Important Organic Compounds...Biological Molecules The most important biological compounds are...
Transcript of Important Organic Compounds...Biological Molecules The most important biological compounds are...

Important Organic Compounds
Biological Molecules

The most important biological compounds are polymerspolymers
Polymers (poly = manymany)
The polymers are: proteins, carbohydrates, lipidsproteins, carbohydrates, lipids (fats), and nucleic acidsnucleic acids (DNA/RNA).
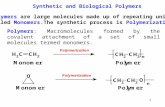
A polymer is made up of a chain of many monomersmonomers linked together

moNomers (mono = one)
Monomers are: amino acids, sugars, fatty acids, amino acids, sugars, fatty acids, and nucleotides.nucleotides.
These are made or broken down over and over in living cells.

Large polymers are also called ______________________________ macromoleculesmacromolecules

MONOMER (building block)
POLYMER (Biological organic
molecule)
Monosaccharide (glucose)
Carbohydrate
Glycerol and fatty acid Lipid (fat)
Amino acid Protein
Nucleotide Nucleic acid

• MONOMER
H - � - OH
• POLYMER
H - � - � - � - � - � - OH

Process to build polymers
• Dehydration synthesis Dehydration synthesis = covalently bonding monomers together by removing waterremoving water
• Called condensation synthesis in text

____________ are joined together during dehydration synthesis.
Chains of monomers are called _________
MONOMERS MONOMERS
POLYMERSPOLYMERS

Dehydration Synthesis of carbohydrates

To break apart polymers
• HydrolysisHydrolysis: Add H: Add H22OO
H - � - � - � - � - OH + 3H20
4 H - � - OH
• 1 H2O will be consumed for every 1 covalent bond to be broken

PolymersPolymersa) Carbohydratesb) Proteinsc) Lipids (fats)d) DNA/RNA (nucleic acids)
MonomersMonomersa) Simple sugarsb) Amino Acidsc) Fatty Acids & Glycerold) Nucleotides
H2O & Energy
HydrolysisDehydration
Synthesis
H2O & Energy
These reactions require:
1. ATP energy
2. Water
3. Enzymes

Organic molecules:1. Carbohydrates
2. Lipids
3. Proteins
1. Nucleic Acids
**always contains C & H & covalent bonds
• C may share electrons with other C

1. Carbohydrates

Where does the name come from?Where does the name come from?Hydrated Carbons: (CH(CH220)n0)n
Carbohydrates have the empirical formula of (CH(CH220)n0)n where n = the # of times the chain is repeated.
The carbons, hydrogens and oxygens are found in the ratio
of 1:2:11:2:1 and are made up of a repeating chain of sugars.
Sugars are also known as saccaridessaccarides.Carbohydrates usually end in ‘oseose’. Can you think of any examples?
(CH20)3 = (CH20)6 =CC33HH660033 CC66HH12120066

The basic sugar molecule is GLUCOSEGLUCOSE: CC66 H H12 12 OO66..
Glucose has a ringring structure.
Other monosaccharides include fructose, ribose, deoxyribosefructose, ribose, deoxyribose

Three ways to represent the structure of glucose.
Actual (molecular) formula for glucose

FructoseFructose GalactoseGalactose
GlucoseGlucose

When two sugars bind together via DEHYDRATION DEHYDRATION SYNTHESISSYNTHESIS

Examples:– glucose + glucose = maltose + water– glucose + galactose = lactose (milk sugar) + water– glucose + fructose = sucrose (table sugar) + water
C12H22011


Complex Carbohydrates = Polysaccharides– Polymer of identical monosaccharides (typically
glucose)
i.i. Starch Starch
ii.ii. Glycogen Glycogen
i.i. Cellulose Cellulose

i) Starchi) Starch• Storage form of glucose in plants (long glucose chains)• Few or no side chains
•

ii) Glycogenii) Glycogen• Animals store their energy (extra glucose)
as glycogen in the liver and muscles• Long chains of glucose with many side
chains

iii) Celluloseiii) Cellulose• Cell walls of plants are made of cellulose • Long chains of glucose with no side chains and
have alternating position of linking oxygen atoms
• No mammals can break this bond (indigestible) and serves as fibre

Complete carbohydrate review
Source Monomer Polymer Characteristic
Animal
Plant
.

CH2O (cont`d)
• Functions: Functions: • Energy for cells
• Energy storage (starch, glycogen)
• Cell recognition role = glycoprotein or glycolipid
• Basis for A, B, and O blood groups


2. Lipids

2. Lipids• Characteristics:
– made up of C, H, O C, H, O (sometimes P or N)– large, insoluble large, insoluble in water
• Ex. Water in oil
– 2 monomers:1.1. GlycerolGlycerol
2.2. Fatty acids Fatty acids (long hydrocarbon chains)

Lipid Building Blocks

Synthesis and degradation of a fat molecule

3 types of LipidsA. TriglyceridesA. Triglycerides
• aka neutral fats (nonpolar) or “fats and oils”• 2 Types:
a) Fats = animal basedanimal based & solid (e.g. butter, lard)• 3 Functions:
1. Long term energy source
2. Cushions organs
3. Insulation
b)Oil = plant basedplant based & liquid (e.g. olive, corn, etc)• Main energy source for plants

Triglycerides (cont’d)Structure:
– “E” shaped molecule made of one glycerol and 3 fatty acids (synthesized by dehydration of 3 H2O molecules)

Triglycerides (cont’d)
Structure (cont’d):• Fatty acids are hydrocarbon chains with
COOH end– 3 main types of fatty acid
1. Saturated – no C =C which means it is “full” of H, fairly straight, solid at room temp., “fat” (from animals)
2. Unsaturated – at least one C=C bond, structurally bent, liquid at room temp., “oil” (from plants)

Fatty Acids

Unsaturated Triglyceride

Triglycerides (cont’d)
Structure (cont’d):• Fatty acids are hydrocarbon chains with
COOH end (usually 16-18 carbons)– 3 main types of fatty acid
1. Saturated – no C=C which means it is “full” of H, fairly straight, solid @ room temp., “fat”
2. Unsaturated – at least one C=C bond, structurally bent, liquid at room temp., “oil”
3. Polyunsaturated – many C=C bonds so few H’s (e.g veggie oils)

Triglycerides
Important - hydrogenation adds H’s (margarine or shortening) but forms trans fats

B. PhospholipidsB. Phospholipids
• Comprised of 1 gylcerolgylcerol, 1 phosphatephosphate groupgroup & 2 fatty acids fatty acids • think of a triglyceride
except one fatty acid has been replace by a phosphate group)
• Primary components of cellular membranescellular membranes

• Phosphate group• Glycerol
Hydrophilic (polar) head
Hydrophobic (nonpolar) tail
2 Fatty Acids

Phospholