Generalized Juvenile Periodontitis
bull More rare than LJPbull Can affect most teeth but more severe on 1st molar
amp incisorsndash must involve gt 3 other teeth
bull Onset usually under 30 years oldbull Associated with neutrophil disorderbull Generally significant inflammation amp heavy
plaquecalculusbull Children w Gagp seem more prone to ear skin amp
upper respiratory tract infections
Generalized Aggressive Generalized Juvenile Periodontitis
MicroorganismsA actinomycetemcomitansPorphyromas gingivalis Eikenella corrodens
Treatmentscrt pldebridementantibiotics
ndash combo metronidazole wamoxicillin or metro w augmentin
possibly surgeryprompt perio referralbull Suggest family be evaluated (siblings children etc)
Periodontitis as a Manifestation of Systemic Disease
bull Systemic diseases that severely impair host response should be considered a periodontal manifestation of the systemic disease amp primary diagnosis should be the systemic disease according to International Statistical Classification of Disease (ICD)
ndash Excludes diabetes
bull Hematologicacquired neutropenias leukemias
bull Genetic disorderfamilial neutopenias down syndrome leukocyte adhesion deficiency syndrome papillon-lefreve syndrome chediak-higshi histocytosis syndromes Glycogen storage disease genetic agranulcytosis cohen syndrome Ehlers-Danlossyndrome hypophosphatsis
Necrotizing Periodontal Diseases NG amp NP
Etiologybull Unknown
bull Risk factorsexcessive stress lack of rest poor oral hygiene smoking HIV poor immune response
bull More common in underdeveloped countries
bull Less common now in the US
bull Susceptible to reoccurrence
Symptomsbull SUDDEN onset of burning
mouth inability to eat metallic taste excessive salvia amp PAINFUL
Microorganisms
spirochetes
Prevotella intermedia
Fusiform bacillus
Fusobacterium nucleatum
Ulcerative has been eliminated
10
NGSigns
bull 3 key features papilla necrosis bleeding and pain
bull Punched out papillae cratered like depressions covered by a white necrotic pseudomembrane(collection of PMNS) bright red margins spontenousbleeding may occur
bull Distinctive foul odor
bull May have systemic involvement
ndash lymphadenopathy fever
bull May be a systemic
manifestations
ndash HIV
NG Treatmentbull Advise to avoid smoking amp etoh get rest and proper nutrition (rec
multi vitamin soft nutritious diet)+ self care
bull Rinses with frac12 glass warm water amp 1 tbsp hydrogen peroxide w half glass or chlorhexidine
bull Pain medication
bull Antibiotics can be used especially if systemic involvement
ndash metronidazole tetracycline pen vk
bull Initial supragingival debridement then complete
bull Consider complete laboratory work ndashup amp medical consult
ndash (NUG may be the first sign of HIV)
bull May progress to NUP
bull Follow ndashup phone call or visit within 24 hrsndash Re-eval surgery referral debridement wlocal= recurrent nature
NP
bull Progression of NUG
bull May be related to systemic disease
bull HIV nutrition deficiency
bull NUG superimposed on a previous periodontal disease
NP
Signs amp symptoms
bull Intensely red necrosis white pseudomembrane
bull Painful odor punched-out papillae
bull Reports of deep aching pain or jaw pain
bull Extensive bone loss
bull Spontaneous bleeding
Treatment
bull Same as NUG
Peridex culture antibiotics (metronidazole) or antifungals
Refractory
bull Not included in the new guidelines
bull Unresponsive to treatmentndash surgery frequent scrt pl antibiotics
bull Can be localized or generalized
bull Usually smokers
bull Treatment clindamycin metronidazole metriwamoxicillin or Augmentin
Periodontal Phenotype (Biotypes)
bull The term describes the thickness of the gingiva in a bucco-lingual dimension
bull 3 types
Thick flat
Thick scalloped
Thin
bull Thick (85) is more prevalent than thin (15)
11
Thin Gingival Phenotype
bull Triangle shaped teeth vs square
bull Thin tissue
bull Susceptible to recession
bull Dehiscence present
bull Instrumentation must be done
Carefully due to thin biotype
bull Reacts to insult by recession
Thick amp Flat Gingival Phenotype
bull Square shaped
bull Thick tissue
bull Susceptible to pocketing
bull Reacts to insult by pocketing
Thick Scalloped
bull Thick fibrotic gingiva
bull Slender teeth
bull Narrow zone of KT
bull Gingival scalloping
Recession
Type 1 Type 2
Interproximal CEJ
is clinically not
detectable
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is lt to buccal
Type 3
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is gt
buccal
attachment loss
Implants
bull Treat perio prior to implantsbull It takes 2 weeks for the implants to
become colonized by the surrounding teeth
bull No horizontal fibers like a tooth so infection goes straight to bone and perio happens very quickly
bull This perimucosal seal is delicate ndashBe careful during instrumentation
12
Implants
bull The implant coatingsrough surfaces may create more risk for implantitis but better for osteointergration
ndash The calculus is more embedded on these surfaces than the previous smoother surfaces
Stages of Peri-implant DiseasePeri-implant mucositis
bull Reversible inflammation of the soft tissues
bull Occurs in about 50 of implants placed within 9 - 14 years
Peri-implantitis
bull Bone Loss
bull Occurs in 12- 47 of implants 5 years after placement
bull Risk factors-Hx of severe perio poor self care amp lack of maintenance care
bull Cement Implantitis
bull Some evidence linking cement and titanium particles bio corrosion
Peri-implantitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram - Fusobacterium species Prevotella intermedia
bull Implant failure is usually due to the microbial challenge occlusal load or excessive cementndash Cement has been found in the tissues
bull Failure is evidenced by gt2 mm MOBILITY
bull Bone loss buccal and lingual results in dehiscence
Cement Implantitis
New AAP Case definitionPeri-implantitis
bull BOP
bull Probing depth gt 6 mm
bull Bone levels gt 3 mm apical of the most coronal portion of the intraosseous part of the implant
Caton J Armitage G Berglundh T Et al A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri‐implant diseases and conditions ndash Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification Journal of Periodontology 89 S1 (S1-S8) (2018)
Failing Criteria
bull Ailing (Peri-implant mucositis) inflammation present but no mobility
ndash bone appears normal or there may be an incipient lesion
bull Failing Peri-implantitis without mobility
ndash Inflammation has progressed to the bone as evidenced by radiographic lesion
bull Failed Peri-implantitis with mobility
ndash Implant has pronounced bone loss
Probing amp BOP
bull Metal probes on prosthetic part of the crown is fine
bull Some are concerned with metal probes on the threads
bull Must probe implants
bull Probe depths are generally deeper than natural tooth
bull BOP is not normal
threads
13
Treatment
bull Be aggressive amp prevent bone loss because very difficult to treat once initiated
bull Treatment
ndash Debride thoroughly
ndash Chlorhexidine
ndash Systemic antibiotics
ndash Bone grafts
ndash Arestin- local drug delivery
ndash Air flow polishing with glycine
Diagnosis Severity
bull Determining severity is based on CAL and bone loss
bull Clinical attachment level (CAL)
ndashdistance from the junctional epithelium to the CEJ
bull Probe depths alone are lacking because it does not take in account the gingival margin
ndashusing probe depths alone can result in over estimating or underestimating disease
Three possible relationships for gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ
GM
bull Where should the GM be normallyndash 1-2 mm coronal to the CEJ
bull What is the pattern of CEJs interproximallyacross the mouthndash More Flat on the Posteriors
ndash More Curvature on the Anteriors
ndash For interproximal space look at the papillae does it fill the embrasure space
ndash A normal GM on the anteriors could be +1mm
ndash A normal GM on the posteriors could be +2 mm
Clinical attachment level
Depends on position of the gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ (-)
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ (same)
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ (+)
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is coronal to CEJ
1 Measure probe depth
2 Measure from gingival margin to CEJ
3 Subtract second measurement from overall probe depth
FYI-This is a color
coded probe w
markings at 36912
14
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is levelwith CEJ
bull Probe depth is Clinical attachment level
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is apical to CEJ
bull Measure probe depthbull Measure recessionbull Add recession to probe depth
Grading
Bone Loss
Stage 1
Coronal 13
lt 15
Coronal 13
Mid 13
Last 13
15 Normal bone Height
33 stage 2
Stage 3Extends to mid third of root amp beyondStage 4Extends to mid third of root amp beyond
Stage 1
stage 3 amp 4
Predicting Activity
bull BOP
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will not break down
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will breakdown
ndash Sites that do not bleed will not breakdown
ndash The absence of bleeding provides more information than whether bleeding exists
ndash Therefore when sites bleed we say it is active
bull Inflammation
bull Nutrient canals
bull Rough looking crestal bone vs smooth amp well demarcated may indicate activity
15
Predicting Activity
bull Nutrient canals
ndash Highly visible canals may indicate active or rapid destruction
ndash canals are thought to be engorged large blood vessels
Crestal Bone
Rough looking crestal boneSmoother more demarcated crestal bone
Planningbull Systematic Informed consent
bull Diagnosis prognosis options risks benefits
ndashPatients must have all the information
bull Studies indicate slight reductions in PD s gt 6 mm after full-mouth scaling and root planingperformed in one appointment vs over longer intervals
bull These protocols particularly effective in patients with aggressive periodontitis andor pts w systemic conditions
Eberhard J et al J Clin Periodontol 200835591ndash604 amp Fang et al J Periodont Res October 19 2015)
ImplementationTreatment
bull Goals are to eliminate infection and risk factorsbull The objective is to remove all clinically detectable
calculus without excessive root planingndash bacterial endotoxins are weakly adherent to the root
surface (Nakib 1982)
bull The term debridement vs root planing
ImplementationTreatment
bull Treat patientrsquos significant otherbull 40 of the time spouses have the
same microbiotabull Donrsquot kiss dogs amp cats- they may have
periobull Avoid gross scaling
bull risk of abscessbull educationbull more difficult to re-insert
instruments
16
Air Polishing with glycine
ndashGlycine has anti inflammatory ampimmune modulation effectsbull Glycine receptor gingival tissue
ndashPerpulsionndashFDA approval for lt5 mmndashRemoval biofilm amp stainndashPerio maintenance ndashImplantsndashDecontaminate prior to grafts
Host-Modulating Treatmentbull Treating periodontitis by trying to resolve
inflammation
bull Resolvins
ndash Omega 3 Fatty acids correlated with less bone loss
ndash may be due to their ability to generate mediators that fight inflammation and aid in inflammation resolution
bull Low-dose doxycycline 20 mg 2x daily
ndash Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor is the only FDA-approved
ndash Reduction of PD amp CAL gain over 3 months to 9 monthsGolub LM et al Doxycycline i hibits neutrophil (PMN)-type matrix metalloproteinases in human adult periodontitis gingiva J Clin Periodontol 199522100ndash109 amp
Golub LM et al Adjunctive treatment with subantimicrobial doses of doxycycline effects on gingival fluid collagenase activity and attachment loss in adult periodontitis J Clin Periodontol 200128146ndash156
Host-Modulating Treatment
bull NSAIDsndash Reduces PGE 2 which can reduce bone loss
ndash Flurbiprofen and topical (ketorolac)
ndash Case controls demonstrate decrease risk
bull Bisphosphonates ndash Used for treating Pagetrsquos bone pain amp osteoporosis
ndash Alendronate sodium (Fosamax) risedronate (Actonel)
ndash Investigating for its ability to modulate the host
bull Used experimentally in animals to inhibit bone resorption amp bone mineral content amp to interfere w breakdown of collagen in the periodontium
ndash WARNING case reports of bone necrosis after extractions
bull questions scrtpl w pts on drug
Treatment
bull Statins have an anti-inflammatory and immune effects reducing levels of C-Reactive Protein MMP Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
ndash Statins reduce bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclast formation
ndash Some results show lower alveolar bone loss and reduction of clinical signs of inflammation
(meta anyalsis Estanislau etal J Clin Pharmacol 2014 Dec)
ndash Topical gels (simvastatin atorvastatin)
Treatment
bull Probioticsndash Improved biofilm index and probe depths (Shimauchi 2008)
bull Valtrexbull Photodynamic therapy
ndash Light-sensitive drug is applied then a light laser directly on the area treated with the drug
ndash When the light is combined with the drug phototoxic reactions are induced which destroy bacterial cells
ndash Shows short term benefits (Sgolastra 2012)bull Periowave
bull Emdogainndash Enamel matrix derivative for periodontal tissue regeneration in
infrabony defects amp used w SRP to enhance resultsbull Derived from developing pig teethbull Stimulate adherence attachment to cementum
Treatmentbull Topical antioxidants
ndash Antioxidant gel and rinse
ndash Periosciences ndash toothpaste rinse gel
ndash Topical coenzyme COQ10
bull Due to correlation w perio oxidative stress markers amp low level of natural occurring salivary antioxidants looking at polyphenolsantioxidants in the mouth locally delivered
ndash needs more research
bull Hyaluronic acid (HA) gel and mouth rinsendash hyaluronic acid plays a large role in the collagen building 02
hyaluronan gel topically amp subgingivally
ndash Studies have been done to evaluate on wound healing amp improving perio outcomes
ndash Further evidence is needed
17
LasersNeodymium lasersbull Ex NdYAG NdYAP lasers
bull FDA approved-PerioLase (FRNdYAG) patented procedure LANAPshown to regenerate cementum bone amp PDL
bull No histological studies LANAP with regeneration ( Linden E Laser Basics Dimensions of dental hygiene april 2016)
Diode Lasersbull Most commonly used by RDHs
bull Wide range of wavelengths
bull Used to reduce bacteria amp remove inflammatory byproducts
bull Absorbed by pigmented structures hemoglobin amp melanin
bull Warming amp ablation
bull There is insufficient evidence
Evaluation
bull Evaluating the host response
1 week acute or painful conditions
4-6 weeks changes in attachment level
12 weeks microbiota returns to pre TX levels
bull Complete final diagnosis
bull Many lawsuits exist due to lack of follow-up where as before it was due to failure to diagnose
Evaluation
bull Responded well
ndashDetermine appropriate PMP interval
bull Unresponsive
ndashProblem solve
bull Try to determine whyndashVirulent microorganisms Inadequate host
response Ineffective initial therapy or contributory amp risk factors
ndashFormulate new plan
Possible Solutions
bull Improve initial therapyndash re-scale root plan re-root plan
ndash self care
ndash adjunctive chemotherapeutics necessary
bull Reduce risk amp contributory factors
ndash smoking restorative
bull ex Overhangs
bull Medical consult periodontal referral Advanced diagnostic
Advanced Diagnostics
bull A test to determine active disease or predict an active episode of disease
bull currently we are not able to do this well
bull Many new tests are being developed still under investigation and still being assessed for usefulness
bull Many are not available yet or very expensive
bull Provide information that adds to the clinical exam
bull If it would be nice to know but not change anything we need to ask the questionhellip
bull Is the benefit worth the cost
Testing
OralDNA Labs Inc- httpwwworaldnacom
bull Genetic risk bacterial profile HPV-related oral cancers Herpes Candida Chlamydia trachomatis(CT) Neisseria gonorrhea(NG) gene markers related to inflammatory response DNA DrugMaptrade
micro-Ident- DNA probes
bull httpswwwhain-lifesciencecom
Oravital-Toronto based company uses biofilm testing the use of prescribed antibiotic antimicrobial rinses httpswwworavitalcom
Temple Oral Microbiology testing service 800-788-6687
USC Oral microbiology testing Lab 213-740-3163
UNC Oral microbiology Lab oralmicrodentistryuncedu

5
Types of Periodontal diseasesGingival
Dental biofilm Induced Gingivitis Most commonbull Typically biofilm is proportionate
to the amount of inflammation
bull No bone loss no LOA
Types- New
bull Localized = BOPgt 10 amp lt30
bull Generalized plaque induced gingivitis gt 30 BOP
Microorganisms
bull Non-specific includes both Gram - amp Gram +
Treatment
bull self care deplaquingdebridementscaling
bull eliminate local contributory factors
Modifying Factors of Biofilm induced Gingivitis hormonalPregnancy Gingivitis
Etiologybull biofilm amp hormone changes
bull degree of inflammation parallels OH
ndash good OH can prevent pregnancy gingivitis
bull will exacerbate any previous periodontal disease
Pregnancy Gingivitis
Microorganism
bull Prevotella intermedia
Treatment
bull subsides after giving birth
bull exaggerated response can be prevented w excellent OH
bull frequent recalls Oral self care
bull Deplaquingdebridementscaling
Pyogenic Granuloma
Treatment
bull may resolve on own after debridement
bull may need surgical removal
6
Drug-influenced gingivitis
bull Gingival enlargement
ndashAnticonvulsants
bull Phenytoin
ndashCalcium channel blockers
bull Nifedipine 6-43
ndash Immunosuppressants
bull Cyclosporin 25
ndashAnabolic Androgenic Steroid
ndash Prostate cancer treatment
Gingival enlargement
bull Level of biofilm amp drug dosage accumulation can affect the severity of overgrowth
bull Consult w MD for drug substitution
bull Some cases of hypertrophic gingival tissue have been reported as Kaposirsquos sarcoma amp squamous cell carcinoma
Non-biofilm induced related to bull Specific bacteria
ndash Neissera gonorrhea treponema pallidum streptococci
bull Viralndash Herpes simplex 1 amp 2 varicella zoster papillmavirus
bull Fungal
bull Cultured for true diagnosis amp treat appropriately antibiotics antiviral amp or antifungal
bull Not common amp usually not known
Non-plaque induced gingival diseases of fungal origin
Candidosisformally Linear gingivitis
bull Generally fungalcandiasis
bull Linear amp very distinctive band of severe erythema on gingival margin
bull Disproportion of inflammatory intensity for the amount of biofilm present
Candidosis Treatment
ndash OHE consider chlorhexidine
ndash Does not respond well to improved OH or scaling
ndash Biofilm removal debridementscaling
ndash May need additional physician consult
Lichen Planus
Etiologybull Unknownbull Cell mediated Immune pathogenesis bull Systemic Diseases
ndash Diabetes hypertension hepatitis B amp C chronic graft-versus-host disease amp lupus
bull Medicationsndash antimalarial drugs antihypertensives amp non-steroidal anti
inflammatory (NSAIDS)
Signsbull Affects skin and mucous membranesbull Lesions may be mild to moderately painful amp burning
7
Lichen PlanusTypes
Reticular-plaque papular
Erosive Bullous Atrophic ulcerative
bull Erosive- gingival
ndash bulbous forms ulcerative amp painful
ndash red and raw
bull Reticular
ndash asymptomatic keratontic lines called stria
ndash lacy white lines
Lichen Planus
bull severity may relate to stressConsiderationsbull Higher risk for non- reticular types for malignant transformation
ndash LP pts have a 10 fold increased risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma
Treatmentbull Look for triggers allergies sensitivity bull Aloe Vera rinses amp gelbull Corticosteriods
ndash topical- fluocinonide dexamethadone dipropionate spray topical steroids may help- can cause candida
bull Periodic biopsies are necessary for areas that do not respond to treatment
bull Regular recalls
Inflammatory And Immune Conditions And Lesions
Hypersensitivity ReactionsAllergic gingivitis
Other names desquamative Plasma cell gingivitis idiopathic
gingivostomatitis atypical gingivostomatitis allergic gingivostomatitis hypersensitivity and plasmacytosis
Plasma cell gingivitis is an uncommon inflammatory condition usually affecting the anterior maxillary gingiva and of uncertain etiology While some authors have associated plasma cell gingivitis with a hypersensitivity response to antigens in various substances others have raised doubt whether plasma cell gingivitis is a distinct clinicopathologic entity
Allergic gingivitis
Etiology
bull auto immune
bull Allergy
bull Signs
bull sloughing of the epithelium which leaves raw red surface
bull The edematous tissue often extends to the mucogingival junction with a deep red appearance
Allergic gingivitis
Symptoms
painful
Treatment
topicalsystemic steroid therapy
remove etiological factor if possible
-spices toothpaste flavorings peppermint wintergreen menthol cinnamon preservatives mints gum candy
Possible Offending Products to Gingival Tissue
bull Commercially available toothpaste (tartar-control additives and flavoring agents [possibly
cinnamon] that mask the tartar control additives)
bull Mouth rinses
bull Cinnamon aldehyde
bull Sodium benzoate and methyl paraben
bull Food substances such as wheat dairy chocolate eggs peanuts and monosodium glutamate
bull Red wine (sulfides and tartrazine additives)
bull Preservatives
bull Essential oils such as peppermint spearmint and wintergreen found in gums candy and mouth rinses
bull Dark cola drinks
bull Strong spices
bull Chili peppers
bull Clove
bull Cardamom Burkhart NW Toothpaste allergy RDH 2007 27(6) 86107-108
8
Types of Periodontal diseasesPeriodontitis
Periodontitis
bull Chronic
bull Disease will progress unless treated
bull Typical age of onset is 35 yrs of age
bull Bone loss
- slow
ndash rate may vary depending on the modifiers
bull Severity is determined by bone loss and LOA
bull Can become inactive (stable) active (recurrent) refractory
Periodontitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram ndash
bull P gingivalis
bull P intermedia
bull Tannerella forsythensis (B forsythus)
Treatmentbull Self carebull Scrt
pldebridement bull Depending type of
defects amp severity ndashpossibly surgery
amp perio referral
Not includedAggressive
This category includes formally called diseases
bull Juvenile
bullEarly onset
bullPrepubertal
bullRapidly progressive
Localized Aggressive Localized Juvenile Periodontitis
bull More significant bone loss surrounding 1st molars amp incisors ndash typically angular type bone loss amp mirror image bilaterally
bull Rate of bone loss is rapid
bull OH can be good
9
Localized Aggressive LJP
bull Defects in PMNs or macrophagesbull respond slowly
bull chemotaxis defect
bull impaired phagocytosis
bull Onset typically during teenage years
bull Hereditary componentgenetic
bull more common in females amp blacks
Localized Aggressive Localized Juvenile Periodontitis
Microorganisms
Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans
P gingivalis
Treatmentbull scrt pldebridement but typically unresponsivebull Antibiotics to be administered with or just after debridement
ndash combo metronidazole wamoxicillin or metro w augmentinndash Clindamycin Azithromycin
bull possibly surgerybull prompt perio referralbull suggest family be evaluated (siblings children etc)bull sea salt being used as prevention of AA amp Tx
Generalized Aggressive Formally Generalized Juvenile Periodontitis
bull More rare than LJPbull Can affect most teeth but more severe on 1st molar
amp incisorsndash must involve gt 3 other teeth
bull Onset usually under 30 years oldbull Associated with neutrophil disorderbull Generally significant inflammation amp heavy
plaquecalculusbull Children w Gagp seem more prone to ear skin amp
upper respiratory tract infections
Generalized Aggressive Generalized Juvenile Periodontitis
MicroorganismsA actinomycetemcomitansPorphyromas gingivalis Eikenella corrodens
Treatmentscrt pldebridementantibiotics
ndash combo metronidazole wamoxicillin or metro w augmentin
possibly surgeryprompt perio referralbull Suggest family be evaluated (siblings children etc)
Periodontitis as a Manifestation of Systemic Disease
bull Systemic diseases that severely impair host response should be considered a periodontal manifestation of the systemic disease amp primary diagnosis should be the systemic disease according to International Statistical Classification of Disease (ICD)
ndash Excludes diabetes
bull Hematologicacquired neutropenias leukemias
bull Genetic disorderfamilial neutopenias down syndrome leukocyte adhesion deficiency syndrome papillon-lefreve syndrome chediak-higshi histocytosis syndromes Glycogen storage disease genetic agranulcytosis cohen syndrome Ehlers-Danlossyndrome hypophosphatsis
Necrotizing Periodontal Diseases NG amp NP
Etiologybull Unknown
bull Risk factorsexcessive stress lack of rest poor oral hygiene smoking HIV poor immune response
bull More common in underdeveloped countries
bull Less common now in the US
bull Susceptible to reoccurrence
Symptomsbull SUDDEN onset of burning
mouth inability to eat metallic taste excessive salvia amp PAINFUL
Microorganisms
spirochetes
Prevotella intermedia
Fusiform bacillus
Fusobacterium nucleatum
Ulcerative has been eliminated
10
NGSigns
bull 3 key features papilla necrosis bleeding and pain
bull Punched out papillae cratered like depressions covered by a white necrotic pseudomembrane(collection of PMNS) bright red margins spontenousbleeding may occur
bull Distinctive foul odor
bull May have systemic involvement
ndash lymphadenopathy fever
bull May be a systemic
manifestations
ndash HIV
NG Treatmentbull Advise to avoid smoking amp etoh get rest and proper nutrition (rec
multi vitamin soft nutritious diet)+ self care
bull Rinses with frac12 glass warm water amp 1 tbsp hydrogen peroxide w half glass or chlorhexidine
bull Pain medication
bull Antibiotics can be used especially if systemic involvement
ndash metronidazole tetracycline pen vk
bull Initial supragingival debridement then complete
bull Consider complete laboratory work ndashup amp medical consult
ndash (NUG may be the first sign of HIV)
bull May progress to NUP
bull Follow ndashup phone call or visit within 24 hrsndash Re-eval surgery referral debridement wlocal= recurrent nature
NP
bull Progression of NUG
bull May be related to systemic disease
bull HIV nutrition deficiency
bull NUG superimposed on a previous periodontal disease
NP
Signs amp symptoms
bull Intensely red necrosis white pseudomembrane
bull Painful odor punched-out papillae
bull Reports of deep aching pain or jaw pain
bull Extensive bone loss
bull Spontaneous bleeding
Treatment
bull Same as NUG
Peridex culture antibiotics (metronidazole) or antifungals
Refractory
bull Not included in the new guidelines
bull Unresponsive to treatmentndash surgery frequent scrt pl antibiotics
bull Can be localized or generalized
bull Usually smokers
bull Treatment clindamycin metronidazole metriwamoxicillin or Augmentin
Periodontal Phenotype (Biotypes)
bull The term describes the thickness of the gingiva in a bucco-lingual dimension
bull 3 types
Thick flat
Thick scalloped
Thin
bull Thick (85) is more prevalent than thin (15)
11
Thin Gingival Phenotype
bull Triangle shaped teeth vs square
bull Thin tissue
bull Susceptible to recession
bull Dehiscence present
bull Instrumentation must be done
Carefully due to thin biotype
bull Reacts to insult by recession
Thick amp Flat Gingival Phenotype
bull Square shaped
bull Thick tissue
bull Susceptible to pocketing
bull Reacts to insult by pocketing
Thick Scalloped
bull Thick fibrotic gingiva
bull Slender teeth
bull Narrow zone of KT
bull Gingival scalloping
Recession
Type 1 Type 2
Interproximal CEJ
is clinically not
detectable
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is lt to buccal
Type 3
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is gt
buccal
attachment loss
Implants
bull Treat perio prior to implantsbull It takes 2 weeks for the implants to
become colonized by the surrounding teeth
bull No horizontal fibers like a tooth so infection goes straight to bone and perio happens very quickly
bull This perimucosal seal is delicate ndashBe careful during instrumentation
12
Implants
bull The implant coatingsrough surfaces may create more risk for implantitis but better for osteointergration
ndash The calculus is more embedded on these surfaces than the previous smoother surfaces
Stages of Peri-implant DiseasePeri-implant mucositis
bull Reversible inflammation of the soft tissues
bull Occurs in about 50 of implants placed within 9 - 14 years
Peri-implantitis
bull Bone Loss
bull Occurs in 12- 47 of implants 5 years after placement
bull Risk factors-Hx of severe perio poor self care amp lack of maintenance care
bull Cement Implantitis
bull Some evidence linking cement and titanium particles bio corrosion
Peri-implantitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram - Fusobacterium species Prevotella intermedia
bull Implant failure is usually due to the microbial challenge occlusal load or excessive cementndash Cement has been found in the tissues
bull Failure is evidenced by gt2 mm MOBILITY
bull Bone loss buccal and lingual results in dehiscence
Cement Implantitis
New AAP Case definitionPeri-implantitis
bull BOP
bull Probing depth gt 6 mm
bull Bone levels gt 3 mm apical of the most coronal portion of the intraosseous part of the implant
Caton J Armitage G Berglundh T Et al A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri‐implant diseases and conditions ndash Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification Journal of Periodontology 89 S1 (S1-S8) (2018)
Failing Criteria
bull Ailing (Peri-implant mucositis) inflammation present but no mobility
ndash bone appears normal or there may be an incipient lesion
bull Failing Peri-implantitis without mobility
ndash Inflammation has progressed to the bone as evidenced by radiographic lesion
bull Failed Peri-implantitis with mobility
ndash Implant has pronounced bone loss
Probing amp BOP
bull Metal probes on prosthetic part of the crown is fine
bull Some are concerned with metal probes on the threads
bull Must probe implants
bull Probe depths are generally deeper than natural tooth
bull BOP is not normal
threads
13
Treatment
bull Be aggressive amp prevent bone loss because very difficult to treat once initiated
bull Treatment
ndash Debride thoroughly
ndash Chlorhexidine
ndash Systemic antibiotics
ndash Bone grafts
ndash Arestin- local drug delivery
ndash Air flow polishing with glycine
Diagnosis Severity
bull Determining severity is based on CAL and bone loss
bull Clinical attachment level (CAL)
ndashdistance from the junctional epithelium to the CEJ
bull Probe depths alone are lacking because it does not take in account the gingival margin
ndashusing probe depths alone can result in over estimating or underestimating disease
Three possible relationships for gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ
GM
bull Where should the GM be normallyndash 1-2 mm coronal to the CEJ
bull What is the pattern of CEJs interproximallyacross the mouthndash More Flat on the Posteriors
ndash More Curvature on the Anteriors
ndash For interproximal space look at the papillae does it fill the embrasure space
ndash A normal GM on the anteriors could be +1mm
ndash A normal GM on the posteriors could be +2 mm
Clinical attachment level
Depends on position of the gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ (-)
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ (same)
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ (+)
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is coronal to CEJ
1 Measure probe depth
2 Measure from gingival margin to CEJ
3 Subtract second measurement from overall probe depth
FYI-This is a color
coded probe w
markings at 36912
14
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is levelwith CEJ
bull Probe depth is Clinical attachment level
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is apical to CEJ
bull Measure probe depthbull Measure recessionbull Add recession to probe depth
Grading
Bone Loss
Stage 1
Coronal 13
lt 15
Coronal 13
Mid 13
Last 13
15 Normal bone Height
33 stage 2
Stage 3Extends to mid third of root amp beyondStage 4Extends to mid third of root amp beyond
Stage 1
stage 3 amp 4
Predicting Activity
bull BOP
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will not break down
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will breakdown
ndash Sites that do not bleed will not breakdown
ndash The absence of bleeding provides more information than whether bleeding exists
ndash Therefore when sites bleed we say it is active
bull Inflammation
bull Nutrient canals
bull Rough looking crestal bone vs smooth amp well demarcated may indicate activity
15
Predicting Activity
bull Nutrient canals
ndash Highly visible canals may indicate active or rapid destruction
ndash canals are thought to be engorged large blood vessels
Crestal Bone
Rough looking crestal boneSmoother more demarcated crestal bone
Planningbull Systematic Informed consent
bull Diagnosis prognosis options risks benefits
ndashPatients must have all the information
bull Studies indicate slight reductions in PD s gt 6 mm after full-mouth scaling and root planingperformed in one appointment vs over longer intervals
bull These protocols particularly effective in patients with aggressive periodontitis andor pts w systemic conditions
Eberhard J et al J Clin Periodontol 200835591ndash604 amp Fang et al J Periodont Res October 19 2015)
ImplementationTreatment
bull Goals are to eliminate infection and risk factorsbull The objective is to remove all clinically detectable
calculus without excessive root planingndash bacterial endotoxins are weakly adherent to the root
surface (Nakib 1982)
bull The term debridement vs root planing
ImplementationTreatment
bull Treat patientrsquos significant otherbull 40 of the time spouses have the
same microbiotabull Donrsquot kiss dogs amp cats- they may have
periobull Avoid gross scaling
bull risk of abscessbull educationbull more difficult to re-insert
instruments
16
Air Polishing with glycine
ndashGlycine has anti inflammatory ampimmune modulation effectsbull Glycine receptor gingival tissue
ndashPerpulsionndashFDA approval for lt5 mmndashRemoval biofilm amp stainndashPerio maintenance ndashImplantsndashDecontaminate prior to grafts
Host-Modulating Treatmentbull Treating periodontitis by trying to resolve
inflammation
bull Resolvins
ndash Omega 3 Fatty acids correlated with less bone loss
ndash may be due to their ability to generate mediators that fight inflammation and aid in inflammation resolution
bull Low-dose doxycycline 20 mg 2x daily
ndash Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor is the only FDA-approved
ndash Reduction of PD amp CAL gain over 3 months to 9 monthsGolub LM et al Doxycycline i hibits neutrophil (PMN)-type matrix metalloproteinases in human adult periodontitis gingiva J Clin Periodontol 199522100ndash109 amp
Golub LM et al Adjunctive treatment with subantimicrobial doses of doxycycline effects on gingival fluid collagenase activity and attachment loss in adult periodontitis J Clin Periodontol 200128146ndash156
Host-Modulating Treatment
bull NSAIDsndash Reduces PGE 2 which can reduce bone loss
ndash Flurbiprofen and topical (ketorolac)
ndash Case controls demonstrate decrease risk
bull Bisphosphonates ndash Used for treating Pagetrsquos bone pain amp osteoporosis
ndash Alendronate sodium (Fosamax) risedronate (Actonel)
ndash Investigating for its ability to modulate the host
bull Used experimentally in animals to inhibit bone resorption amp bone mineral content amp to interfere w breakdown of collagen in the periodontium
ndash WARNING case reports of bone necrosis after extractions
bull questions scrtpl w pts on drug
Treatment
bull Statins have an anti-inflammatory and immune effects reducing levels of C-Reactive Protein MMP Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
ndash Statins reduce bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclast formation
ndash Some results show lower alveolar bone loss and reduction of clinical signs of inflammation
(meta anyalsis Estanislau etal J Clin Pharmacol 2014 Dec)
ndash Topical gels (simvastatin atorvastatin)
Treatment
bull Probioticsndash Improved biofilm index and probe depths (Shimauchi 2008)
bull Valtrexbull Photodynamic therapy
ndash Light-sensitive drug is applied then a light laser directly on the area treated with the drug
ndash When the light is combined with the drug phototoxic reactions are induced which destroy bacterial cells
ndash Shows short term benefits (Sgolastra 2012)bull Periowave
bull Emdogainndash Enamel matrix derivative for periodontal tissue regeneration in
infrabony defects amp used w SRP to enhance resultsbull Derived from developing pig teethbull Stimulate adherence attachment to cementum
Treatmentbull Topical antioxidants
ndash Antioxidant gel and rinse
ndash Periosciences ndash toothpaste rinse gel
ndash Topical coenzyme COQ10
bull Due to correlation w perio oxidative stress markers amp low level of natural occurring salivary antioxidants looking at polyphenolsantioxidants in the mouth locally delivered
ndash needs more research
bull Hyaluronic acid (HA) gel and mouth rinsendash hyaluronic acid plays a large role in the collagen building 02
hyaluronan gel topically amp subgingivally
ndash Studies have been done to evaluate on wound healing amp improving perio outcomes
ndash Further evidence is needed
17
LasersNeodymium lasersbull Ex NdYAG NdYAP lasers
bull FDA approved-PerioLase (FRNdYAG) patented procedure LANAPshown to regenerate cementum bone amp PDL
bull No histological studies LANAP with regeneration ( Linden E Laser Basics Dimensions of dental hygiene april 2016)
Diode Lasersbull Most commonly used by RDHs
bull Wide range of wavelengths
bull Used to reduce bacteria amp remove inflammatory byproducts
bull Absorbed by pigmented structures hemoglobin amp melanin
bull Warming amp ablation
bull There is insufficient evidence
Evaluation
bull Evaluating the host response
1 week acute or painful conditions
4-6 weeks changes in attachment level
12 weeks microbiota returns to pre TX levels
bull Complete final diagnosis
bull Many lawsuits exist due to lack of follow-up where as before it was due to failure to diagnose
Evaluation
bull Responded well
ndashDetermine appropriate PMP interval
bull Unresponsive
ndashProblem solve
bull Try to determine whyndashVirulent microorganisms Inadequate host
response Ineffective initial therapy or contributory amp risk factors
ndashFormulate new plan
Possible Solutions
bull Improve initial therapyndash re-scale root plan re-root plan
ndash self care
ndash adjunctive chemotherapeutics necessary
bull Reduce risk amp contributory factors
ndash smoking restorative
bull ex Overhangs
bull Medical consult periodontal referral Advanced diagnostic
Advanced Diagnostics
bull A test to determine active disease or predict an active episode of disease
bull currently we are not able to do this well
bull Many new tests are being developed still under investigation and still being assessed for usefulness
bull Many are not available yet or very expensive
bull Provide information that adds to the clinical exam
bull If it would be nice to know but not change anything we need to ask the questionhellip
bull Is the benefit worth the cost
Testing
OralDNA Labs Inc- httpwwworaldnacom
bull Genetic risk bacterial profile HPV-related oral cancers Herpes Candida Chlamydia trachomatis(CT) Neisseria gonorrhea(NG) gene markers related to inflammatory response DNA DrugMaptrade
micro-Ident- DNA probes
bull httpswwwhain-lifesciencecom
Oravital-Toronto based company uses biofilm testing the use of prescribed antibiotic antimicrobial rinses httpswwworavitalcom
Temple Oral Microbiology testing service 800-788-6687
USC Oral microbiology testing Lab 213-740-3163
UNC Oral microbiology Lab oralmicrodentistryuncedu

6
Drug-influenced gingivitis
bull Gingival enlargement
ndashAnticonvulsants
bull Phenytoin
ndashCalcium channel blockers
bull Nifedipine 6-43
ndash Immunosuppressants
bull Cyclosporin 25
ndashAnabolic Androgenic Steroid
ndash Prostate cancer treatment
Gingival enlargement
bull Level of biofilm amp drug dosage accumulation can affect the severity of overgrowth
bull Consult w MD for drug substitution
bull Some cases of hypertrophic gingival tissue have been reported as Kaposirsquos sarcoma amp squamous cell carcinoma
Non-biofilm induced related to bull Specific bacteria
ndash Neissera gonorrhea treponema pallidum streptococci
bull Viralndash Herpes simplex 1 amp 2 varicella zoster papillmavirus
bull Fungal
bull Cultured for true diagnosis amp treat appropriately antibiotics antiviral amp or antifungal
bull Not common amp usually not known
Non-plaque induced gingival diseases of fungal origin
Candidosisformally Linear gingivitis
bull Generally fungalcandiasis
bull Linear amp very distinctive band of severe erythema on gingival margin
bull Disproportion of inflammatory intensity for the amount of biofilm present
Candidosis Treatment
ndash OHE consider chlorhexidine
ndash Does not respond well to improved OH or scaling
ndash Biofilm removal debridementscaling
ndash May need additional physician consult
Lichen Planus
Etiologybull Unknownbull Cell mediated Immune pathogenesis bull Systemic Diseases
ndash Diabetes hypertension hepatitis B amp C chronic graft-versus-host disease amp lupus
bull Medicationsndash antimalarial drugs antihypertensives amp non-steroidal anti
inflammatory (NSAIDS)
Signsbull Affects skin and mucous membranesbull Lesions may be mild to moderately painful amp burning
7
Lichen PlanusTypes
Reticular-plaque papular
Erosive Bullous Atrophic ulcerative
bull Erosive- gingival
ndash bulbous forms ulcerative amp painful
ndash red and raw
bull Reticular
ndash asymptomatic keratontic lines called stria
ndash lacy white lines
Lichen Planus
bull severity may relate to stressConsiderationsbull Higher risk for non- reticular types for malignant transformation
ndash LP pts have a 10 fold increased risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma
Treatmentbull Look for triggers allergies sensitivity bull Aloe Vera rinses amp gelbull Corticosteriods
ndash topical- fluocinonide dexamethadone dipropionate spray topical steroids may help- can cause candida
bull Periodic biopsies are necessary for areas that do not respond to treatment
bull Regular recalls
Inflammatory And Immune Conditions And Lesions
Hypersensitivity ReactionsAllergic gingivitis
Other names desquamative Plasma cell gingivitis idiopathic
gingivostomatitis atypical gingivostomatitis allergic gingivostomatitis hypersensitivity and plasmacytosis
Plasma cell gingivitis is an uncommon inflammatory condition usually affecting the anterior maxillary gingiva and of uncertain etiology While some authors have associated plasma cell gingivitis with a hypersensitivity response to antigens in various substances others have raised doubt whether plasma cell gingivitis is a distinct clinicopathologic entity
Allergic gingivitis
Etiology
bull auto immune
bull Allergy
bull Signs
bull sloughing of the epithelium which leaves raw red surface
bull The edematous tissue often extends to the mucogingival junction with a deep red appearance
Allergic gingivitis
Symptoms
painful
Treatment
topicalsystemic steroid therapy
remove etiological factor if possible
-spices toothpaste flavorings peppermint wintergreen menthol cinnamon preservatives mints gum candy
Possible Offending Products to Gingival Tissue
bull Commercially available toothpaste (tartar-control additives and flavoring agents [possibly
cinnamon] that mask the tartar control additives)
bull Mouth rinses
bull Cinnamon aldehyde
bull Sodium benzoate and methyl paraben
bull Food substances such as wheat dairy chocolate eggs peanuts and monosodium glutamate
bull Red wine (sulfides and tartrazine additives)
bull Preservatives
bull Essential oils such as peppermint spearmint and wintergreen found in gums candy and mouth rinses
bull Dark cola drinks
bull Strong spices
bull Chili peppers
bull Clove
bull Cardamom Burkhart NW Toothpaste allergy RDH 2007 27(6) 86107-108
8
Types of Periodontal diseasesPeriodontitis
Periodontitis
bull Chronic
bull Disease will progress unless treated
bull Typical age of onset is 35 yrs of age
bull Bone loss
- slow
ndash rate may vary depending on the modifiers
bull Severity is determined by bone loss and LOA
bull Can become inactive (stable) active (recurrent) refractory
Periodontitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram ndash
bull P gingivalis
bull P intermedia
bull Tannerella forsythensis (B forsythus)
Treatmentbull Self carebull Scrt
pldebridement bull Depending type of
defects amp severity ndashpossibly surgery
amp perio referral
Not includedAggressive
This category includes formally called diseases
bull Juvenile
bullEarly onset
bullPrepubertal
bullRapidly progressive
Localized Aggressive Localized Juvenile Periodontitis
bull More significant bone loss surrounding 1st molars amp incisors ndash typically angular type bone loss amp mirror image bilaterally
bull Rate of bone loss is rapid
bull OH can be good
9
Localized Aggressive LJP
bull Defects in PMNs or macrophagesbull respond slowly
bull chemotaxis defect
bull impaired phagocytosis
bull Onset typically during teenage years
bull Hereditary componentgenetic
bull more common in females amp blacks
Localized Aggressive Localized Juvenile Periodontitis
Microorganisms
Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans
P gingivalis
Treatmentbull scrt pldebridement but typically unresponsivebull Antibiotics to be administered with or just after debridement
ndash combo metronidazole wamoxicillin or metro w augmentinndash Clindamycin Azithromycin
bull possibly surgerybull prompt perio referralbull suggest family be evaluated (siblings children etc)bull sea salt being used as prevention of AA amp Tx
Generalized Aggressive Formally Generalized Juvenile Periodontitis
bull More rare than LJPbull Can affect most teeth but more severe on 1st molar
amp incisorsndash must involve gt 3 other teeth
bull Onset usually under 30 years oldbull Associated with neutrophil disorderbull Generally significant inflammation amp heavy
plaquecalculusbull Children w Gagp seem more prone to ear skin amp
upper respiratory tract infections
Generalized Aggressive Generalized Juvenile Periodontitis
MicroorganismsA actinomycetemcomitansPorphyromas gingivalis Eikenella corrodens
Treatmentscrt pldebridementantibiotics
ndash combo metronidazole wamoxicillin or metro w augmentin
possibly surgeryprompt perio referralbull Suggest family be evaluated (siblings children etc)
Periodontitis as a Manifestation of Systemic Disease
bull Systemic diseases that severely impair host response should be considered a periodontal manifestation of the systemic disease amp primary diagnosis should be the systemic disease according to International Statistical Classification of Disease (ICD)
ndash Excludes diabetes
bull Hematologicacquired neutropenias leukemias
bull Genetic disorderfamilial neutopenias down syndrome leukocyte adhesion deficiency syndrome papillon-lefreve syndrome chediak-higshi histocytosis syndromes Glycogen storage disease genetic agranulcytosis cohen syndrome Ehlers-Danlossyndrome hypophosphatsis
Necrotizing Periodontal Diseases NG amp NP
Etiologybull Unknown
bull Risk factorsexcessive stress lack of rest poor oral hygiene smoking HIV poor immune response
bull More common in underdeveloped countries
bull Less common now in the US
bull Susceptible to reoccurrence
Symptomsbull SUDDEN onset of burning
mouth inability to eat metallic taste excessive salvia amp PAINFUL
Microorganisms
spirochetes
Prevotella intermedia
Fusiform bacillus
Fusobacterium nucleatum
Ulcerative has been eliminated
10
NGSigns
bull 3 key features papilla necrosis bleeding and pain
bull Punched out papillae cratered like depressions covered by a white necrotic pseudomembrane(collection of PMNS) bright red margins spontenousbleeding may occur
bull Distinctive foul odor
bull May have systemic involvement
ndash lymphadenopathy fever
bull May be a systemic
manifestations
ndash HIV
NG Treatmentbull Advise to avoid smoking amp etoh get rest and proper nutrition (rec
multi vitamin soft nutritious diet)+ self care
bull Rinses with frac12 glass warm water amp 1 tbsp hydrogen peroxide w half glass or chlorhexidine
bull Pain medication
bull Antibiotics can be used especially if systemic involvement
ndash metronidazole tetracycline pen vk
bull Initial supragingival debridement then complete
bull Consider complete laboratory work ndashup amp medical consult
ndash (NUG may be the first sign of HIV)
bull May progress to NUP
bull Follow ndashup phone call or visit within 24 hrsndash Re-eval surgery referral debridement wlocal= recurrent nature
NP
bull Progression of NUG
bull May be related to systemic disease
bull HIV nutrition deficiency
bull NUG superimposed on a previous periodontal disease
NP
Signs amp symptoms
bull Intensely red necrosis white pseudomembrane
bull Painful odor punched-out papillae
bull Reports of deep aching pain or jaw pain
bull Extensive bone loss
bull Spontaneous bleeding
Treatment
bull Same as NUG
Peridex culture antibiotics (metronidazole) or antifungals
Refractory
bull Not included in the new guidelines
bull Unresponsive to treatmentndash surgery frequent scrt pl antibiotics
bull Can be localized or generalized
bull Usually smokers
bull Treatment clindamycin metronidazole metriwamoxicillin or Augmentin
Periodontal Phenotype (Biotypes)
bull The term describes the thickness of the gingiva in a bucco-lingual dimension
bull 3 types
Thick flat
Thick scalloped
Thin
bull Thick (85) is more prevalent than thin (15)
11
Thin Gingival Phenotype
bull Triangle shaped teeth vs square
bull Thin tissue
bull Susceptible to recession
bull Dehiscence present
bull Instrumentation must be done
Carefully due to thin biotype
bull Reacts to insult by recession
Thick amp Flat Gingival Phenotype
bull Square shaped
bull Thick tissue
bull Susceptible to pocketing
bull Reacts to insult by pocketing
Thick Scalloped
bull Thick fibrotic gingiva
bull Slender teeth
bull Narrow zone of KT
bull Gingival scalloping
Recession
Type 1 Type 2
Interproximal CEJ
is clinically not
detectable
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is lt to buccal
Type 3
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is gt
buccal
attachment loss
Implants
bull Treat perio prior to implantsbull It takes 2 weeks for the implants to
become colonized by the surrounding teeth
bull No horizontal fibers like a tooth so infection goes straight to bone and perio happens very quickly
bull This perimucosal seal is delicate ndashBe careful during instrumentation
12
Implants
bull The implant coatingsrough surfaces may create more risk for implantitis but better for osteointergration
ndash The calculus is more embedded on these surfaces than the previous smoother surfaces
Stages of Peri-implant DiseasePeri-implant mucositis
bull Reversible inflammation of the soft tissues
bull Occurs in about 50 of implants placed within 9 - 14 years
Peri-implantitis
bull Bone Loss
bull Occurs in 12- 47 of implants 5 years after placement
bull Risk factors-Hx of severe perio poor self care amp lack of maintenance care
bull Cement Implantitis
bull Some evidence linking cement and titanium particles bio corrosion
Peri-implantitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram - Fusobacterium species Prevotella intermedia
bull Implant failure is usually due to the microbial challenge occlusal load or excessive cementndash Cement has been found in the tissues
bull Failure is evidenced by gt2 mm MOBILITY
bull Bone loss buccal and lingual results in dehiscence
Cement Implantitis
New AAP Case definitionPeri-implantitis
bull BOP
bull Probing depth gt 6 mm
bull Bone levels gt 3 mm apical of the most coronal portion of the intraosseous part of the implant
Caton J Armitage G Berglundh T Et al A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri‐implant diseases and conditions ndash Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification Journal of Periodontology 89 S1 (S1-S8) (2018)
Failing Criteria
bull Ailing (Peri-implant mucositis) inflammation present but no mobility
ndash bone appears normal or there may be an incipient lesion
bull Failing Peri-implantitis without mobility
ndash Inflammation has progressed to the bone as evidenced by radiographic lesion
bull Failed Peri-implantitis with mobility
ndash Implant has pronounced bone loss
Probing amp BOP
bull Metal probes on prosthetic part of the crown is fine
bull Some are concerned with metal probes on the threads
bull Must probe implants
bull Probe depths are generally deeper than natural tooth
bull BOP is not normal
threads
13
Treatment
bull Be aggressive amp prevent bone loss because very difficult to treat once initiated
bull Treatment
ndash Debride thoroughly
ndash Chlorhexidine
ndash Systemic antibiotics
ndash Bone grafts
ndash Arestin- local drug delivery
ndash Air flow polishing with glycine
Diagnosis Severity
bull Determining severity is based on CAL and bone loss
bull Clinical attachment level (CAL)
ndashdistance from the junctional epithelium to the CEJ
bull Probe depths alone are lacking because it does not take in account the gingival margin
ndashusing probe depths alone can result in over estimating or underestimating disease
Three possible relationships for gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ
GM
bull Where should the GM be normallyndash 1-2 mm coronal to the CEJ
bull What is the pattern of CEJs interproximallyacross the mouthndash More Flat on the Posteriors
ndash More Curvature on the Anteriors
ndash For interproximal space look at the papillae does it fill the embrasure space
ndash A normal GM on the anteriors could be +1mm
ndash A normal GM on the posteriors could be +2 mm
Clinical attachment level
Depends on position of the gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ (-)
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ (same)
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ (+)
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is coronal to CEJ
1 Measure probe depth
2 Measure from gingival margin to CEJ
3 Subtract second measurement from overall probe depth
FYI-This is a color
coded probe w
markings at 36912
14
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is levelwith CEJ
bull Probe depth is Clinical attachment level
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is apical to CEJ
bull Measure probe depthbull Measure recessionbull Add recession to probe depth
Grading
Bone Loss
Stage 1
Coronal 13
lt 15
Coronal 13
Mid 13
Last 13
15 Normal bone Height
33 stage 2
Stage 3Extends to mid third of root amp beyondStage 4Extends to mid third of root amp beyond
Stage 1
stage 3 amp 4
Predicting Activity
bull BOP
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will not break down
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will breakdown
ndash Sites that do not bleed will not breakdown
ndash The absence of bleeding provides more information than whether bleeding exists
ndash Therefore when sites bleed we say it is active
bull Inflammation
bull Nutrient canals
bull Rough looking crestal bone vs smooth amp well demarcated may indicate activity
15
Predicting Activity
bull Nutrient canals
ndash Highly visible canals may indicate active or rapid destruction
ndash canals are thought to be engorged large blood vessels
Crestal Bone
Rough looking crestal boneSmoother more demarcated crestal bone
Planningbull Systematic Informed consent
bull Diagnosis prognosis options risks benefits
ndashPatients must have all the information
bull Studies indicate slight reductions in PD s gt 6 mm after full-mouth scaling and root planingperformed in one appointment vs over longer intervals
bull These protocols particularly effective in patients with aggressive periodontitis andor pts w systemic conditions
Eberhard J et al J Clin Periodontol 200835591ndash604 amp Fang et al J Periodont Res October 19 2015)
ImplementationTreatment
bull Goals are to eliminate infection and risk factorsbull The objective is to remove all clinically detectable
calculus without excessive root planingndash bacterial endotoxins are weakly adherent to the root
surface (Nakib 1982)
bull The term debridement vs root planing
ImplementationTreatment
bull Treat patientrsquos significant otherbull 40 of the time spouses have the
same microbiotabull Donrsquot kiss dogs amp cats- they may have
periobull Avoid gross scaling
bull risk of abscessbull educationbull more difficult to re-insert
instruments
16
Air Polishing with glycine
ndashGlycine has anti inflammatory ampimmune modulation effectsbull Glycine receptor gingival tissue
ndashPerpulsionndashFDA approval for lt5 mmndashRemoval biofilm amp stainndashPerio maintenance ndashImplantsndashDecontaminate prior to grafts
Host-Modulating Treatmentbull Treating periodontitis by trying to resolve
inflammation
bull Resolvins
ndash Omega 3 Fatty acids correlated with less bone loss
ndash may be due to their ability to generate mediators that fight inflammation and aid in inflammation resolution
bull Low-dose doxycycline 20 mg 2x daily
ndash Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor is the only FDA-approved
ndash Reduction of PD amp CAL gain over 3 months to 9 monthsGolub LM et al Doxycycline i hibits neutrophil (PMN)-type matrix metalloproteinases in human adult periodontitis gingiva J Clin Periodontol 199522100ndash109 amp
Golub LM et al Adjunctive treatment with subantimicrobial doses of doxycycline effects on gingival fluid collagenase activity and attachment loss in adult periodontitis J Clin Periodontol 200128146ndash156
Host-Modulating Treatment
bull NSAIDsndash Reduces PGE 2 which can reduce bone loss
ndash Flurbiprofen and topical (ketorolac)
ndash Case controls demonstrate decrease risk
bull Bisphosphonates ndash Used for treating Pagetrsquos bone pain amp osteoporosis
ndash Alendronate sodium (Fosamax) risedronate (Actonel)
ndash Investigating for its ability to modulate the host
bull Used experimentally in animals to inhibit bone resorption amp bone mineral content amp to interfere w breakdown of collagen in the periodontium
ndash WARNING case reports of bone necrosis after extractions
bull questions scrtpl w pts on drug
Treatment
bull Statins have an anti-inflammatory and immune effects reducing levels of C-Reactive Protein MMP Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
ndash Statins reduce bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclast formation
ndash Some results show lower alveolar bone loss and reduction of clinical signs of inflammation
(meta anyalsis Estanislau etal J Clin Pharmacol 2014 Dec)
ndash Topical gels (simvastatin atorvastatin)
Treatment
bull Probioticsndash Improved biofilm index and probe depths (Shimauchi 2008)
bull Valtrexbull Photodynamic therapy
ndash Light-sensitive drug is applied then a light laser directly on the area treated with the drug
ndash When the light is combined with the drug phototoxic reactions are induced which destroy bacterial cells
ndash Shows short term benefits (Sgolastra 2012)bull Periowave
bull Emdogainndash Enamel matrix derivative for periodontal tissue regeneration in
infrabony defects amp used w SRP to enhance resultsbull Derived from developing pig teethbull Stimulate adherence attachment to cementum
Treatmentbull Topical antioxidants
ndash Antioxidant gel and rinse
ndash Periosciences ndash toothpaste rinse gel
ndash Topical coenzyme COQ10
bull Due to correlation w perio oxidative stress markers amp low level of natural occurring salivary antioxidants looking at polyphenolsantioxidants in the mouth locally delivered
ndash needs more research
bull Hyaluronic acid (HA) gel and mouth rinsendash hyaluronic acid plays a large role in the collagen building 02
hyaluronan gel topically amp subgingivally
ndash Studies have been done to evaluate on wound healing amp improving perio outcomes
ndash Further evidence is needed
17
LasersNeodymium lasersbull Ex NdYAG NdYAP lasers
bull FDA approved-PerioLase (FRNdYAG) patented procedure LANAPshown to regenerate cementum bone amp PDL
bull No histological studies LANAP with regeneration ( Linden E Laser Basics Dimensions of dental hygiene april 2016)
Diode Lasersbull Most commonly used by RDHs
bull Wide range of wavelengths
bull Used to reduce bacteria amp remove inflammatory byproducts
bull Absorbed by pigmented structures hemoglobin amp melanin
bull Warming amp ablation
bull There is insufficient evidence
Evaluation
bull Evaluating the host response
1 week acute or painful conditions
4-6 weeks changes in attachment level
12 weeks microbiota returns to pre TX levels
bull Complete final diagnosis
bull Many lawsuits exist due to lack of follow-up where as before it was due to failure to diagnose
Evaluation
bull Responded well
ndashDetermine appropriate PMP interval
bull Unresponsive
ndashProblem solve
bull Try to determine whyndashVirulent microorganisms Inadequate host
response Ineffective initial therapy or contributory amp risk factors
ndashFormulate new plan
Possible Solutions
bull Improve initial therapyndash re-scale root plan re-root plan
ndash self care
ndash adjunctive chemotherapeutics necessary
bull Reduce risk amp contributory factors
ndash smoking restorative
bull ex Overhangs
bull Medical consult periodontal referral Advanced diagnostic
Advanced Diagnostics
bull A test to determine active disease or predict an active episode of disease
bull currently we are not able to do this well
bull Many new tests are being developed still under investigation and still being assessed for usefulness
bull Many are not available yet or very expensive
bull Provide information that adds to the clinical exam
bull If it would be nice to know but not change anything we need to ask the questionhellip
bull Is the benefit worth the cost
Testing
OralDNA Labs Inc- httpwwworaldnacom
bull Genetic risk bacterial profile HPV-related oral cancers Herpes Candida Chlamydia trachomatis(CT) Neisseria gonorrhea(NG) gene markers related to inflammatory response DNA DrugMaptrade
micro-Ident- DNA probes
bull httpswwwhain-lifesciencecom
Oravital-Toronto based company uses biofilm testing the use of prescribed antibiotic antimicrobial rinses httpswwworavitalcom
Temple Oral Microbiology testing service 800-788-6687
USC Oral microbiology testing Lab 213-740-3163
UNC Oral microbiology Lab oralmicrodentistryuncedu

7
Lichen PlanusTypes
Reticular-plaque papular
Erosive Bullous Atrophic ulcerative
bull Erosive- gingival
ndash bulbous forms ulcerative amp painful
ndash red and raw
bull Reticular
ndash asymptomatic keratontic lines called stria
ndash lacy white lines
Lichen Planus
bull severity may relate to stressConsiderationsbull Higher risk for non- reticular types for malignant transformation
ndash LP pts have a 10 fold increased risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma
Treatmentbull Look for triggers allergies sensitivity bull Aloe Vera rinses amp gelbull Corticosteriods
ndash topical- fluocinonide dexamethadone dipropionate spray topical steroids may help- can cause candida
bull Periodic biopsies are necessary for areas that do not respond to treatment
bull Regular recalls
Inflammatory And Immune Conditions And Lesions
Hypersensitivity ReactionsAllergic gingivitis
Other names desquamative Plasma cell gingivitis idiopathic
gingivostomatitis atypical gingivostomatitis allergic gingivostomatitis hypersensitivity and plasmacytosis
Plasma cell gingivitis is an uncommon inflammatory condition usually affecting the anterior maxillary gingiva and of uncertain etiology While some authors have associated plasma cell gingivitis with a hypersensitivity response to antigens in various substances others have raised doubt whether plasma cell gingivitis is a distinct clinicopathologic entity
Allergic gingivitis
Etiology
bull auto immune
bull Allergy
bull Signs
bull sloughing of the epithelium which leaves raw red surface
bull The edematous tissue often extends to the mucogingival junction with a deep red appearance
Allergic gingivitis
Symptoms
painful
Treatment
topicalsystemic steroid therapy
remove etiological factor if possible
-spices toothpaste flavorings peppermint wintergreen menthol cinnamon preservatives mints gum candy
Possible Offending Products to Gingival Tissue
bull Commercially available toothpaste (tartar-control additives and flavoring agents [possibly
cinnamon] that mask the tartar control additives)
bull Mouth rinses
bull Cinnamon aldehyde
bull Sodium benzoate and methyl paraben
bull Food substances such as wheat dairy chocolate eggs peanuts and monosodium glutamate
bull Red wine (sulfides and tartrazine additives)
bull Preservatives
bull Essential oils such as peppermint spearmint and wintergreen found in gums candy and mouth rinses
bull Dark cola drinks
bull Strong spices
bull Chili peppers
bull Clove
bull Cardamom Burkhart NW Toothpaste allergy RDH 2007 27(6) 86107-108
8
Types of Periodontal diseasesPeriodontitis
Periodontitis
bull Chronic
bull Disease will progress unless treated
bull Typical age of onset is 35 yrs of age
bull Bone loss
- slow
ndash rate may vary depending on the modifiers
bull Severity is determined by bone loss and LOA
bull Can become inactive (stable) active (recurrent) refractory
Periodontitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram ndash
bull P gingivalis
bull P intermedia
bull Tannerella forsythensis (B forsythus)
Treatmentbull Self carebull Scrt
pldebridement bull Depending type of
defects amp severity ndashpossibly surgery
amp perio referral
Not includedAggressive
This category includes formally called diseases
bull Juvenile
bullEarly onset
bullPrepubertal
bullRapidly progressive
Localized Aggressive Localized Juvenile Periodontitis
bull More significant bone loss surrounding 1st molars amp incisors ndash typically angular type bone loss amp mirror image bilaterally
bull Rate of bone loss is rapid
bull OH can be good
9
Localized Aggressive LJP
bull Defects in PMNs or macrophagesbull respond slowly
bull chemotaxis defect
bull impaired phagocytosis
bull Onset typically during teenage years
bull Hereditary componentgenetic
bull more common in females amp blacks
Localized Aggressive Localized Juvenile Periodontitis
Microorganisms
Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans
P gingivalis
Treatmentbull scrt pldebridement but typically unresponsivebull Antibiotics to be administered with or just after debridement
ndash combo metronidazole wamoxicillin or metro w augmentinndash Clindamycin Azithromycin
bull possibly surgerybull prompt perio referralbull suggest family be evaluated (siblings children etc)bull sea salt being used as prevention of AA amp Tx
Generalized Aggressive Formally Generalized Juvenile Periodontitis
bull More rare than LJPbull Can affect most teeth but more severe on 1st molar
amp incisorsndash must involve gt 3 other teeth
bull Onset usually under 30 years oldbull Associated with neutrophil disorderbull Generally significant inflammation amp heavy
plaquecalculusbull Children w Gagp seem more prone to ear skin amp
upper respiratory tract infections
Generalized Aggressive Generalized Juvenile Periodontitis
MicroorganismsA actinomycetemcomitansPorphyromas gingivalis Eikenella corrodens
Treatmentscrt pldebridementantibiotics
ndash combo metronidazole wamoxicillin or metro w augmentin
possibly surgeryprompt perio referralbull Suggest family be evaluated (siblings children etc)
Periodontitis as a Manifestation of Systemic Disease
bull Systemic diseases that severely impair host response should be considered a periodontal manifestation of the systemic disease amp primary diagnosis should be the systemic disease according to International Statistical Classification of Disease (ICD)
ndash Excludes diabetes
bull Hematologicacquired neutropenias leukemias
bull Genetic disorderfamilial neutopenias down syndrome leukocyte adhesion deficiency syndrome papillon-lefreve syndrome chediak-higshi histocytosis syndromes Glycogen storage disease genetic agranulcytosis cohen syndrome Ehlers-Danlossyndrome hypophosphatsis
Necrotizing Periodontal Diseases NG amp NP
Etiologybull Unknown
bull Risk factorsexcessive stress lack of rest poor oral hygiene smoking HIV poor immune response
bull More common in underdeveloped countries
bull Less common now in the US
bull Susceptible to reoccurrence
Symptomsbull SUDDEN onset of burning
mouth inability to eat metallic taste excessive salvia amp PAINFUL
Microorganisms
spirochetes
Prevotella intermedia
Fusiform bacillus
Fusobacterium nucleatum
Ulcerative has been eliminated
10
NGSigns
bull 3 key features papilla necrosis bleeding and pain
bull Punched out papillae cratered like depressions covered by a white necrotic pseudomembrane(collection of PMNS) bright red margins spontenousbleeding may occur
bull Distinctive foul odor
bull May have systemic involvement
ndash lymphadenopathy fever
bull May be a systemic
manifestations
ndash HIV
NG Treatmentbull Advise to avoid smoking amp etoh get rest and proper nutrition (rec
multi vitamin soft nutritious diet)+ self care
bull Rinses with frac12 glass warm water amp 1 tbsp hydrogen peroxide w half glass or chlorhexidine
bull Pain medication
bull Antibiotics can be used especially if systemic involvement
ndash metronidazole tetracycline pen vk
bull Initial supragingival debridement then complete
bull Consider complete laboratory work ndashup amp medical consult
ndash (NUG may be the first sign of HIV)
bull May progress to NUP
bull Follow ndashup phone call or visit within 24 hrsndash Re-eval surgery referral debridement wlocal= recurrent nature
NP
bull Progression of NUG
bull May be related to systemic disease
bull HIV nutrition deficiency
bull NUG superimposed on a previous periodontal disease
NP
Signs amp symptoms
bull Intensely red necrosis white pseudomembrane
bull Painful odor punched-out papillae
bull Reports of deep aching pain or jaw pain
bull Extensive bone loss
bull Spontaneous bleeding
Treatment
bull Same as NUG
Peridex culture antibiotics (metronidazole) or antifungals
Refractory
bull Not included in the new guidelines
bull Unresponsive to treatmentndash surgery frequent scrt pl antibiotics
bull Can be localized or generalized
bull Usually smokers
bull Treatment clindamycin metronidazole metriwamoxicillin or Augmentin
Periodontal Phenotype (Biotypes)
bull The term describes the thickness of the gingiva in a bucco-lingual dimension
bull 3 types
Thick flat
Thick scalloped
Thin
bull Thick (85) is more prevalent than thin (15)
11
Thin Gingival Phenotype
bull Triangle shaped teeth vs square
bull Thin tissue
bull Susceptible to recession
bull Dehiscence present
bull Instrumentation must be done
Carefully due to thin biotype
bull Reacts to insult by recession
Thick amp Flat Gingival Phenotype
bull Square shaped
bull Thick tissue
bull Susceptible to pocketing
bull Reacts to insult by pocketing
Thick Scalloped
bull Thick fibrotic gingiva
bull Slender teeth
bull Narrow zone of KT
bull Gingival scalloping
Recession
Type 1 Type 2
Interproximal CEJ
is clinically not
detectable
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is lt to buccal
Type 3
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is gt
buccal
attachment loss
Implants
bull Treat perio prior to implantsbull It takes 2 weeks for the implants to
become colonized by the surrounding teeth
bull No horizontal fibers like a tooth so infection goes straight to bone and perio happens very quickly
bull This perimucosal seal is delicate ndashBe careful during instrumentation
12
Implants
bull The implant coatingsrough surfaces may create more risk for implantitis but better for osteointergration
ndash The calculus is more embedded on these surfaces than the previous smoother surfaces
Stages of Peri-implant DiseasePeri-implant mucositis
bull Reversible inflammation of the soft tissues
bull Occurs in about 50 of implants placed within 9 - 14 years
Peri-implantitis
bull Bone Loss
bull Occurs in 12- 47 of implants 5 years after placement
bull Risk factors-Hx of severe perio poor self care amp lack of maintenance care
bull Cement Implantitis
bull Some evidence linking cement and titanium particles bio corrosion
Peri-implantitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram - Fusobacterium species Prevotella intermedia
bull Implant failure is usually due to the microbial challenge occlusal load or excessive cementndash Cement has been found in the tissues
bull Failure is evidenced by gt2 mm MOBILITY
bull Bone loss buccal and lingual results in dehiscence
Cement Implantitis
New AAP Case definitionPeri-implantitis
bull BOP
bull Probing depth gt 6 mm
bull Bone levels gt 3 mm apical of the most coronal portion of the intraosseous part of the implant
Caton J Armitage G Berglundh T Et al A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri‐implant diseases and conditions ndash Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification Journal of Periodontology 89 S1 (S1-S8) (2018)
Failing Criteria
bull Ailing (Peri-implant mucositis) inflammation present but no mobility
ndash bone appears normal or there may be an incipient lesion
bull Failing Peri-implantitis without mobility
ndash Inflammation has progressed to the bone as evidenced by radiographic lesion
bull Failed Peri-implantitis with mobility
ndash Implant has pronounced bone loss
Probing amp BOP
bull Metal probes on prosthetic part of the crown is fine
bull Some are concerned with metal probes on the threads
bull Must probe implants
bull Probe depths are generally deeper than natural tooth
bull BOP is not normal
threads
13
Treatment
bull Be aggressive amp prevent bone loss because very difficult to treat once initiated
bull Treatment
ndash Debride thoroughly
ndash Chlorhexidine
ndash Systemic antibiotics
ndash Bone grafts
ndash Arestin- local drug delivery
ndash Air flow polishing with glycine
Diagnosis Severity
bull Determining severity is based on CAL and bone loss
bull Clinical attachment level (CAL)
ndashdistance from the junctional epithelium to the CEJ
bull Probe depths alone are lacking because it does not take in account the gingival margin
ndashusing probe depths alone can result in over estimating or underestimating disease
Three possible relationships for gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ
GM
bull Where should the GM be normallyndash 1-2 mm coronal to the CEJ
bull What is the pattern of CEJs interproximallyacross the mouthndash More Flat on the Posteriors
ndash More Curvature on the Anteriors
ndash For interproximal space look at the papillae does it fill the embrasure space
ndash A normal GM on the anteriors could be +1mm
ndash A normal GM on the posteriors could be +2 mm
Clinical attachment level
Depends on position of the gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ (-)
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ (same)
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ (+)
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is coronal to CEJ
1 Measure probe depth
2 Measure from gingival margin to CEJ
3 Subtract second measurement from overall probe depth
FYI-This is a color
coded probe w
markings at 36912
14
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is levelwith CEJ
bull Probe depth is Clinical attachment level
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is apical to CEJ
bull Measure probe depthbull Measure recessionbull Add recession to probe depth
Grading
Bone Loss
Stage 1
Coronal 13
lt 15
Coronal 13
Mid 13
Last 13
15 Normal bone Height
33 stage 2
Stage 3Extends to mid third of root amp beyondStage 4Extends to mid third of root amp beyond
Stage 1
stage 3 amp 4
Predicting Activity
bull BOP
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will not break down
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will breakdown
ndash Sites that do not bleed will not breakdown
ndash The absence of bleeding provides more information than whether bleeding exists
ndash Therefore when sites bleed we say it is active
bull Inflammation
bull Nutrient canals
bull Rough looking crestal bone vs smooth amp well demarcated may indicate activity
15
Predicting Activity
bull Nutrient canals
ndash Highly visible canals may indicate active or rapid destruction
ndash canals are thought to be engorged large blood vessels
Crestal Bone
Rough looking crestal boneSmoother more demarcated crestal bone
Planningbull Systematic Informed consent
bull Diagnosis prognosis options risks benefits
ndashPatients must have all the information
bull Studies indicate slight reductions in PD s gt 6 mm after full-mouth scaling and root planingperformed in one appointment vs over longer intervals
bull These protocols particularly effective in patients with aggressive periodontitis andor pts w systemic conditions
Eberhard J et al J Clin Periodontol 200835591ndash604 amp Fang et al J Periodont Res October 19 2015)
ImplementationTreatment
bull Goals are to eliminate infection and risk factorsbull The objective is to remove all clinically detectable
calculus without excessive root planingndash bacterial endotoxins are weakly adherent to the root
surface (Nakib 1982)
bull The term debridement vs root planing
ImplementationTreatment
bull Treat patientrsquos significant otherbull 40 of the time spouses have the
same microbiotabull Donrsquot kiss dogs amp cats- they may have
periobull Avoid gross scaling
bull risk of abscessbull educationbull more difficult to re-insert
instruments
16
Air Polishing with glycine
ndashGlycine has anti inflammatory ampimmune modulation effectsbull Glycine receptor gingival tissue
ndashPerpulsionndashFDA approval for lt5 mmndashRemoval biofilm amp stainndashPerio maintenance ndashImplantsndashDecontaminate prior to grafts
Host-Modulating Treatmentbull Treating periodontitis by trying to resolve
inflammation
bull Resolvins
ndash Omega 3 Fatty acids correlated with less bone loss
ndash may be due to their ability to generate mediators that fight inflammation and aid in inflammation resolution
bull Low-dose doxycycline 20 mg 2x daily
ndash Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor is the only FDA-approved
ndash Reduction of PD amp CAL gain over 3 months to 9 monthsGolub LM et al Doxycycline i hibits neutrophil (PMN)-type matrix metalloproteinases in human adult periodontitis gingiva J Clin Periodontol 199522100ndash109 amp
Golub LM et al Adjunctive treatment with subantimicrobial doses of doxycycline effects on gingival fluid collagenase activity and attachment loss in adult periodontitis J Clin Periodontol 200128146ndash156
Host-Modulating Treatment
bull NSAIDsndash Reduces PGE 2 which can reduce bone loss
ndash Flurbiprofen and topical (ketorolac)
ndash Case controls demonstrate decrease risk
bull Bisphosphonates ndash Used for treating Pagetrsquos bone pain amp osteoporosis
ndash Alendronate sodium (Fosamax) risedronate (Actonel)
ndash Investigating for its ability to modulate the host
bull Used experimentally in animals to inhibit bone resorption amp bone mineral content amp to interfere w breakdown of collagen in the periodontium
ndash WARNING case reports of bone necrosis after extractions
bull questions scrtpl w pts on drug
Treatment
bull Statins have an anti-inflammatory and immune effects reducing levels of C-Reactive Protein MMP Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
ndash Statins reduce bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclast formation
ndash Some results show lower alveolar bone loss and reduction of clinical signs of inflammation
(meta anyalsis Estanislau etal J Clin Pharmacol 2014 Dec)
ndash Topical gels (simvastatin atorvastatin)
Treatment
bull Probioticsndash Improved biofilm index and probe depths (Shimauchi 2008)
bull Valtrexbull Photodynamic therapy
ndash Light-sensitive drug is applied then a light laser directly on the area treated with the drug
ndash When the light is combined with the drug phototoxic reactions are induced which destroy bacterial cells
ndash Shows short term benefits (Sgolastra 2012)bull Periowave
bull Emdogainndash Enamel matrix derivative for periodontal tissue regeneration in
infrabony defects amp used w SRP to enhance resultsbull Derived from developing pig teethbull Stimulate adherence attachment to cementum
Treatmentbull Topical antioxidants
ndash Antioxidant gel and rinse
ndash Periosciences ndash toothpaste rinse gel
ndash Topical coenzyme COQ10
bull Due to correlation w perio oxidative stress markers amp low level of natural occurring salivary antioxidants looking at polyphenolsantioxidants in the mouth locally delivered
ndash needs more research
bull Hyaluronic acid (HA) gel and mouth rinsendash hyaluronic acid plays a large role in the collagen building 02
hyaluronan gel topically amp subgingivally
ndash Studies have been done to evaluate on wound healing amp improving perio outcomes
ndash Further evidence is needed
17
LasersNeodymium lasersbull Ex NdYAG NdYAP lasers
bull FDA approved-PerioLase (FRNdYAG) patented procedure LANAPshown to regenerate cementum bone amp PDL
bull No histological studies LANAP with regeneration ( Linden E Laser Basics Dimensions of dental hygiene april 2016)
Diode Lasersbull Most commonly used by RDHs
bull Wide range of wavelengths
bull Used to reduce bacteria amp remove inflammatory byproducts
bull Absorbed by pigmented structures hemoglobin amp melanin
bull Warming amp ablation
bull There is insufficient evidence
Evaluation
bull Evaluating the host response
1 week acute or painful conditions
4-6 weeks changes in attachment level
12 weeks microbiota returns to pre TX levels
bull Complete final diagnosis
bull Many lawsuits exist due to lack of follow-up where as before it was due to failure to diagnose
Evaluation
bull Responded well
ndashDetermine appropriate PMP interval
bull Unresponsive
ndashProblem solve
bull Try to determine whyndashVirulent microorganisms Inadequate host
response Ineffective initial therapy or contributory amp risk factors
ndashFormulate new plan
Possible Solutions
bull Improve initial therapyndash re-scale root plan re-root plan
ndash self care
ndash adjunctive chemotherapeutics necessary
bull Reduce risk amp contributory factors
ndash smoking restorative
bull ex Overhangs
bull Medical consult periodontal referral Advanced diagnostic
Advanced Diagnostics
bull A test to determine active disease or predict an active episode of disease
bull currently we are not able to do this well
bull Many new tests are being developed still under investigation and still being assessed for usefulness
bull Many are not available yet or very expensive
bull Provide information that adds to the clinical exam
bull If it would be nice to know but not change anything we need to ask the questionhellip
bull Is the benefit worth the cost
Testing
OralDNA Labs Inc- httpwwworaldnacom
bull Genetic risk bacterial profile HPV-related oral cancers Herpes Candida Chlamydia trachomatis(CT) Neisseria gonorrhea(NG) gene markers related to inflammatory response DNA DrugMaptrade
micro-Ident- DNA probes
bull httpswwwhain-lifesciencecom
Oravital-Toronto based company uses biofilm testing the use of prescribed antibiotic antimicrobial rinses httpswwworavitalcom
Temple Oral Microbiology testing service 800-788-6687
USC Oral microbiology testing Lab 213-740-3163
UNC Oral microbiology Lab oralmicrodentistryuncedu

8
Types of Periodontal diseasesPeriodontitis
Periodontitis
bull Chronic
bull Disease will progress unless treated
bull Typical age of onset is 35 yrs of age
bull Bone loss
- slow
ndash rate may vary depending on the modifiers
bull Severity is determined by bone loss and LOA
bull Can become inactive (stable) active (recurrent) refractory
Periodontitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram ndash
bull P gingivalis
bull P intermedia
bull Tannerella forsythensis (B forsythus)
Treatmentbull Self carebull Scrt
pldebridement bull Depending type of
defects amp severity ndashpossibly surgery
amp perio referral
Not includedAggressive
This category includes formally called diseases
bull Juvenile
bullEarly onset
bullPrepubertal
bullRapidly progressive
Localized Aggressive Localized Juvenile Periodontitis
bull More significant bone loss surrounding 1st molars amp incisors ndash typically angular type bone loss amp mirror image bilaterally
bull Rate of bone loss is rapid
bull OH can be good
9
Localized Aggressive LJP
bull Defects in PMNs or macrophagesbull respond slowly
bull chemotaxis defect
bull impaired phagocytosis
bull Onset typically during teenage years
bull Hereditary componentgenetic
bull more common in females amp blacks
Localized Aggressive Localized Juvenile Periodontitis
Microorganisms
Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans
P gingivalis
Treatmentbull scrt pldebridement but typically unresponsivebull Antibiotics to be administered with or just after debridement
ndash combo metronidazole wamoxicillin or metro w augmentinndash Clindamycin Azithromycin
bull possibly surgerybull prompt perio referralbull suggest family be evaluated (siblings children etc)bull sea salt being used as prevention of AA amp Tx
Generalized Aggressive Formally Generalized Juvenile Periodontitis
bull More rare than LJPbull Can affect most teeth but more severe on 1st molar
amp incisorsndash must involve gt 3 other teeth
bull Onset usually under 30 years oldbull Associated with neutrophil disorderbull Generally significant inflammation amp heavy
plaquecalculusbull Children w Gagp seem more prone to ear skin amp
upper respiratory tract infections
Generalized Aggressive Generalized Juvenile Periodontitis
MicroorganismsA actinomycetemcomitansPorphyromas gingivalis Eikenella corrodens
Treatmentscrt pldebridementantibiotics
ndash combo metronidazole wamoxicillin or metro w augmentin
possibly surgeryprompt perio referralbull Suggest family be evaluated (siblings children etc)
Periodontitis as a Manifestation of Systemic Disease
bull Systemic diseases that severely impair host response should be considered a periodontal manifestation of the systemic disease amp primary diagnosis should be the systemic disease according to International Statistical Classification of Disease (ICD)
ndash Excludes diabetes
bull Hematologicacquired neutropenias leukemias
bull Genetic disorderfamilial neutopenias down syndrome leukocyte adhesion deficiency syndrome papillon-lefreve syndrome chediak-higshi histocytosis syndromes Glycogen storage disease genetic agranulcytosis cohen syndrome Ehlers-Danlossyndrome hypophosphatsis
Necrotizing Periodontal Diseases NG amp NP
Etiologybull Unknown
bull Risk factorsexcessive stress lack of rest poor oral hygiene smoking HIV poor immune response
bull More common in underdeveloped countries
bull Less common now in the US
bull Susceptible to reoccurrence
Symptomsbull SUDDEN onset of burning
mouth inability to eat metallic taste excessive salvia amp PAINFUL
Microorganisms
spirochetes
Prevotella intermedia
Fusiform bacillus
Fusobacterium nucleatum
Ulcerative has been eliminated
10
NGSigns
bull 3 key features papilla necrosis bleeding and pain
bull Punched out papillae cratered like depressions covered by a white necrotic pseudomembrane(collection of PMNS) bright red margins spontenousbleeding may occur
bull Distinctive foul odor
bull May have systemic involvement
ndash lymphadenopathy fever
bull May be a systemic
manifestations
ndash HIV
NG Treatmentbull Advise to avoid smoking amp etoh get rest and proper nutrition (rec
multi vitamin soft nutritious diet)+ self care
bull Rinses with frac12 glass warm water amp 1 tbsp hydrogen peroxide w half glass or chlorhexidine
bull Pain medication
bull Antibiotics can be used especially if systemic involvement
ndash metronidazole tetracycline pen vk
bull Initial supragingival debridement then complete
bull Consider complete laboratory work ndashup amp medical consult
ndash (NUG may be the first sign of HIV)
bull May progress to NUP
bull Follow ndashup phone call or visit within 24 hrsndash Re-eval surgery referral debridement wlocal= recurrent nature
NP
bull Progression of NUG
bull May be related to systemic disease
bull HIV nutrition deficiency
bull NUG superimposed on a previous periodontal disease
NP
Signs amp symptoms
bull Intensely red necrosis white pseudomembrane
bull Painful odor punched-out papillae
bull Reports of deep aching pain or jaw pain
bull Extensive bone loss
bull Spontaneous bleeding
Treatment
bull Same as NUG
Peridex culture antibiotics (metronidazole) or antifungals
Refractory
bull Not included in the new guidelines
bull Unresponsive to treatmentndash surgery frequent scrt pl antibiotics
bull Can be localized or generalized
bull Usually smokers
bull Treatment clindamycin metronidazole metriwamoxicillin or Augmentin
Periodontal Phenotype (Biotypes)
bull The term describes the thickness of the gingiva in a bucco-lingual dimension
bull 3 types
Thick flat
Thick scalloped
Thin
bull Thick (85) is more prevalent than thin (15)
11
Thin Gingival Phenotype
bull Triangle shaped teeth vs square
bull Thin tissue
bull Susceptible to recession
bull Dehiscence present
bull Instrumentation must be done
Carefully due to thin biotype
bull Reacts to insult by recession
Thick amp Flat Gingival Phenotype
bull Square shaped
bull Thick tissue
bull Susceptible to pocketing
bull Reacts to insult by pocketing
Thick Scalloped
bull Thick fibrotic gingiva
bull Slender teeth
bull Narrow zone of KT
bull Gingival scalloping
Recession
Type 1 Type 2
Interproximal CEJ
is clinically not
detectable
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is lt to buccal
Type 3
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is gt
buccal
attachment loss
Implants
bull Treat perio prior to implantsbull It takes 2 weeks for the implants to
become colonized by the surrounding teeth
bull No horizontal fibers like a tooth so infection goes straight to bone and perio happens very quickly
bull This perimucosal seal is delicate ndashBe careful during instrumentation
12
Implants
bull The implant coatingsrough surfaces may create more risk for implantitis but better for osteointergration
ndash The calculus is more embedded on these surfaces than the previous smoother surfaces
Stages of Peri-implant DiseasePeri-implant mucositis
bull Reversible inflammation of the soft tissues
bull Occurs in about 50 of implants placed within 9 - 14 years
Peri-implantitis
bull Bone Loss
bull Occurs in 12- 47 of implants 5 years after placement
bull Risk factors-Hx of severe perio poor self care amp lack of maintenance care
bull Cement Implantitis
bull Some evidence linking cement and titanium particles bio corrosion
Peri-implantitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram - Fusobacterium species Prevotella intermedia
bull Implant failure is usually due to the microbial challenge occlusal load or excessive cementndash Cement has been found in the tissues
bull Failure is evidenced by gt2 mm MOBILITY
bull Bone loss buccal and lingual results in dehiscence
Cement Implantitis
New AAP Case definitionPeri-implantitis
bull BOP
bull Probing depth gt 6 mm
bull Bone levels gt 3 mm apical of the most coronal portion of the intraosseous part of the implant
Caton J Armitage G Berglundh T Et al A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri‐implant diseases and conditions ndash Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification Journal of Periodontology 89 S1 (S1-S8) (2018)
Failing Criteria
bull Ailing (Peri-implant mucositis) inflammation present but no mobility
ndash bone appears normal or there may be an incipient lesion
bull Failing Peri-implantitis without mobility
ndash Inflammation has progressed to the bone as evidenced by radiographic lesion
bull Failed Peri-implantitis with mobility
ndash Implant has pronounced bone loss
Probing amp BOP
bull Metal probes on prosthetic part of the crown is fine
bull Some are concerned with metal probes on the threads
bull Must probe implants
bull Probe depths are generally deeper than natural tooth
bull BOP is not normal
threads
13
Treatment
bull Be aggressive amp prevent bone loss because very difficult to treat once initiated
bull Treatment
ndash Debride thoroughly
ndash Chlorhexidine
ndash Systemic antibiotics
ndash Bone grafts
ndash Arestin- local drug delivery
ndash Air flow polishing with glycine
Diagnosis Severity
bull Determining severity is based on CAL and bone loss
bull Clinical attachment level (CAL)
ndashdistance from the junctional epithelium to the CEJ
bull Probe depths alone are lacking because it does not take in account the gingival margin
ndashusing probe depths alone can result in over estimating or underestimating disease
Three possible relationships for gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ
GM
bull Where should the GM be normallyndash 1-2 mm coronal to the CEJ
bull What is the pattern of CEJs interproximallyacross the mouthndash More Flat on the Posteriors
ndash More Curvature on the Anteriors
ndash For interproximal space look at the papillae does it fill the embrasure space
ndash A normal GM on the anteriors could be +1mm
ndash A normal GM on the posteriors could be +2 mm
Clinical attachment level
Depends on position of the gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ (-)
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ (same)
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ (+)
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is coronal to CEJ
1 Measure probe depth
2 Measure from gingival margin to CEJ
3 Subtract second measurement from overall probe depth
FYI-This is a color
coded probe w
markings at 36912
14
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is levelwith CEJ
bull Probe depth is Clinical attachment level
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is apical to CEJ
bull Measure probe depthbull Measure recessionbull Add recession to probe depth
Grading
Bone Loss
Stage 1
Coronal 13
lt 15
Coronal 13
Mid 13
Last 13
15 Normal bone Height
33 stage 2
Stage 3Extends to mid third of root amp beyondStage 4Extends to mid third of root amp beyond
Stage 1
stage 3 amp 4
Predicting Activity
bull BOP
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will not break down
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will breakdown
ndash Sites that do not bleed will not breakdown
ndash The absence of bleeding provides more information than whether bleeding exists
ndash Therefore when sites bleed we say it is active
bull Inflammation
bull Nutrient canals
bull Rough looking crestal bone vs smooth amp well demarcated may indicate activity
15
Predicting Activity
bull Nutrient canals
ndash Highly visible canals may indicate active or rapid destruction
ndash canals are thought to be engorged large blood vessels
Crestal Bone
Rough looking crestal boneSmoother more demarcated crestal bone
Planningbull Systematic Informed consent
bull Diagnosis prognosis options risks benefits
ndashPatients must have all the information
bull Studies indicate slight reductions in PD s gt 6 mm after full-mouth scaling and root planingperformed in one appointment vs over longer intervals
bull These protocols particularly effective in patients with aggressive periodontitis andor pts w systemic conditions
Eberhard J et al J Clin Periodontol 200835591ndash604 amp Fang et al J Periodont Res October 19 2015)
ImplementationTreatment
bull Goals are to eliminate infection and risk factorsbull The objective is to remove all clinically detectable
calculus without excessive root planingndash bacterial endotoxins are weakly adherent to the root
surface (Nakib 1982)
bull The term debridement vs root planing
ImplementationTreatment
bull Treat patientrsquos significant otherbull 40 of the time spouses have the
same microbiotabull Donrsquot kiss dogs amp cats- they may have
periobull Avoid gross scaling
bull risk of abscessbull educationbull more difficult to re-insert
instruments
16
Air Polishing with glycine
ndashGlycine has anti inflammatory ampimmune modulation effectsbull Glycine receptor gingival tissue
ndashPerpulsionndashFDA approval for lt5 mmndashRemoval biofilm amp stainndashPerio maintenance ndashImplantsndashDecontaminate prior to grafts
Host-Modulating Treatmentbull Treating periodontitis by trying to resolve
inflammation
bull Resolvins
ndash Omega 3 Fatty acids correlated with less bone loss
ndash may be due to their ability to generate mediators that fight inflammation and aid in inflammation resolution
bull Low-dose doxycycline 20 mg 2x daily
ndash Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor is the only FDA-approved
ndash Reduction of PD amp CAL gain over 3 months to 9 monthsGolub LM et al Doxycycline i hibits neutrophil (PMN)-type matrix metalloproteinases in human adult periodontitis gingiva J Clin Periodontol 199522100ndash109 amp
Golub LM et al Adjunctive treatment with subantimicrobial doses of doxycycline effects on gingival fluid collagenase activity and attachment loss in adult periodontitis J Clin Periodontol 200128146ndash156
Host-Modulating Treatment
bull NSAIDsndash Reduces PGE 2 which can reduce bone loss
ndash Flurbiprofen and topical (ketorolac)
ndash Case controls demonstrate decrease risk
bull Bisphosphonates ndash Used for treating Pagetrsquos bone pain amp osteoporosis
ndash Alendronate sodium (Fosamax) risedronate (Actonel)
ndash Investigating for its ability to modulate the host
bull Used experimentally in animals to inhibit bone resorption amp bone mineral content amp to interfere w breakdown of collagen in the periodontium
ndash WARNING case reports of bone necrosis after extractions
bull questions scrtpl w pts on drug
Treatment
bull Statins have an anti-inflammatory and immune effects reducing levels of C-Reactive Protein MMP Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
ndash Statins reduce bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclast formation
ndash Some results show lower alveolar bone loss and reduction of clinical signs of inflammation
(meta anyalsis Estanislau etal J Clin Pharmacol 2014 Dec)
ndash Topical gels (simvastatin atorvastatin)
Treatment
bull Probioticsndash Improved biofilm index and probe depths (Shimauchi 2008)
bull Valtrexbull Photodynamic therapy
ndash Light-sensitive drug is applied then a light laser directly on the area treated with the drug
ndash When the light is combined with the drug phototoxic reactions are induced which destroy bacterial cells
ndash Shows short term benefits (Sgolastra 2012)bull Periowave
bull Emdogainndash Enamel matrix derivative for periodontal tissue regeneration in
infrabony defects amp used w SRP to enhance resultsbull Derived from developing pig teethbull Stimulate adherence attachment to cementum
Treatmentbull Topical antioxidants
ndash Antioxidant gel and rinse
ndash Periosciences ndash toothpaste rinse gel
ndash Topical coenzyme COQ10
bull Due to correlation w perio oxidative stress markers amp low level of natural occurring salivary antioxidants looking at polyphenolsantioxidants in the mouth locally delivered
ndash needs more research
bull Hyaluronic acid (HA) gel and mouth rinsendash hyaluronic acid plays a large role in the collagen building 02
hyaluronan gel topically amp subgingivally
ndash Studies have been done to evaluate on wound healing amp improving perio outcomes
ndash Further evidence is needed
17
LasersNeodymium lasersbull Ex NdYAG NdYAP lasers
bull FDA approved-PerioLase (FRNdYAG) patented procedure LANAPshown to regenerate cementum bone amp PDL
bull No histological studies LANAP with regeneration ( Linden E Laser Basics Dimensions of dental hygiene april 2016)
Diode Lasersbull Most commonly used by RDHs
bull Wide range of wavelengths
bull Used to reduce bacteria amp remove inflammatory byproducts
bull Absorbed by pigmented structures hemoglobin amp melanin
bull Warming amp ablation
bull There is insufficient evidence
Evaluation
bull Evaluating the host response
1 week acute or painful conditions
4-6 weeks changes in attachment level
12 weeks microbiota returns to pre TX levels
bull Complete final diagnosis
bull Many lawsuits exist due to lack of follow-up where as before it was due to failure to diagnose
Evaluation
bull Responded well
ndashDetermine appropriate PMP interval
bull Unresponsive
ndashProblem solve
bull Try to determine whyndashVirulent microorganisms Inadequate host
response Ineffective initial therapy or contributory amp risk factors
ndashFormulate new plan
Possible Solutions
bull Improve initial therapyndash re-scale root plan re-root plan
ndash self care
ndash adjunctive chemotherapeutics necessary
bull Reduce risk amp contributory factors
ndash smoking restorative
bull ex Overhangs
bull Medical consult periodontal referral Advanced diagnostic
Advanced Diagnostics
bull A test to determine active disease or predict an active episode of disease
bull currently we are not able to do this well
bull Many new tests are being developed still under investigation and still being assessed for usefulness
bull Many are not available yet or very expensive
bull Provide information that adds to the clinical exam
bull If it would be nice to know but not change anything we need to ask the questionhellip
bull Is the benefit worth the cost
Testing
OralDNA Labs Inc- httpwwworaldnacom
bull Genetic risk bacterial profile HPV-related oral cancers Herpes Candida Chlamydia trachomatis(CT) Neisseria gonorrhea(NG) gene markers related to inflammatory response DNA DrugMaptrade
micro-Ident- DNA probes
bull httpswwwhain-lifesciencecom
Oravital-Toronto based company uses biofilm testing the use of prescribed antibiotic antimicrobial rinses httpswwworavitalcom
Temple Oral Microbiology testing service 800-788-6687
USC Oral microbiology testing Lab 213-740-3163
UNC Oral microbiology Lab oralmicrodentistryuncedu

9
Localized Aggressive LJP
bull Defects in PMNs or macrophagesbull respond slowly
bull chemotaxis defect
bull impaired phagocytosis
bull Onset typically during teenage years
bull Hereditary componentgenetic
bull more common in females amp blacks
Localized Aggressive Localized Juvenile Periodontitis
Microorganisms
Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans
P gingivalis
Treatmentbull scrt pldebridement but typically unresponsivebull Antibiotics to be administered with or just after debridement
ndash combo metronidazole wamoxicillin or metro w augmentinndash Clindamycin Azithromycin
bull possibly surgerybull prompt perio referralbull suggest family be evaluated (siblings children etc)bull sea salt being used as prevention of AA amp Tx
Generalized Aggressive Formally Generalized Juvenile Periodontitis
bull More rare than LJPbull Can affect most teeth but more severe on 1st molar
amp incisorsndash must involve gt 3 other teeth
bull Onset usually under 30 years oldbull Associated with neutrophil disorderbull Generally significant inflammation amp heavy
plaquecalculusbull Children w Gagp seem more prone to ear skin amp
upper respiratory tract infections
Generalized Aggressive Generalized Juvenile Periodontitis
MicroorganismsA actinomycetemcomitansPorphyromas gingivalis Eikenella corrodens
Treatmentscrt pldebridementantibiotics
ndash combo metronidazole wamoxicillin or metro w augmentin
possibly surgeryprompt perio referralbull Suggest family be evaluated (siblings children etc)
Periodontitis as a Manifestation of Systemic Disease
bull Systemic diseases that severely impair host response should be considered a periodontal manifestation of the systemic disease amp primary diagnosis should be the systemic disease according to International Statistical Classification of Disease (ICD)
ndash Excludes diabetes
bull Hematologicacquired neutropenias leukemias
bull Genetic disorderfamilial neutopenias down syndrome leukocyte adhesion deficiency syndrome papillon-lefreve syndrome chediak-higshi histocytosis syndromes Glycogen storage disease genetic agranulcytosis cohen syndrome Ehlers-Danlossyndrome hypophosphatsis
Necrotizing Periodontal Diseases NG amp NP
Etiologybull Unknown
bull Risk factorsexcessive stress lack of rest poor oral hygiene smoking HIV poor immune response
bull More common in underdeveloped countries
bull Less common now in the US
bull Susceptible to reoccurrence
Symptomsbull SUDDEN onset of burning
mouth inability to eat metallic taste excessive salvia amp PAINFUL
Microorganisms
spirochetes
Prevotella intermedia
Fusiform bacillus
Fusobacterium nucleatum
Ulcerative has been eliminated
10
NGSigns
bull 3 key features papilla necrosis bleeding and pain
bull Punched out papillae cratered like depressions covered by a white necrotic pseudomembrane(collection of PMNS) bright red margins spontenousbleeding may occur
bull Distinctive foul odor
bull May have systemic involvement
ndash lymphadenopathy fever
bull May be a systemic
manifestations
ndash HIV
NG Treatmentbull Advise to avoid smoking amp etoh get rest and proper nutrition (rec
multi vitamin soft nutritious diet)+ self care
bull Rinses with frac12 glass warm water amp 1 tbsp hydrogen peroxide w half glass or chlorhexidine
bull Pain medication
bull Antibiotics can be used especially if systemic involvement
ndash metronidazole tetracycline pen vk
bull Initial supragingival debridement then complete
bull Consider complete laboratory work ndashup amp medical consult
ndash (NUG may be the first sign of HIV)
bull May progress to NUP
bull Follow ndashup phone call or visit within 24 hrsndash Re-eval surgery referral debridement wlocal= recurrent nature
NP
bull Progression of NUG
bull May be related to systemic disease
bull HIV nutrition deficiency
bull NUG superimposed on a previous periodontal disease
NP
Signs amp symptoms
bull Intensely red necrosis white pseudomembrane
bull Painful odor punched-out papillae
bull Reports of deep aching pain or jaw pain
bull Extensive bone loss
bull Spontaneous bleeding
Treatment
bull Same as NUG
Peridex culture antibiotics (metronidazole) or antifungals
Refractory
bull Not included in the new guidelines
bull Unresponsive to treatmentndash surgery frequent scrt pl antibiotics
bull Can be localized or generalized
bull Usually smokers
bull Treatment clindamycin metronidazole metriwamoxicillin or Augmentin
Periodontal Phenotype (Biotypes)
bull The term describes the thickness of the gingiva in a bucco-lingual dimension
bull 3 types
Thick flat
Thick scalloped
Thin
bull Thick (85) is more prevalent than thin (15)
11
Thin Gingival Phenotype
bull Triangle shaped teeth vs square
bull Thin tissue
bull Susceptible to recession
bull Dehiscence present
bull Instrumentation must be done
Carefully due to thin biotype
bull Reacts to insult by recession
Thick amp Flat Gingival Phenotype
bull Square shaped
bull Thick tissue
bull Susceptible to pocketing
bull Reacts to insult by pocketing
Thick Scalloped
bull Thick fibrotic gingiva
bull Slender teeth
bull Narrow zone of KT
bull Gingival scalloping
Recession
Type 1 Type 2
Interproximal CEJ
is clinically not
detectable
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is lt to buccal
Type 3
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is gt
buccal
attachment loss
Implants
bull Treat perio prior to implantsbull It takes 2 weeks for the implants to
become colonized by the surrounding teeth
bull No horizontal fibers like a tooth so infection goes straight to bone and perio happens very quickly
bull This perimucosal seal is delicate ndashBe careful during instrumentation
12
Implants
bull The implant coatingsrough surfaces may create more risk for implantitis but better for osteointergration
ndash The calculus is more embedded on these surfaces than the previous smoother surfaces
Stages of Peri-implant DiseasePeri-implant mucositis
bull Reversible inflammation of the soft tissues
bull Occurs in about 50 of implants placed within 9 - 14 years
Peri-implantitis
bull Bone Loss
bull Occurs in 12- 47 of implants 5 years after placement
bull Risk factors-Hx of severe perio poor self care amp lack of maintenance care
bull Cement Implantitis
bull Some evidence linking cement and titanium particles bio corrosion
Peri-implantitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram - Fusobacterium species Prevotella intermedia
bull Implant failure is usually due to the microbial challenge occlusal load or excessive cementndash Cement has been found in the tissues
bull Failure is evidenced by gt2 mm MOBILITY
bull Bone loss buccal and lingual results in dehiscence
Cement Implantitis
New AAP Case definitionPeri-implantitis
bull BOP
bull Probing depth gt 6 mm
bull Bone levels gt 3 mm apical of the most coronal portion of the intraosseous part of the implant
Caton J Armitage G Berglundh T Et al A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri‐implant diseases and conditions ndash Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification Journal of Periodontology 89 S1 (S1-S8) (2018)
Failing Criteria
bull Ailing (Peri-implant mucositis) inflammation present but no mobility
ndash bone appears normal or there may be an incipient lesion
bull Failing Peri-implantitis without mobility
ndash Inflammation has progressed to the bone as evidenced by radiographic lesion
bull Failed Peri-implantitis with mobility
ndash Implant has pronounced bone loss
Probing amp BOP
bull Metal probes on prosthetic part of the crown is fine
bull Some are concerned with metal probes on the threads
bull Must probe implants
bull Probe depths are generally deeper than natural tooth
bull BOP is not normal
threads
13
Treatment
bull Be aggressive amp prevent bone loss because very difficult to treat once initiated
bull Treatment
ndash Debride thoroughly
ndash Chlorhexidine
ndash Systemic antibiotics
ndash Bone grafts
ndash Arestin- local drug delivery
ndash Air flow polishing with glycine
Diagnosis Severity
bull Determining severity is based on CAL and bone loss
bull Clinical attachment level (CAL)
ndashdistance from the junctional epithelium to the CEJ
bull Probe depths alone are lacking because it does not take in account the gingival margin
ndashusing probe depths alone can result in over estimating or underestimating disease
Three possible relationships for gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ
GM
bull Where should the GM be normallyndash 1-2 mm coronal to the CEJ
bull What is the pattern of CEJs interproximallyacross the mouthndash More Flat on the Posteriors
ndash More Curvature on the Anteriors
ndash For interproximal space look at the papillae does it fill the embrasure space
ndash A normal GM on the anteriors could be +1mm
ndash A normal GM on the posteriors could be +2 mm
Clinical attachment level
Depends on position of the gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ (-)
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ (same)
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ (+)
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is coronal to CEJ
1 Measure probe depth
2 Measure from gingival margin to CEJ
3 Subtract second measurement from overall probe depth
FYI-This is a color
coded probe w
markings at 36912
14
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is levelwith CEJ
bull Probe depth is Clinical attachment level
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is apical to CEJ
bull Measure probe depthbull Measure recessionbull Add recession to probe depth
Grading
Bone Loss
Stage 1
Coronal 13
lt 15
Coronal 13
Mid 13
Last 13
15 Normal bone Height
33 stage 2
Stage 3Extends to mid third of root amp beyondStage 4Extends to mid third of root amp beyond
Stage 1
stage 3 amp 4
Predicting Activity
bull BOP
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will not break down
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will breakdown
ndash Sites that do not bleed will not breakdown
ndash The absence of bleeding provides more information than whether bleeding exists
ndash Therefore when sites bleed we say it is active
bull Inflammation
bull Nutrient canals
bull Rough looking crestal bone vs smooth amp well demarcated may indicate activity
15
Predicting Activity
bull Nutrient canals
ndash Highly visible canals may indicate active or rapid destruction
ndash canals are thought to be engorged large blood vessels
Crestal Bone
Rough looking crestal boneSmoother more demarcated crestal bone
Planningbull Systematic Informed consent
bull Diagnosis prognosis options risks benefits
ndashPatients must have all the information
bull Studies indicate slight reductions in PD s gt 6 mm after full-mouth scaling and root planingperformed in one appointment vs over longer intervals
bull These protocols particularly effective in patients with aggressive periodontitis andor pts w systemic conditions
Eberhard J et al J Clin Periodontol 200835591ndash604 amp Fang et al J Periodont Res October 19 2015)
ImplementationTreatment
bull Goals are to eliminate infection and risk factorsbull The objective is to remove all clinically detectable
calculus without excessive root planingndash bacterial endotoxins are weakly adherent to the root
surface (Nakib 1982)
bull The term debridement vs root planing
ImplementationTreatment
bull Treat patientrsquos significant otherbull 40 of the time spouses have the
same microbiotabull Donrsquot kiss dogs amp cats- they may have
periobull Avoid gross scaling
bull risk of abscessbull educationbull more difficult to re-insert
instruments
16
Air Polishing with glycine
ndashGlycine has anti inflammatory ampimmune modulation effectsbull Glycine receptor gingival tissue
ndashPerpulsionndashFDA approval for lt5 mmndashRemoval biofilm amp stainndashPerio maintenance ndashImplantsndashDecontaminate prior to grafts
Host-Modulating Treatmentbull Treating periodontitis by trying to resolve
inflammation
bull Resolvins
ndash Omega 3 Fatty acids correlated with less bone loss
ndash may be due to their ability to generate mediators that fight inflammation and aid in inflammation resolution
bull Low-dose doxycycline 20 mg 2x daily
ndash Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor is the only FDA-approved
ndash Reduction of PD amp CAL gain over 3 months to 9 monthsGolub LM et al Doxycycline i hibits neutrophil (PMN)-type matrix metalloproteinases in human adult periodontitis gingiva J Clin Periodontol 199522100ndash109 amp
Golub LM et al Adjunctive treatment with subantimicrobial doses of doxycycline effects on gingival fluid collagenase activity and attachment loss in adult periodontitis J Clin Periodontol 200128146ndash156
Host-Modulating Treatment
bull NSAIDsndash Reduces PGE 2 which can reduce bone loss
ndash Flurbiprofen and topical (ketorolac)
ndash Case controls demonstrate decrease risk
bull Bisphosphonates ndash Used for treating Pagetrsquos bone pain amp osteoporosis
ndash Alendronate sodium (Fosamax) risedronate (Actonel)
ndash Investigating for its ability to modulate the host
bull Used experimentally in animals to inhibit bone resorption amp bone mineral content amp to interfere w breakdown of collagen in the periodontium
ndash WARNING case reports of bone necrosis after extractions
bull questions scrtpl w pts on drug
Treatment
bull Statins have an anti-inflammatory and immune effects reducing levels of C-Reactive Protein MMP Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
ndash Statins reduce bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclast formation
ndash Some results show lower alveolar bone loss and reduction of clinical signs of inflammation
(meta anyalsis Estanislau etal J Clin Pharmacol 2014 Dec)
ndash Topical gels (simvastatin atorvastatin)
Treatment
bull Probioticsndash Improved biofilm index and probe depths (Shimauchi 2008)
bull Valtrexbull Photodynamic therapy
ndash Light-sensitive drug is applied then a light laser directly on the area treated with the drug
ndash When the light is combined with the drug phototoxic reactions are induced which destroy bacterial cells
ndash Shows short term benefits (Sgolastra 2012)bull Periowave
bull Emdogainndash Enamel matrix derivative for periodontal tissue regeneration in
infrabony defects amp used w SRP to enhance resultsbull Derived from developing pig teethbull Stimulate adherence attachment to cementum
Treatmentbull Topical antioxidants
ndash Antioxidant gel and rinse
ndash Periosciences ndash toothpaste rinse gel
ndash Topical coenzyme COQ10
bull Due to correlation w perio oxidative stress markers amp low level of natural occurring salivary antioxidants looking at polyphenolsantioxidants in the mouth locally delivered
ndash needs more research
bull Hyaluronic acid (HA) gel and mouth rinsendash hyaluronic acid plays a large role in the collagen building 02
hyaluronan gel topically amp subgingivally
ndash Studies have been done to evaluate on wound healing amp improving perio outcomes
ndash Further evidence is needed
17
LasersNeodymium lasersbull Ex NdYAG NdYAP lasers
bull FDA approved-PerioLase (FRNdYAG) patented procedure LANAPshown to regenerate cementum bone amp PDL
bull No histological studies LANAP with regeneration ( Linden E Laser Basics Dimensions of dental hygiene april 2016)
Diode Lasersbull Most commonly used by RDHs
bull Wide range of wavelengths
bull Used to reduce bacteria amp remove inflammatory byproducts
bull Absorbed by pigmented structures hemoglobin amp melanin
bull Warming amp ablation
bull There is insufficient evidence
Evaluation
bull Evaluating the host response
1 week acute or painful conditions
4-6 weeks changes in attachment level
12 weeks microbiota returns to pre TX levels
bull Complete final diagnosis
bull Many lawsuits exist due to lack of follow-up where as before it was due to failure to diagnose
Evaluation
bull Responded well
ndashDetermine appropriate PMP interval
bull Unresponsive
ndashProblem solve
bull Try to determine whyndashVirulent microorganisms Inadequate host
response Ineffective initial therapy or contributory amp risk factors
ndashFormulate new plan
Possible Solutions
bull Improve initial therapyndash re-scale root plan re-root plan
ndash self care
ndash adjunctive chemotherapeutics necessary
bull Reduce risk amp contributory factors
ndash smoking restorative
bull ex Overhangs
bull Medical consult periodontal referral Advanced diagnostic
Advanced Diagnostics
bull A test to determine active disease or predict an active episode of disease
bull currently we are not able to do this well
bull Many new tests are being developed still under investigation and still being assessed for usefulness
bull Many are not available yet or very expensive
bull Provide information that adds to the clinical exam
bull If it would be nice to know but not change anything we need to ask the questionhellip
bull Is the benefit worth the cost
Testing
OralDNA Labs Inc- httpwwworaldnacom
bull Genetic risk bacterial profile HPV-related oral cancers Herpes Candida Chlamydia trachomatis(CT) Neisseria gonorrhea(NG) gene markers related to inflammatory response DNA DrugMaptrade
micro-Ident- DNA probes
bull httpswwwhain-lifesciencecom
Oravital-Toronto based company uses biofilm testing the use of prescribed antibiotic antimicrobial rinses httpswwworavitalcom
Temple Oral Microbiology testing service 800-788-6687
USC Oral microbiology testing Lab 213-740-3163
UNC Oral microbiology Lab oralmicrodentistryuncedu

10
NGSigns
bull 3 key features papilla necrosis bleeding and pain
bull Punched out papillae cratered like depressions covered by a white necrotic pseudomembrane(collection of PMNS) bright red margins spontenousbleeding may occur
bull Distinctive foul odor
bull May have systemic involvement
ndash lymphadenopathy fever
bull May be a systemic
manifestations
ndash HIV
NG Treatmentbull Advise to avoid smoking amp etoh get rest and proper nutrition (rec
multi vitamin soft nutritious diet)+ self care
bull Rinses with frac12 glass warm water amp 1 tbsp hydrogen peroxide w half glass or chlorhexidine
bull Pain medication
bull Antibiotics can be used especially if systemic involvement
ndash metronidazole tetracycline pen vk
bull Initial supragingival debridement then complete
bull Consider complete laboratory work ndashup amp medical consult
ndash (NUG may be the first sign of HIV)
bull May progress to NUP
bull Follow ndashup phone call or visit within 24 hrsndash Re-eval surgery referral debridement wlocal= recurrent nature
NP
bull Progression of NUG
bull May be related to systemic disease
bull HIV nutrition deficiency
bull NUG superimposed on a previous periodontal disease
NP
Signs amp symptoms
bull Intensely red necrosis white pseudomembrane
bull Painful odor punched-out papillae
bull Reports of deep aching pain or jaw pain
bull Extensive bone loss
bull Spontaneous bleeding
Treatment
bull Same as NUG
Peridex culture antibiotics (metronidazole) or antifungals
Refractory
bull Not included in the new guidelines
bull Unresponsive to treatmentndash surgery frequent scrt pl antibiotics
bull Can be localized or generalized
bull Usually smokers
bull Treatment clindamycin metronidazole metriwamoxicillin or Augmentin
Periodontal Phenotype (Biotypes)
bull The term describes the thickness of the gingiva in a bucco-lingual dimension
bull 3 types
Thick flat
Thick scalloped
Thin
bull Thick (85) is more prevalent than thin (15)
11
Thin Gingival Phenotype
bull Triangle shaped teeth vs square
bull Thin tissue
bull Susceptible to recession
bull Dehiscence present
bull Instrumentation must be done
Carefully due to thin biotype
bull Reacts to insult by recession
Thick amp Flat Gingival Phenotype
bull Square shaped
bull Thick tissue
bull Susceptible to pocketing
bull Reacts to insult by pocketing
Thick Scalloped
bull Thick fibrotic gingiva
bull Slender teeth
bull Narrow zone of KT
bull Gingival scalloping
Recession
Type 1 Type 2
Interproximal CEJ
is clinically not
detectable
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is lt to buccal
Type 3
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is gt
buccal
attachment loss
Implants
bull Treat perio prior to implantsbull It takes 2 weeks for the implants to
become colonized by the surrounding teeth
bull No horizontal fibers like a tooth so infection goes straight to bone and perio happens very quickly
bull This perimucosal seal is delicate ndashBe careful during instrumentation
12
Implants
bull The implant coatingsrough surfaces may create more risk for implantitis but better for osteointergration
ndash The calculus is more embedded on these surfaces than the previous smoother surfaces
Stages of Peri-implant DiseasePeri-implant mucositis
bull Reversible inflammation of the soft tissues
bull Occurs in about 50 of implants placed within 9 - 14 years
Peri-implantitis
bull Bone Loss
bull Occurs in 12- 47 of implants 5 years after placement
bull Risk factors-Hx of severe perio poor self care amp lack of maintenance care
bull Cement Implantitis
bull Some evidence linking cement and titanium particles bio corrosion
Peri-implantitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram - Fusobacterium species Prevotella intermedia
bull Implant failure is usually due to the microbial challenge occlusal load or excessive cementndash Cement has been found in the tissues
bull Failure is evidenced by gt2 mm MOBILITY
bull Bone loss buccal and lingual results in dehiscence
Cement Implantitis
New AAP Case definitionPeri-implantitis
bull BOP
bull Probing depth gt 6 mm
bull Bone levels gt 3 mm apical of the most coronal portion of the intraosseous part of the implant
Caton J Armitage G Berglundh T Et al A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri‐implant diseases and conditions ndash Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification Journal of Periodontology 89 S1 (S1-S8) (2018)
Failing Criteria
bull Ailing (Peri-implant mucositis) inflammation present but no mobility
ndash bone appears normal or there may be an incipient lesion
bull Failing Peri-implantitis without mobility
ndash Inflammation has progressed to the bone as evidenced by radiographic lesion
bull Failed Peri-implantitis with mobility
ndash Implant has pronounced bone loss
Probing amp BOP
bull Metal probes on prosthetic part of the crown is fine
bull Some are concerned with metal probes on the threads
bull Must probe implants
bull Probe depths are generally deeper than natural tooth
bull BOP is not normal
threads
13
Treatment
bull Be aggressive amp prevent bone loss because very difficult to treat once initiated
bull Treatment
ndash Debride thoroughly
ndash Chlorhexidine
ndash Systemic antibiotics
ndash Bone grafts
ndash Arestin- local drug delivery
ndash Air flow polishing with glycine
Diagnosis Severity
bull Determining severity is based on CAL and bone loss
bull Clinical attachment level (CAL)
ndashdistance from the junctional epithelium to the CEJ
bull Probe depths alone are lacking because it does not take in account the gingival margin
ndashusing probe depths alone can result in over estimating or underestimating disease
Three possible relationships for gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ
GM
bull Where should the GM be normallyndash 1-2 mm coronal to the CEJ
bull What is the pattern of CEJs interproximallyacross the mouthndash More Flat on the Posteriors
ndash More Curvature on the Anteriors
ndash For interproximal space look at the papillae does it fill the embrasure space
ndash A normal GM on the anteriors could be +1mm
ndash A normal GM on the posteriors could be +2 mm
Clinical attachment level
Depends on position of the gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ (-)
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ (same)
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ (+)
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is coronal to CEJ
1 Measure probe depth
2 Measure from gingival margin to CEJ
3 Subtract second measurement from overall probe depth
FYI-This is a color
coded probe w
markings at 36912
14
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is levelwith CEJ
bull Probe depth is Clinical attachment level
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is apical to CEJ
bull Measure probe depthbull Measure recessionbull Add recession to probe depth
Grading
Bone Loss
Stage 1
Coronal 13
lt 15
Coronal 13
Mid 13
Last 13
15 Normal bone Height
33 stage 2
Stage 3Extends to mid third of root amp beyondStage 4Extends to mid third of root amp beyond
Stage 1
stage 3 amp 4
Predicting Activity
bull BOP
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will not break down
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will breakdown
ndash Sites that do not bleed will not breakdown
ndash The absence of bleeding provides more information than whether bleeding exists
ndash Therefore when sites bleed we say it is active
bull Inflammation
bull Nutrient canals
bull Rough looking crestal bone vs smooth amp well demarcated may indicate activity
15
Predicting Activity
bull Nutrient canals
ndash Highly visible canals may indicate active or rapid destruction
ndash canals are thought to be engorged large blood vessels
Crestal Bone
Rough looking crestal boneSmoother more demarcated crestal bone
Planningbull Systematic Informed consent
bull Diagnosis prognosis options risks benefits
ndashPatients must have all the information
bull Studies indicate slight reductions in PD s gt 6 mm after full-mouth scaling and root planingperformed in one appointment vs over longer intervals
bull These protocols particularly effective in patients with aggressive periodontitis andor pts w systemic conditions
Eberhard J et al J Clin Periodontol 200835591ndash604 amp Fang et al J Periodont Res October 19 2015)
ImplementationTreatment
bull Goals are to eliminate infection and risk factorsbull The objective is to remove all clinically detectable
calculus without excessive root planingndash bacterial endotoxins are weakly adherent to the root
surface (Nakib 1982)
bull The term debridement vs root planing
ImplementationTreatment
bull Treat patientrsquos significant otherbull 40 of the time spouses have the
same microbiotabull Donrsquot kiss dogs amp cats- they may have
periobull Avoid gross scaling
bull risk of abscessbull educationbull more difficult to re-insert
instruments
16
Air Polishing with glycine
ndashGlycine has anti inflammatory ampimmune modulation effectsbull Glycine receptor gingival tissue
ndashPerpulsionndashFDA approval for lt5 mmndashRemoval biofilm amp stainndashPerio maintenance ndashImplantsndashDecontaminate prior to grafts
Host-Modulating Treatmentbull Treating periodontitis by trying to resolve
inflammation
bull Resolvins
ndash Omega 3 Fatty acids correlated with less bone loss
ndash may be due to their ability to generate mediators that fight inflammation and aid in inflammation resolution
bull Low-dose doxycycline 20 mg 2x daily
ndash Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor is the only FDA-approved
ndash Reduction of PD amp CAL gain over 3 months to 9 monthsGolub LM et al Doxycycline i hibits neutrophil (PMN)-type matrix metalloproteinases in human adult periodontitis gingiva J Clin Periodontol 199522100ndash109 amp
Golub LM et al Adjunctive treatment with subantimicrobial doses of doxycycline effects on gingival fluid collagenase activity and attachment loss in adult periodontitis J Clin Periodontol 200128146ndash156
Host-Modulating Treatment
bull NSAIDsndash Reduces PGE 2 which can reduce bone loss
ndash Flurbiprofen and topical (ketorolac)
ndash Case controls demonstrate decrease risk
bull Bisphosphonates ndash Used for treating Pagetrsquos bone pain amp osteoporosis
ndash Alendronate sodium (Fosamax) risedronate (Actonel)
ndash Investigating for its ability to modulate the host
bull Used experimentally in animals to inhibit bone resorption amp bone mineral content amp to interfere w breakdown of collagen in the periodontium
ndash WARNING case reports of bone necrosis after extractions
bull questions scrtpl w pts on drug
Treatment
bull Statins have an anti-inflammatory and immune effects reducing levels of C-Reactive Protein MMP Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
ndash Statins reduce bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclast formation
ndash Some results show lower alveolar bone loss and reduction of clinical signs of inflammation
(meta anyalsis Estanislau etal J Clin Pharmacol 2014 Dec)
ndash Topical gels (simvastatin atorvastatin)
Treatment
bull Probioticsndash Improved biofilm index and probe depths (Shimauchi 2008)
bull Valtrexbull Photodynamic therapy
ndash Light-sensitive drug is applied then a light laser directly on the area treated with the drug
ndash When the light is combined with the drug phototoxic reactions are induced which destroy bacterial cells
ndash Shows short term benefits (Sgolastra 2012)bull Periowave
bull Emdogainndash Enamel matrix derivative for periodontal tissue regeneration in
infrabony defects amp used w SRP to enhance resultsbull Derived from developing pig teethbull Stimulate adherence attachment to cementum
Treatmentbull Topical antioxidants
ndash Antioxidant gel and rinse
ndash Periosciences ndash toothpaste rinse gel
ndash Topical coenzyme COQ10
bull Due to correlation w perio oxidative stress markers amp low level of natural occurring salivary antioxidants looking at polyphenolsantioxidants in the mouth locally delivered
ndash needs more research
bull Hyaluronic acid (HA) gel and mouth rinsendash hyaluronic acid plays a large role in the collagen building 02
hyaluronan gel topically amp subgingivally
ndash Studies have been done to evaluate on wound healing amp improving perio outcomes
ndash Further evidence is needed
17
LasersNeodymium lasersbull Ex NdYAG NdYAP lasers
bull FDA approved-PerioLase (FRNdYAG) patented procedure LANAPshown to regenerate cementum bone amp PDL
bull No histological studies LANAP with regeneration ( Linden E Laser Basics Dimensions of dental hygiene april 2016)
Diode Lasersbull Most commonly used by RDHs
bull Wide range of wavelengths
bull Used to reduce bacteria amp remove inflammatory byproducts
bull Absorbed by pigmented structures hemoglobin amp melanin
bull Warming amp ablation
bull There is insufficient evidence
Evaluation
bull Evaluating the host response
1 week acute or painful conditions
4-6 weeks changes in attachment level
12 weeks microbiota returns to pre TX levels
bull Complete final diagnosis
bull Many lawsuits exist due to lack of follow-up where as before it was due to failure to diagnose
Evaluation
bull Responded well
ndashDetermine appropriate PMP interval
bull Unresponsive
ndashProblem solve
bull Try to determine whyndashVirulent microorganisms Inadequate host
response Ineffective initial therapy or contributory amp risk factors
ndashFormulate new plan
Possible Solutions
bull Improve initial therapyndash re-scale root plan re-root plan
ndash self care
ndash adjunctive chemotherapeutics necessary
bull Reduce risk amp contributory factors
ndash smoking restorative
bull ex Overhangs
bull Medical consult periodontal referral Advanced diagnostic
Advanced Diagnostics
bull A test to determine active disease or predict an active episode of disease
bull currently we are not able to do this well
bull Many new tests are being developed still under investigation and still being assessed for usefulness
bull Many are not available yet or very expensive
bull Provide information that adds to the clinical exam
bull If it would be nice to know but not change anything we need to ask the questionhellip
bull Is the benefit worth the cost
Testing
OralDNA Labs Inc- httpwwworaldnacom
bull Genetic risk bacterial profile HPV-related oral cancers Herpes Candida Chlamydia trachomatis(CT) Neisseria gonorrhea(NG) gene markers related to inflammatory response DNA DrugMaptrade
micro-Ident- DNA probes
bull httpswwwhain-lifesciencecom
Oravital-Toronto based company uses biofilm testing the use of prescribed antibiotic antimicrobial rinses httpswwworavitalcom
Temple Oral Microbiology testing service 800-788-6687
USC Oral microbiology testing Lab 213-740-3163
UNC Oral microbiology Lab oralmicrodentistryuncedu

11
Thin Gingival Phenotype
bull Triangle shaped teeth vs square
bull Thin tissue
bull Susceptible to recession
bull Dehiscence present
bull Instrumentation must be done
Carefully due to thin biotype
bull Reacts to insult by recession
Thick amp Flat Gingival Phenotype
bull Square shaped
bull Thick tissue
bull Susceptible to pocketing
bull Reacts to insult by pocketing
Thick Scalloped
bull Thick fibrotic gingiva
bull Slender teeth
bull Narrow zone of KT
bull Gingival scalloping
Recession
Type 1 Type 2
Interproximal CEJ
is clinically not
detectable
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is lt to buccal
Type 3
The amount of
interproximal
attachment loss
is gt
buccal
attachment loss
Implants
bull Treat perio prior to implantsbull It takes 2 weeks for the implants to
become colonized by the surrounding teeth
bull No horizontal fibers like a tooth so infection goes straight to bone and perio happens very quickly
bull This perimucosal seal is delicate ndashBe careful during instrumentation
12
Implants
bull The implant coatingsrough surfaces may create more risk for implantitis but better for osteointergration
ndash The calculus is more embedded on these surfaces than the previous smoother surfaces
Stages of Peri-implant DiseasePeri-implant mucositis
bull Reversible inflammation of the soft tissues
bull Occurs in about 50 of implants placed within 9 - 14 years
Peri-implantitis
bull Bone Loss
bull Occurs in 12- 47 of implants 5 years after placement
bull Risk factors-Hx of severe perio poor self care amp lack of maintenance care
bull Cement Implantitis
bull Some evidence linking cement and titanium particles bio corrosion
Peri-implantitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram - Fusobacterium species Prevotella intermedia
bull Implant failure is usually due to the microbial challenge occlusal load or excessive cementndash Cement has been found in the tissues
bull Failure is evidenced by gt2 mm MOBILITY
bull Bone loss buccal and lingual results in dehiscence
Cement Implantitis
New AAP Case definitionPeri-implantitis
bull BOP
bull Probing depth gt 6 mm
bull Bone levels gt 3 mm apical of the most coronal portion of the intraosseous part of the implant
Caton J Armitage G Berglundh T Et al A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri‐implant diseases and conditions ndash Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification Journal of Periodontology 89 S1 (S1-S8) (2018)
Failing Criteria
bull Ailing (Peri-implant mucositis) inflammation present but no mobility
ndash bone appears normal or there may be an incipient lesion
bull Failing Peri-implantitis without mobility
ndash Inflammation has progressed to the bone as evidenced by radiographic lesion
bull Failed Peri-implantitis with mobility
ndash Implant has pronounced bone loss
Probing amp BOP
bull Metal probes on prosthetic part of the crown is fine
bull Some are concerned with metal probes on the threads
bull Must probe implants
bull Probe depths are generally deeper than natural tooth
bull BOP is not normal
threads
13
Treatment
bull Be aggressive amp prevent bone loss because very difficult to treat once initiated
bull Treatment
ndash Debride thoroughly
ndash Chlorhexidine
ndash Systemic antibiotics
ndash Bone grafts
ndash Arestin- local drug delivery
ndash Air flow polishing with glycine
Diagnosis Severity
bull Determining severity is based on CAL and bone loss
bull Clinical attachment level (CAL)
ndashdistance from the junctional epithelium to the CEJ
bull Probe depths alone are lacking because it does not take in account the gingival margin
ndashusing probe depths alone can result in over estimating or underestimating disease
Three possible relationships for gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ
GM
bull Where should the GM be normallyndash 1-2 mm coronal to the CEJ
bull What is the pattern of CEJs interproximallyacross the mouthndash More Flat on the Posteriors
ndash More Curvature on the Anteriors
ndash For interproximal space look at the papillae does it fill the embrasure space
ndash A normal GM on the anteriors could be +1mm
ndash A normal GM on the posteriors could be +2 mm
Clinical attachment level
Depends on position of the gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ (-)
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ (same)
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ (+)
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is coronal to CEJ
1 Measure probe depth
2 Measure from gingival margin to CEJ
3 Subtract second measurement from overall probe depth
FYI-This is a color
coded probe w
markings at 36912
14
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is levelwith CEJ
bull Probe depth is Clinical attachment level
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is apical to CEJ
bull Measure probe depthbull Measure recessionbull Add recession to probe depth
Grading
Bone Loss
Stage 1
Coronal 13
lt 15
Coronal 13
Mid 13
Last 13
15 Normal bone Height
33 stage 2
Stage 3Extends to mid third of root amp beyondStage 4Extends to mid third of root amp beyond
Stage 1
stage 3 amp 4
Predicting Activity
bull BOP
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will not break down
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will breakdown
ndash Sites that do not bleed will not breakdown
ndash The absence of bleeding provides more information than whether bleeding exists
ndash Therefore when sites bleed we say it is active
bull Inflammation
bull Nutrient canals
bull Rough looking crestal bone vs smooth amp well demarcated may indicate activity
15
Predicting Activity
bull Nutrient canals
ndash Highly visible canals may indicate active or rapid destruction
ndash canals are thought to be engorged large blood vessels
Crestal Bone
Rough looking crestal boneSmoother more demarcated crestal bone
Planningbull Systematic Informed consent
bull Diagnosis prognosis options risks benefits
ndashPatients must have all the information
bull Studies indicate slight reductions in PD s gt 6 mm after full-mouth scaling and root planingperformed in one appointment vs over longer intervals
bull These protocols particularly effective in patients with aggressive periodontitis andor pts w systemic conditions
Eberhard J et al J Clin Periodontol 200835591ndash604 amp Fang et al J Periodont Res October 19 2015)
ImplementationTreatment
bull Goals are to eliminate infection and risk factorsbull The objective is to remove all clinically detectable
calculus without excessive root planingndash bacterial endotoxins are weakly adherent to the root
surface (Nakib 1982)
bull The term debridement vs root planing
ImplementationTreatment
bull Treat patientrsquos significant otherbull 40 of the time spouses have the
same microbiotabull Donrsquot kiss dogs amp cats- they may have
periobull Avoid gross scaling
bull risk of abscessbull educationbull more difficult to re-insert
instruments
16
Air Polishing with glycine
ndashGlycine has anti inflammatory ampimmune modulation effectsbull Glycine receptor gingival tissue
ndashPerpulsionndashFDA approval for lt5 mmndashRemoval biofilm amp stainndashPerio maintenance ndashImplantsndashDecontaminate prior to grafts
Host-Modulating Treatmentbull Treating periodontitis by trying to resolve
inflammation
bull Resolvins
ndash Omega 3 Fatty acids correlated with less bone loss
ndash may be due to their ability to generate mediators that fight inflammation and aid in inflammation resolution
bull Low-dose doxycycline 20 mg 2x daily
ndash Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor is the only FDA-approved
ndash Reduction of PD amp CAL gain over 3 months to 9 monthsGolub LM et al Doxycycline i hibits neutrophil (PMN)-type matrix metalloproteinases in human adult periodontitis gingiva J Clin Periodontol 199522100ndash109 amp
Golub LM et al Adjunctive treatment with subantimicrobial doses of doxycycline effects on gingival fluid collagenase activity and attachment loss in adult periodontitis J Clin Periodontol 200128146ndash156
Host-Modulating Treatment
bull NSAIDsndash Reduces PGE 2 which can reduce bone loss
ndash Flurbiprofen and topical (ketorolac)
ndash Case controls demonstrate decrease risk
bull Bisphosphonates ndash Used for treating Pagetrsquos bone pain amp osteoporosis
ndash Alendronate sodium (Fosamax) risedronate (Actonel)
ndash Investigating for its ability to modulate the host
bull Used experimentally in animals to inhibit bone resorption amp bone mineral content amp to interfere w breakdown of collagen in the periodontium
ndash WARNING case reports of bone necrosis after extractions
bull questions scrtpl w pts on drug
Treatment
bull Statins have an anti-inflammatory and immune effects reducing levels of C-Reactive Protein MMP Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
ndash Statins reduce bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclast formation
ndash Some results show lower alveolar bone loss and reduction of clinical signs of inflammation
(meta anyalsis Estanislau etal J Clin Pharmacol 2014 Dec)
ndash Topical gels (simvastatin atorvastatin)
Treatment
bull Probioticsndash Improved biofilm index and probe depths (Shimauchi 2008)
bull Valtrexbull Photodynamic therapy
ndash Light-sensitive drug is applied then a light laser directly on the area treated with the drug
ndash When the light is combined with the drug phototoxic reactions are induced which destroy bacterial cells
ndash Shows short term benefits (Sgolastra 2012)bull Periowave
bull Emdogainndash Enamel matrix derivative for periodontal tissue regeneration in
infrabony defects amp used w SRP to enhance resultsbull Derived from developing pig teethbull Stimulate adherence attachment to cementum
Treatmentbull Topical antioxidants
ndash Antioxidant gel and rinse
ndash Periosciences ndash toothpaste rinse gel
ndash Topical coenzyme COQ10
bull Due to correlation w perio oxidative stress markers amp low level of natural occurring salivary antioxidants looking at polyphenolsantioxidants in the mouth locally delivered
ndash needs more research
bull Hyaluronic acid (HA) gel and mouth rinsendash hyaluronic acid plays a large role in the collagen building 02
hyaluronan gel topically amp subgingivally
ndash Studies have been done to evaluate on wound healing amp improving perio outcomes
ndash Further evidence is needed
17
LasersNeodymium lasersbull Ex NdYAG NdYAP lasers
bull FDA approved-PerioLase (FRNdYAG) patented procedure LANAPshown to regenerate cementum bone amp PDL
bull No histological studies LANAP with regeneration ( Linden E Laser Basics Dimensions of dental hygiene april 2016)
Diode Lasersbull Most commonly used by RDHs
bull Wide range of wavelengths
bull Used to reduce bacteria amp remove inflammatory byproducts
bull Absorbed by pigmented structures hemoglobin amp melanin
bull Warming amp ablation
bull There is insufficient evidence
Evaluation
bull Evaluating the host response
1 week acute or painful conditions
4-6 weeks changes in attachment level
12 weeks microbiota returns to pre TX levels
bull Complete final diagnosis
bull Many lawsuits exist due to lack of follow-up where as before it was due to failure to diagnose
Evaluation
bull Responded well
ndashDetermine appropriate PMP interval
bull Unresponsive
ndashProblem solve
bull Try to determine whyndashVirulent microorganisms Inadequate host
response Ineffective initial therapy or contributory amp risk factors
ndashFormulate new plan
Possible Solutions
bull Improve initial therapyndash re-scale root plan re-root plan
ndash self care
ndash adjunctive chemotherapeutics necessary
bull Reduce risk amp contributory factors
ndash smoking restorative
bull ex Overhangs
bull Medical consult periodontal referral Advanced diagnostic
Advanced Diagnostics
bull A test to determine active disease or predict an active episode of disease
bull currently we are not able to do this well
bull Many new tests are being developed still under investigation and still being assessed for usefulness
bull Many are not available yet or very expensive
bull Provide information that adds to the clinical exam
bull If it would be nice to know but not change anything we need to ask the questionhellip
bull Is the benefit worth the cost
Testing
OralDNA Labs Inc- httpwwworaldnacom
bull Genetic risk bacterial profile HPV-related oral cancers Herpes Candida Chlamydia trachomatis(CT) Neisseria gonorrhea(NG) gene markers related to inflammatory response DNA DrugMaptrade
micro-Ident- DNA probes
bull httpswwwhain-lifesciencecom
Oravital-Toronto based company uses biofilm testing the use of prescribed antibiotic antimicrobial rinses httpswwworavitalcom
Temple Oral Microbiology testing service 800-788-6687
USC Oral microbiology testing Lab 213-740-3163
UNC Oral microbiology Lab oralmicrodentistryuncedu

12
Implants
bull The implant coatingsrough surfaces may create more risk for implantitis but better for osteointergration
ndash The calculus is more embedded on these surfaces than the previous smoother surfaces
Stages of Peri-implant DiseasePeri-implant mucositis
bull Reversible inflammation of the soft tissues
bull Occurs in about 50 of implants placed within 9 - 14 years
Peri-implantitis
bull Bone Loss
bull Occurs in 12- 47 of implants 5 years after placement
bull Risk factors-Hx of severe perio poor self care amp lack of maintenance care
bull Cement Implantitis
bull Some evidence linking cement and titanium particles bio corrosion
Peri-implantitis
Microorganisms
bull Gram - Fusobacterium species Prevotella intermedia
bull Implant failure is usually due to the microbial challenge occlusal load or excessive cementndash Cement has been found in the tissues
bull Failure is evidenced by gt2 mm MOBILITY
bull Bone loss buccal and lingual results in dehiscence
Cement Implantitis
New AAP Case definitionPeri-implantitis
bull BOP
bull Probing depth gt 6 mm
bull Bone levels gt 3 mm apical of the most coronal portion of the intraosseous part of the implant
Caton J Armitage G Berglundh T Et al A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri‐implant diseases and conditions ndash Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification Journal of Periodontology 89 S1 (S1-S8) (2018)
Failing Criteria
bull Ailing (Peri-implant mucositis) inflammation present but no mobility
ndash bone appears normal or there may be an incipient lesion
bull Failing Peri-implantitis without mobility
ndash Inflammation has progressed to the bone as evidenced by radiographic lesion
bull Failed Peri-implantitis with mobility
ndash Implant has pronounced bone loss
Probing amp BOP
bull Metal probes on prosthetic part of the crown is fine
bull Some are concerned with metal probes on the threads
bull Must probe implants
bull Probe depths are generally deeper than natural tooth
bull BOP is not normal
threads
13
Treatment
bull Be aggressive amp prevent bone loss because very difficult to treat once initiated
bull Treatment
ndash Debride thoroughly
ndash Chlorhexidine
ndash Systemic antibiotics
ndash Bone grafts
ndash Arestin- local drug delivery
ndash Air flow polishing with glycine
Diagnosis Severity
bull Determining severity is based on CAL and bone loss
bull Clinical attachment level (CAL)
ndashdistance from the junctional epithelium to the CEJ
bull Probe depths alone are lacking because it does not take in account the gingival margin
ndashusing probe depths alone can result in over estimating or underestimating disease
Three possible relationships for gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ
GM
bull Where should the GM be normallyndash 1-2 mm coronal to the CEJ
bull What is the pattern of CEJs interproximallyacross the mouthndash More Flat on the Posteriors
ndash More Curvature on the Anteriors
ndash For interproximal space look at the papillae does it fill the embrasure space
ndash A normal GM on the anteriors could be +1mm
ndash A normal GM on the posteriors could be +2 mm
Clinical attachment level
Depends on position of the gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ (-)
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ (same)
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ (+)
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is coronal to CEJ
1 Measure probe depth
2 Measure from gingival margin to CEJ
3 Subtract second measurement from overall probe depth
FYI-This is a color
coded probe w
markings at 36912
14
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is levelwith CEJ
bull Probe depth is Clinical attachment level
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is apical to CEJ
bull Measure probe depthbull Measure recessionbull Add recession to probe depth
Grading
Bone Loss
Stage 1
Coronal 13
lt 15
Coronal 13
Mid 13
Last 13
15 Normal bone Height
33 stage 2
Stage 3Extends to mid third of root amp beyondStage 4Extends to mid third of root amp beyond
Stage 1
stage 3 amp 4
Predicting Activity
bull BOP
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will not break down
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will breakdown
ndash Sites that do not bleed will not breakdown
ndash The absence of bleeding provides more information than whether bleeding exists
ndash Therefore when sites bleed we say it is active
bull Inflammation
bull Nutrient canals
bull Rough looking crestal bone vs smooth amp well demarcated may indicate activity
15
Predicting Activity
bull Nutrient canals
ndash Highly visible canals may indicate active or rapid destruction
ndash canals are thought to be engorged large blood vessels
Crestal Bone
Rough looking crestal boneSmoother more demarcated crestal bone
Planningbull Systematic Informed consent
bull Diagnosis prognosis options risks benefits
ndashPatients must have all the information
bull Studies indicate slight reductions in PD s gt 6 mm after full-mouth scaling and root planingperformed in one appointment vs over longer intervals
bull These protocols particularly effective in patients with aggressive periodontitis andor pts w systemic conditions
Eberhard J et al J Clin Periodontol 200835591ndash604 amp Fang et al J Periodont Res October 19 2015)
ImplementationTreatment
bull Goals are to eliminate infection and risk factorsbull The objective is to remove all clinically detectable
calculus without excessive root planingndash bacterial endotoxins are weakly adherent to the root
surface (Nakib 1982)
bull The term debridement vs root planing
ImplementationTreatment
bull Treat patientrsquos significant otherbull 40 of the time spouses have the
same microbiotabull Donrsquot kiss dogs amp cats- they may have
periobull Avoid gross scaling
bull risk of abscessbull educationbull more difficult to re-insert
instruments
16
Air Polishing with glycine
ndashGlycine has anti inflammatory ampimmune modulation effectsbull Glycine receptor gingival tissue
ndashPerpulsionndashFDA approval for lt5 mmndashRemoval biofilm amp stainndashPerio maintenance ndashImplantsndashDecontaminate prior to grafts
Host-Modulating Treatmentbull Treating periodontitis by trying to resolve
inflammation
bull Resolvins
ndash Omega 3 Fatty acids correlated with less bone loss
ndash may be due to their ability to generate mediators that fight inflammation and aid in inflammation resolution
bull Low-dose doxycycline 20 mg 2x daily
ndash Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor is the only FDA-approved
ndash Reduction of PD amp CAL gain over 3 months to 9 monthsGolub LM et al Doxycycline i hibits neutrophil (PMN)-type matrix metalloproteinases in human adult periodontitis gingiva J Clin Periodontol 199522100ndash109 amp
Golub LM et al Adjunctive treatment with subantimicrobial doses of doxycycline effects on gingival fluid collagenase activity and attachment loss in adult periodontitis J Clin Periodontol 200128146ndash156
Host-Modulating Treatment
bull NSAIDsndash Reduces PGE 2 which can reduce bone loss
ndash Flurbiprofen and topical (ketorolac)
ndash Case controls demonstrate decrease risk
bull Bisphosphonates ndash Used for treating Pagetrsquos bone pain amp osteoporosis
ndash Alendronate sodium (Fosamax) risedronate (Actonel)
ndash Investigating for its ability to modulate the host
bull Used experimentally in animals to inhibit bone resorption amp bone mineral content amp to interfere w breakdown of collagen in the periodontium
ndash WARNING case reports of bone necrosis after extractions
bull questions scrtpl w pts on drug
Treatment
bull Statins have an anti-inflammatory and immune effects reducing levels of C-Reactive Protein MMP Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
ndash Statins reduce bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclast formation
ndash Some results show lower alveolar bone loss and reduction of clinical signs of inflammation
(meta anyalsis Estanislau etal J Clin Pharmacol 2014 Dec)
ndash Topical gels (simvastatin atorvastatin)
Treatment
bull Probioticsndash Improved biofilm index and probe depths (Shimauchi 2008)
bull Valtrexbull Photodynamic therapy
ndash Light-sensitive drug is applied then a light laser directly on the area treated with the drug
ndash When the light is combined with the drug phototoxic reactions are induced which destroy bacterial cells
ndash Shows short term benefits (Sgolastra 2012)bull Periowave
bull Emdogainndash Enamel matrix derivative for periodontal tissue regeneration in
infrabony defects amp used w SRP to enhance resultsbull Derived from developing pig teethbull Stimulate adherence attachment to cementum
Treatmentbull Topical antioxidants
ndash Antioxidant gel and rinse
ndash Periosciences ndash toothpaste rinse gel
ndash Topical coenzyme COQ10
bull Due to correlation w perio oxidative stress markers amp low level of natural occurring salivary antioxidants looking at polyphenolsantioxidants in the mouth locally delivered
ndash needs more research
bull Hyaluronic acid (HA) gel and mouth rinsendash hyaluronic acid plays a large role in the collagen building 02
hyaluronan gel topically amp subgingivally
ndash Studies have been done to evaluate on wound healing amp improving perio outcomes
ndash Further evidence is needed
17
LasersNeodymium lasersbull Ex NdYAG NdYAP lasers
bull FDA approved-PerioLase (FRNdYAG) patented procedure LANAPshown to regenerate cementum bone amp PDL
bull No histological studies LANAP with regeneration ( Linden E Laser Basics Dimensions of dental hygiene april 2016)
Diode Lasersbull Most commonly used by RDHs
bull Wide range of wavelengths
bull Used to reduce bacteria amp remove inflammatory byproducts
bull Absorbed by pigmented structures hemoglobin amp melanin
bull Warming amp ablation
bull There is insufficient evidence
Evaluation
bull Evaluating the host response
1 week acute or painful conditions
4-6 weeks changes in attachment level
12 weeks microbiota returns to pre TX levels
bull Complete final diagnosis
bull Many lawsuits exist due to lack of follow-up where as before it was due to failure to diagnose
Evaluation
bull Responded well
ndashDetermine appropriate PMP interval
bull Unresponsive
ndashProblem solve
bull Try to determine whyndashVirulent microorganisms Inadequate host
response Ineffective initial therapy or contributory amp risk factors
ndashFormulate new plan
Possible Solutions
bull Improve initial therapyndash re-scale root plan re-root plan
ndash self care
ndash adjunctive chemotherapeutics necessary
bull Reduce risk amp contributory factors
ndash smoking restorative
bull ex Overhangs
bull Medical consult periodontal referral Advanced diagnostic
Advanced Diagnostics
bull A test to determine active disease or predict an active episode of disease
bull currently we are not able to do this well
bull Many new tests are being developed still under investigation and still being assessed for usefulness
bull Many are not available yet or very expensive
bull Provide information that adds to the clinical exam
bull If it would be nice to know but not change anything we need to ask the questionhellip
bull Is the benefit worth the cost
Testing
OralDNA Labs Inc- httpwwworaldnacom
bull Genetic risk bacterial profile HPV-related oral cancers Herpes Candida Chlamydia trachomatis(CT) Neisseria gonorrhea(NG) gene markers related to inflammatory response DNA DrugMaptrade
micro-Ident- DNA probes
bull httpswwwhain-lifesciencecom
Oravital-Toronto based company uses biofilm testing the use of prescribed antibiotic antimicrobial rinses httpswwworavitalcom
Temple Oral Microbiology testing service 800-788-6687
USC Oral microbiology testing Lab 213-740-3163
UNC Oral microbiology Lab oralmicrodentistryuncedu

13
Treatment
bull Be aggressive amp prevent bone loss because very difficult to treat once initiated
bull Treatment
ndash Debride thoroughly
ndash Chlorhexidine
ndash Systemic antibiotics
ndash Bone grafts
ndash Arestin- local drug delivery
ndash Air flow polishing with glycine
Diagnosis Severity
bull Determining severity is based on CAL and bone loss
bull Clinical attachment level (CAL)
ndashdistance from the junctional epithelium to the CEJ
bull Probe depths alone are lacking because it does not take in account the gingival margin
ndashusing probe depths alone can result in over estimating or underestimating disease
Three possible relationships for gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ
GM
bull Where should the GM be normallyndash 1-2 mm coronal to the CEJ
bull What is the pattern of CEJs interproximallyacross the mouthndash More Flat on the Posteriors
ndash More Curvature on the Anteriors
ndash For interproximal space look at the papillae does it fill the embrasure space
ndash A normal GM on the anteriors could be +1mm
ndash A normal GM on the posteriors could be +2 mm
Clinical attachment level
Depends on position of the gingival margin and CEJ
bull Gingival margin could be coronal to CEJ (-)
bull Gingival margin could be level with CEJ (same)
bull Gingival margin could be apical to CEJ (+)
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is coronal to CEJ
1 Measure probe depth
2 Measure from gingival margin to CEJ
3 Subtract second measurement from overall probe depth
FYI-This is a color
coded probe w
markings at 36912
14
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is levelwith CEJ
bull Probe depth is Clinical attachment level
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is apical to CEJ
bull Measure probe depthbull Measure recessionbull Add recession to probe depth
Grading
Bone Loss
Stage 1
Coronal 13
lt 15
Coronal 13
Mid 13
Last 13
15 Normal bone Height
33 stage 2
Stage 3Extends to mid third of root amp beyondStage 4Extends to mid third of root amp beyond
Stage 1
stage 3 amp 4
Predicting Activity
bull BOP
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will not break down
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will breakdown
ndash Sites that do not bleed will not breakdown
ndash The absence of bleeding provides more information than whether bleeding exists
ndash Therefore when sites bleed we say it is active
bull Inflammation
bull Nutrient canals
bull Rough looking crestal bone vs smooth amp well demarcated may indicate activity
15
Predicting Activity
bull Nutrient canals
ndash Highly visible canals may indicate active or rapid destruction
ndash canals are thought to be engorged large blood vessels
Crestal Bone
Rough looking crestal boneSmoother more demarcated crestal bone
Planningbull Systematic Informed consent
bull Diagnosis prognosis options risks benefits
ndashPatients must have all the information
bull Studies indicate slight reductions in PD s gt 6 mm after full-mouth scaling and root planingperformed in one appointment vs over longer intervals
bull These protocols particularly effective in patients with aggressive periodontitis andor pts w systemic conditions
Eberhard J et al J Clin Periodontol 200835591ndash604 amp Fang et al J Periodont Res October 19 2015)
ImplementationTreatment
bull Goals are to eliminate infection and risk factorsbull The objective is to remove all clinically detectable
calculus without excessive root planingndash bacterial endotoxins are weakly adherent to the root
surface (Nakib 1982)
bull The term debridement vs root planing
ImplementationTreatment
bull Treat patientrsquos significant otherbull 40 of the time spouses have the
same microbiotabull Donrsquot kiss dogs amp cats- they may have
periobull Avoid gross scaling
bull risk of abscessbull educationbull more difficult to re-insert
instruments
16
Air Polishing with glycine
ndashGlycine has anti inflammatory ampimmune modulation effectsbull Glycine receptor gingival tissue
ndashPerpulsionndashFDA approval for lt5 mmndashRemoval biofilm amp stainndashPerio maintenance ndashImplantsndashDecontaminate prior to grafts
Host-Modulating Treatmentbull Treating periodontitis by trying to resolve
inflammation
bull Resolvins
ndash Omega 3 Fatty acids correlated with less bone loss
ndash may be due to their ability to generate mediators that fight inflammation and aid in inflammation resolution
bull Low-dose doxycycline 20 mg 2x daily
ndash Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor is the only FDA-approved
ndash Reduction of PD amp CAL gain over 3 months to 9 monthsGolub LM et al Doxycycline i hibits neutrophil (PMN)-type matrix metalloproteinases in human adult periodontitis gingiva J Clin Periodontol 199522100ndash109 amp
Golub LM et al Adjunctive treatment with subantimicrobial doses of doxycycline effects on gingival fluid collagenase activity and attachment loss in adult periodontitis J Clin Periodontol 200128146ndash156
Host-Modulating Treatment
bull NSAIDsndash Reduces PGE 2 which can reduce bone loss
ndash Flurbiprofen and topical (ketorolac)
ndash Case controls demonstrate decrease risk
bull Bisphosphonates ndash Used for treating Pagetrsquos bone pain amp osteoporosis
ndash Alendronate sodium (Fosamax) risedronate (Actonel)
ndash Investigating for its ability to modulate the host
bull Used experimentally in animals to inhibit bone resorption amp bone mineral content amp to interfere w breakdown of collagen in the periodontium
ndash WARNING case reports of bone necrosis after extractions
bull questions scrtpl w pts on drug
Treatment
bull Statins have an anti-inflammatory and immune effects reducing levels of C-Reactive Protein MMP Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
ndash Statins reduce bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclast formation
ndash Some results show lower alveolar bone loss and reduction of clinical signs of inflammation
(meta anyalsis Estanislau etal J Clin Pharmacol 2014 Dec)
ndash Topical gels (simvastatin atorvastatin)
Treatment
bull Probioticsndash Improved biofilm index and probe depths (Shimauchi 2008)
bull Valtrexbull Photodynamic therapy
ndash Light-sensitive drug is applied then a light laser directly on the area treated with the drug
ndash When the light is combined with the drug phototoxic reactions are induced which destroy bacterial cells
ndash Shows short term benefits (Sgolastra 2012)bull Periowave
bull Emdogainndash Enamel matrix derivative for periodontal tissue regeneration in
infrabony defects amp used w SRP to enhance resultsbull Derived from developing pig teethbull Stimulate adherence attachment to cementum
Treatmentbull Topical antioxidants
ndash Antioxidant gel and rinse
ndash Periosciences ndash toothpaste rinse gel
ndash Topical coenzyme COQ10
bull Due to correlation w perio oxidative stress markers amp low level of natural occurring salivary antioxidants looking at polyphenolsantioxidants in the mouth locally delivered
ndash needs more research
bull Hyaluronic acid (HA) gel and mouth rinsendash hyaluronic acid plays a large role in the collagen building 02
hyaluronan gel topically amp subgingivally
ndash Studies have been done to evaluate on wound healing amp improving perio outcomes
ndash Further evidence is needed
17
LasersNeodymium lasersbull Ex NdYAG NdYAP lasers
bull FDA approved-PerioLase (FRNdYAG) patented procedure LANAPshown to regenerate cementum bone amp PDL
bull No histological studies LANAP with regeneration ( Linden E Laser Basics Dimensions of dental hygiene april 2016)
Diode Lasersbull Most commonly used by RDHs
bull Wide range of wavelengths
bull Used to reduce bacteria amp remove inflammatory byproducts
bull Absorbed by pigmented structures hemoglobin amp melanin
bull Warming amp ablation
bull There is insufficient evidence
Evaluation
bull Evaluating the host response
1 week acute or painful conditions
4-6 weeks changes in attachment level
12 weeks microbiota returns to pre TX levels
bull Complete final diagnosis
bull Many lawsuits exist due to lack of follow-up where as before it was due to failure to diagnose
Evaluation
bull Responded well
ndashDetermine appropriate PMP interval
bull Unresponsive
ndashProblem solve
bull Try to determine whyndashVirulent microorganisms Inadequate host
response Ineffective initial therapy or contributory amp risk factors
ndashFormulate new plan
Possible Solutions
bull Improve initial therapyndash re-scale root plan re-root plan
ndash self care
ndash adjunctive chemotherapeutics necessary
bull Reduce risk amp contributory factors
ndash smoking restorative
bull ex Overhangs
bull Medical consult periodontal referral Advanced diagnostic
Advanced Diagnostics
bull A test to determine active disease or predict an active episode of disease
bull currently we are not able to do this well
bull Many new tests are being developed still under investigation and still being assessed for usefulness
bull Many are not available yet or very expensive
bull Provide information that adds to the clinical exam
bull If it would be nice to know but not change anything we need to ask the questionhellip
bull Is the benefit worth the cost
Testing
OralDNA Labs Inc- httpwwworaldnacom
bull Genetic risk bacterial profile HPV-related oral cancers Herpes Candida Chlamydia trachomatis(CT) Neisseria gonorrhea(NG) gene markers related to inflammatory response DNA DrugMaptrade
micro-Ident- DNA probes
bull httpswwwhain-lifesciencecom
Oravital-Toronto based company uses biofilm testing the use of prescribed antibiotic antimicrobial rinses httpswwworavitalcom
Temple Oral Microbiology testing service 800-788-6687
USC Oral microbiology testing Lab 213-740-3163
UNC Oral microbiology Lab oralmicrodentistryuncedu

14
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is levelwith CEJ
bull Probe depth is Clinical attachment level
Measuring CAL when gingival margin is apical to CEJ
bull Measure probe depthbull Measure recessionbull Add recession to probe depth
Grading
Bone Loss
Stage 1
Coronal 13
lt 15
Coronal 13
Mid 13
Last 13
15 Normal bone Height
33 stage 2
Stage 3Extends to mid third of root amp beyondStage 4Extends to mid third of root amp beyond
Stage 1
stage 3 amp 4
Predicting Activity
bull BOP
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will not break down
ndash 50 of all bleeding sites will breakdown
ndash Sites that do not bleed will not breakdown
ndash The absence of bleeding provides more information than whether bleeding exists
ndash Therefore when sites bleed we say it is active
bull Inflammation
bull Nutrient canals
bull Rough looking crestal bone vs smooth amp well demarcated may indicate activity
15
Predicting Activity
bull Nutrient canals
ndash Highly visible canals may indicate active or rapid destruction
ndash canals are thought to be engorged large blood vessels
Crestal Bone
Rough looking crestal boneSmoother more demarcated crestal bone
Planningbull Systematic Informed consent
bull Diagnosis prognosis options risks benefits
ndashPatients must have all the information
bull Studies indicate slight reductions in PD s gt 6 mm after full-mouth scaling and root planingperformed in one appointment vs over longer intervals
bull These protocols particularly effective in patients with aggressive periodontitis andor pts w systemic conditions
Eberhard J et al J Clin Periodontol 200835591ndash604 amp Fang et al J Periodont Res October 19 2015)
ImplementationTreatment
bull Goals are to eliminate infection and risk factorsbull The objective is to remove all clinically detectable
calculus without excessive root planingndash bacterial endotoxins are weakly adherent to the root
surface (Nakib 1982)
bull The term debridement vs root planing
ImplementationTreatment
bull Treat patientrsquos significant otherbull 40 of the time spouses have the
same microbiotabull Donrsquot kiss dogs amp cats- they may have
periobull Avoid gross scaling
bull risk of abscessbull educationbull more difficult to re-insert
instruments
16
Air Polishing with glycine
ndashGlycine has anti inflammatory ampimmune modulation effectsbull Glycine receptor gingival tissue
ndashPerpulsionndashFDA approval for lt5 mmndashRemoval biofilm amp stainndashPerio maintenance ndashImplantsndashDecontaminate prior to grafts
Host-Modulating Treatmentbull Treating periodontitis by trying to resolve
inflammation
bull Resolvins
ndash Omega 3 Fatty acids correlated with less bone loss
ndash may be due to their ability to generate mediators that fight inflammation and aid in inflammation resolution
bull Low-dose doxycycline 20 mg 2x daily
ndash Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor is the only FDA-approved
ndash Reduction of PD amp CAL gain over 3 months to 9 monthsGolub LM et al Doxycycline i hibits neutrophil (PMN)-type matrix metalloproteinases in human adult periodontitis gingiva J Clin Periodontol 199522100ndash109 amp
Golub LM et al Adjunctive treatment with subantimicrobial doses of doxycycline effects on gingival fluid collagenase activity and attachment loss in adult periodontitis J Clin Periodontol 200128146ndash156
Host-Modulating Treatment
bull NSAIDsndash Reduces PGE 2 which can reduce bone loss
ndash Flurbiprofen and topical (ketorolac)
ndash Case controls demonstrate decrease risk
bull Bisphosphonates ndash Used for treating Pagetrsquos bone pain amp osteoporosis
ndash Alendronate sodium (Fosamax) risedronate (Actonel)
ndash Investigating for its ability to modulate the host
bull Used experimentally in animals to inhibit bone resorption amp bone mineral content amp to interfere w breakdown of collagen in the periodontium
ndash WARNING case reports of bone necrosis after extractions
bull questions scrtpl w pts on drug
Treatment
bull Statins have an anti-inflammatory and immune effects reducing levels of C-Reactive Protein MMP Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
ndash Statins reduce bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclast formation
ndash Some results show lower alveolar bone loss and reduction of clinical signs of inflammation
(meta anyalsis Estanislau etal J Clin Pharmacol 2014 Dec)
ndash Topical gels (simvastatin atorvastatin)
Treatment
bull Probioticsndash Improved biofilm index and probe depths (Shimauchi 2008)
bull Valtrexbull Photodynamic therapy
ndash Light-sensitive drug is applied then a light laser directly on the area treated with the drug
ndash When the light is combined with the drug phototoxic reactions are induced which destroy bacterial cells
ndash Shows short term benefits (Sgolastra 2012)bull Periowave
bull Emdogainndash Enamel matrix derivative for periodontal tissue regeneration in
infrabony defects amp used w SRP to enhance resultsbull Derived from developing pig teethbull Stimulate adherence attachment to cementum
Treatmentbull Topical antioxidants
ndash Antioxidant gel and rinse
ndash Periosciences ndash toothpaste rinse gel
ndash Topical coenzyme COQ10
bull Due to correlation w perio oxidative stress markers amp low level of natural occurring salivary antioxidants looking at polyphenolsantioxidants in the mouth locally delivered
ndash needs more research
bull Hyaluronic acid (HA) gel and mouth rinsendash hyaluronic acid plays a large role in the collagen building 02
hyaluronan gel topically amp subgingivally
ndash Studies have been done to evaluate on wound healing amp improving perio outcomes
ndash Further evidence is needed
17
LasersNeodymium lasersbull Ex NdYAG NdYAP lasers
bull FDA approved-PerioLase (FRNdYAG) patented procedure LANAPshown to regenerate cementum bone amp PDL
bull No histological studies LANAP with regeneration ( Linden E Laser Basics Dimensions of dental hygiene april 2016)
Diode Lasersbull Most commonly used by RDHs
bull Wide range of wavelengths
bull Used to reduce bacteria amp remove inflammatory byproducts
bull Absorbed by pigmented structures hemoglobin amp melanin
bull Warming amp ablation
bull There is insufficient evidence
Evaluation
bull Evaluating the host response
1 week acute or painful conditions
4-6 weeks changes in attachment level
12 weeks microbiota returns to pre TX levels
bull Complete final diagnosis
bull Many lawsuits exist due to lack of follow-up where as before it was due to failure to diagnose
Evaluation
bull Responded well
ndashDetermine appropriate PMP interval
bull Unresponsive
ndashProblem solve
bull Try to determine whyndashVirulent microorganisms Inadequate host
response Ineffective initial therapy or contributory amp risk factors
ndashFormulate new plan
Possible Solutions
bull Improve initial therapyndash re-scale root plan re-root plan
ndash self care
ndash adjunctive chemotherapeutics necessary
bull Reduce risk amp contributory factors
ndash smoking restorative
bull ex Overhangs
bull Medical consult periodontal referral Advanced diagnostic
Advanced Diagnostics
bull A test to determine active disease or predict an active episode of disease
bull currently we are not able to do this well
bull Many new tests are being developed still under investigation and still being assessed for usefulness
bull Many are not available yet or very expensive
bull Provide information that adds to the clinical exam
bull If it would be nice to know but not change anything we need to ask the questionhellip
bull Is the benefit worth the cost
Testing
OralDNA Labs Inc- httpwwworaldnacom
bull Genetic risk bacterial profile HPV-related oral cancers Herpes Candida Chlamydia trachomatis(CT) Neisseria gonorrhea(NG) gene markers related to inflammatory response DNA DrugMaptrade
micro-Ident- DNA probes
bull httpswwwhain-lifesciencecom
Oravital-Toronto based company uses biofilm testing the use of prescribed antibiotic antimicrobial rinses httpswwworavitalcom
Temple Oral Microbiology testing service 800-788-6687
USC Oral microbiology testing Lab 213-740-3163
UNC Oral microbiology Lab oralmicrodentistryuncedu

15
Predicting Activity
bull Nutrient canals
ndash Highly visible canals may indicate active or rapid destruction
ndash canals are thought to be engorged large blood vessels
Crestal Bone
Rough looking crestal boneSmoother more demarcated crestal bone
Planningbull Systematic Informed consent
bull Diagnosis prognosis options risks benefits
ndashPatients must have all the information
bull Studies indicate slight reductions in PD s gt 6 mm after full-mouth scaling and root planingperformed in one appointment vs over longer intervals
bull These protocols particularly effective in patients with aggressive periodontitis andor pts w systemic conditions
Eberhard J et al J Clin Periodontol 200835591ndash604 amp Fang et al J Periodont Res October 19 2015)
ImplementationTreatment
bull Goals are to eliminate infection and risk factorsbull The objective is to remove all clinically detectable
calculus without excessive root planingndash bacterial endotoxins are weakly adherent to the root
surface (Nakib 1982)
bull The term debridement vs root planing
ImplementationTreatment
bull Treat patientrsquos significant otherbull 40 of the time spouses have the
same microbiotabull Donrsquot kiss dogs amp cats- they may have
periobull Avoid gross scaling
bull risk of abscessbull educationbull more difficult to re-insert
instruments
16
Air Polishing with glycine
ndashGlycine has anti inflammatory ampimmune modulation effectsbull Glycine receptor gingival tissue
ndashPerpulsionndashFDA approval for lt5 mmndashRemoval biofilm amp stainndashPerio maintenance ndashImplantsndashDecontaminate prior to grafts
Host-Modulating Treatmentbull Treating periodontitis by trying to resolve
inflammation
bull Resolvins
ndash Omega 3 Fatty acids correlated with less bone loss
ndash may be due to their ability to generate mediators that fight inflammation and aid in inflammation resolution
bull Low-dose doxycycline 20 mg 2x daily
ndash Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor is the only FDA-approved
ndash Reduction of PD amp CAL gain over 3 months to 9 monthsGolub LM et al Doxycycline i hibits neutrophil (PMN)-type matrix metalloproteinases in human adult periodontitis gingiva J Clin Periodontol 199522100ndash109 amp
Golub LM et al Adjunctive treatment with subantimicrobial doses of doxycycline effects on gingival fluid collagenase activity and attachment loss in adult periodontitis J Clin Periodontol 200128146ndash156
Host-Modulating Treatment
bull NSAIDsndash Reduces PGE 2 which can reduce bone loss
ndash Flurbiprofen and topical (ketorolac)
ndash Case controls demonstrate decrease risk
bull Bisphosphonates ndash Used for treating Pagetrsquos bone pain amp osteoporosis
ndash Alendronate sodium (Fosamax) risedronate (Actonel)
ndash Investigating for its ability to modulate the host
bull Used experimentally in animals to inhibit bone resorption amp bone mineral content amp to interfere w breakdown of collagen in the periodontium
ndash WARNING case reports of bone necrosis after extractions
bull questions scrtpl w pts on drug
Treatment
bull Statins have an anti-inflammatory and immune effects reducing levels of C-Reactive Protein MMP Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
ndash Statins reduce bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclast formation
ndash Some results show lower alveolar bone loss and reduction of clinical signs of inflammation
(meta anyalsis Estanislau etal J Clin Pharmacol 2014 Dec)
ndash Topical gels (simvastatin atorvastatin)
Treatment
bull Probioticsndash Improved biofilm index and probe depths (Shimauchi 2008)
bull Valtrexbull Photodynamic therapy
ndash Light-sensitive drug is applied then a light laser directly on the area treated with the drug
ndash When the light is combined with the drug phototoxic reactions are induced which destroy bacterial cells
ndash Shows short term benefits (Sgolastra 2012)bull Periowave
bull Emdogainndash Enamel matrix derivative for periodontal tissue regeneration in
infrabony defects amp used w SRP to enhance resultsbull Derived from developing pig teethbull Stimulate adherence attachment to cementum
Treatmentbull Topical antioxidants
ndash Antioxidant gel and rinse
ndash Periosciences ndash toothpaste rinse gel
ndash Topical coenzyme COQ10
bull Due to correlation w perio oxidative stress markers amp low level of natural occurring salivary antioxidants looking at polyphenolsantioxidants in the mouth locally delivered
ndash needs more research
bull Hyaluronic acid (HA) gel and mouth rinsendash hyaluronic acid plays a large role in the collagen building 02
hyaluronan gel topically amp subgingivally
ndash Studies have been done to evaluate on wound healing amp improving perio outcomes
ndash Further evidence is needed
17
LasersNeodymium lasersbull Ex NdYAG NdYAP lasers
bull FDA approved-PerioLase (FRNdYAG) patented procedure LANAPshown to regenerate cementum bone amp PDL
bull No histological studies LANAP with regeneration ( Linden E Laser Basics Dimensions of dental hygiene april 2016)
Diode Lasersbull Most commonly used by RDHs
bull Wide range of wavelengths
bull Used to reduce bacteria amp remove inflammatory byproducts
bull Absorbed by pigmented structures hemoglobin amp melanin
bull Warming amp ablation
bull There is insufficient evidence
Evaluation
bull Evaluating the host response
1 week acute or painful conditions
4-6 weeks changes in attachment level
12 weeks microbiota returns to pre TX levels
bull Complete final diagnosis
bull Many lawsuits exist due to lack of follow-up where as before it was due to failure to diagnose
Evaluation
bull Responded well
ndashDetermine appropriate PMP interval
bull Unresponsive
ndashProblem solve
bull Try to determine whyndashVirulent microorganisms Inadequate host
response Ineffective initial therapy or contributory amp risk factors
ndashFormulate new plan
Possible Solutions
bull Improve initial therapyndash re-scale root plan re-root plan
ndash self care
ndash adjunctive chemotherapeutics necessary
bull Reduce risk amp contributory factors
ndash smoking restorative
bull ex Overhangs
bull Medical consult periodontal referral Advanced diagnostic
Advanced Diagnostics
bull A test to determine active disease or predict an active episode of disease
bull currently we are not able to do this well
bull Many new tests are being developed still under investigation and still being assessed for usefulness
bull Many are not available yet or very expensive
bull Provide information that adds to the clinical exam
bull If it would be nice to know but not change anything we need to ask the questionhellip
bull Is the benefit worth the cost
Testing
OralDNA Labs Inc- httpwwworaldnacom
bull Genetic risk bacterial profile HPV-related oral cancers Herpes Candida Chlamydia trachomatis(CT) Neisseria gonorrhea(NG) gene markers related to inflammatory response DNA DrugMaptrade
micro-Ident- DNA probes
bull httpswwwhain-lifesciencecom
Oravital-Toronto based company uses biofilm testing the use of prescribed antibiotic antimicrobial rinses httpswwworavitalcom
Temple Oral Microbiology testing service 800-788-6687
USC Oral microbiology testing Lab 213-740-3163
UNC Oral microbiology Lab oralmicrodentistryuncedu

16
Air Polishing with glycine
ndashGlycine has anti inflammatory ampimmune modulation effectsbull Glycine receptor gingival tissue
ndashPerpulsionndashFDA approval for lt5 mmndashRemoval biofilm amp stainndashPerio maintenance ndashImplantsndashDecontaminate prior to grafts
Host-Modulating Treatmentbull Treating periodontitis by trying to resolve
inflammation
bull Resolvins
ndash Omega 3 Fatty acids correlated with less bone loss
ndash may be due to their ability to generate mediators that fight inflammation and aid in inflammation resolution
bull Low-dose doxycycline 20 mg 2x daily
ndash Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor is the only FDA-approved
ndash Reduction of PD amp CAL gain over 3 months to 9 monthsGolub LM et al Doxycycline i hibits neutrophil (PMN)-type matrix metalloproteinases in human adult periodontitis gingiva J Clin Periodontol 199522100ndash109 amp
Golub LM et al Adjunctive treatment with subantimicrobial doses of doxycycline effects on gingival fluid collagenase activity and attachment loss in adult periodontitis J Clin Periodontol 200128146ndash156
Host-Modulating Treatment
bull NSAIDsndash Reduces PGE 2 which can reduce bone loss
ndash Flurbiprofen and topical (ketorolac)
ndash Case controls demonstrate decrease risk
bull Bisphosphonates ndash Used for treating Pagetrsquos bone pain amp osteoporosis
ndash Alendronate sodium (Fosamax) risedronate (Actonel)
ndash Investigating for its ability to modulate the host
bull Used experimentally in animals to inhibit bone resorption amp bone mineral content amp to interfere w breakdown of collagen in the periodontium
ndash WARNING case reports of bone necrosis after extractions
bull questions scrtpl w pts on drug
Treatment
bull Statins have an anti-inflammatory and immune effects reducing levels of C-Reactive Protein MMP Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
ndash Statins reduce bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclast formation
ndash Some results show lower alveolar bone loss and reduction of clinical signs of inflammation
(meta anyalsis Estanislau etal J Clin Pharmacol 2014 Dec)
ndash Topical gels (simvastatin atorvastatin)
Treatment
bull Probioticsndash Improved biofilm index and probe depths (Shimauchi 2008)
bull Valtrexbull Photodynamic therapy
ndash Light-sensitive drug is applied then a light laser directly on the area treated with the drug
ndash When the light is combined with the drug phototoxic reactions are induced which destroy bacterial cells
ndash Shows short term benefits (Sgolastra 2012)bull Periowave
bull Emdogainndash Enamel matrix derivative for periodontal tissue regeneration in
infrabony defects amp used w SRP to enhance resultsbull Derived from developing pig teethbull Stimulate adherence attachment to cementum
Treatmentbull Topical antioxidants
ndash Antioxidant gel and rinse
ndash Periosciences ndash toothpaste rinse gel
ndash Topical coenzyme COQ10
bull Due to correlation w perio oxidative stress markers amp low level of natural occurring salivary antioxidants looking at polyphenolsantioxidants in the mouth locally delivered
ndash needs more research
bull Hyaluronic acid (HA) gel and mouth rinsendash hyaluronic acid plays a large role in the collagen building 02
hyaluronan gel topically amp subgingivally
ndash Studies have been done to evaluate on wound healing amp improving perio outcomes
ndash Further evidence is needed
17
LasersNeodymium lasersbull Ex NdYAG NdYAP lasers
bull FDA approved-PerioLase (FRNdYAG) patented procedure LANAPshown to regenerate cementum bone amp PDL
bull No histological studies LANAP with regeneration ( Linden E Laser Basics Dimensions of dental hygiene april 2016)
Diode Lasersbull Most commonly used by RDHs
bull Wide range of wavelengths
bull Used to reduce bacteria amp remove inflammatory byproducts
bull Absorbed by pigmented structures hemoglobin amp melanin
bull Warming amp ablation
bull There is insufficient evidence
Evaluation
bull Evaluating the host response
1 week acute or painful conditions
4-6 weeks changes in attachment level
12 weeks microbiota returns to pre TX levels
bull Complete final diagnosis
bull Many lawsuits exist due to lack of follow-up where as before it was due to failure to diagnose
Evaluation
bull Responded well
ndashDetermine appropriate PMP interval
bull Unresponsive
ndashProblem solve
bull Try to determine whyndashVirulent microorganisms Inadequate host
response Ineffective initial therapy or contributory amp risk factors
ndashFormulate new plan
Possible Solutions
bull Improve initial therapyndash re-scale root plan re-root plan
ndash self care
ndash adjunctive chemotherapeutics necessary
bull Reduce risk amp contributory factors
ndash smoking restorative
bull ex Overhangs
bull Medical consult periodontal referral Advanced diagnostic
Advanced Diagnostics
bull A test to determine active disease or predict an active episode of disease
bull currently we are not able to do this well
bull Many new tests are being developed still under investigation and still being assessed for usefulness
bull Many are not available yet or very expensive
bull Provide information that adds to the clinical exam
bull If it would be nice to know but not change anything we need to ask the questionhellip
bull Is the benefit worth the cost
Testing
OralDNA Labs Inc- httpwwworaldnacom
bull Genetic risk bacterial profile HPV-related oral cancers Herpes Candida Chlamydia trachomatis(CT) Neisseria gonorrhea(NG) gene markers related to inflammatory response DNA DrugMaptrade
micro-Ident- DNA probes
bull httpswwwhain-lifesciencecom
Oravital-Toronto based company uses biofilm testing the use of prescribed antibiotic antimicrobial rinses httpswwworavitalcom
Temple Oral Microbiology testing service 800-788-6687
USC Oral microbiology testing Lab 213-740-3163
UNC Oral microbiology Lab oralmicrodentistryuncedu

17
LasersNeodymium lasersbull Ex NdYAG NdYAP lasers
bull FDA approved-PerioLase (FRNdYAG) patented procedure LANAPshown to regenerate cementum bone amp PDL
bull No histological studies LANAP with regeneration ( Linden E Laser Basics Dimensions of dental hygiene april 2016)
Diode Lasersbull Most commonly used by RDHs
bull Wide range of wavelengths
bull Used to reduce bacteria amp remove inflammatory byproducts
bull Absorbed by pigmented structures hemoglobin amp melanin
bull Warming amp ablation
bull There is insufficient evidence
Evaluation
bull Evaluating the host response
1 week acute or painful conditions
4-6 weeks changes in attachment level
12 weeks microbiota returns to pre TX levels
bull Complete final diagnosis
bull Many lawsuits exist due to lack of follow-up where as before it was due to failure to diagnose
Evaluation
bull Responded well
ndashDetermine appropriate PMP interval
bull Unresponsive
ndashProblem solve
bull Try to determine whyndashVirulent microorganisms Inadequate host
response Ineffective initial therapy or contributory amp risk factors
ndashFormulate new plan
Possible Solutions
bull Improve initial therapyndash re-scale root plan re-root plan
ndash self care
ndash adjunctive chemotherapeutics necessary
bull Reduce risk amp contributory factors
ndash smoking restorative
bull ex Overhangs
bull Medical consult periodontal referral Advanced diagnostic
Advanced Diagnostics
bull A test to determine active disease or predict an active episode of disease
bull currently we are not able to do this well
bull Many new tests are being developed still under investigation and still being assessed for usefulness
bull Many are not available yet or very expensive
bull Provide information that adds to the clinical exam
bull If it would be nice to know but not change anything we need to ask the questionhellip
bull Is the benefit worth the cost
Testing
OralDNA Labs Inc- httpwwworaldnacom
bull Genetic risk bacterial profile HPV-related oral cancers Herpes Candida Chlamydia trachomatis(CT) Neisseria gonorrhea(NG) gene markers related to inflammatory response DNA DrugMaptrade
micro-Ident- DNA probes
bull httpswwwhain-lifesciencecom
Oravital-Toronto based company uses biofilm testing the use of prescribed antibiotic antimicrobial rinses httpswwworavitalcom
Temple Oral Microbiology testing service 800-788-6687
USC Oral microbiology testing Lab 213-740-3163
UNC Oral microbiology Lab oralmicrodentistryuncedu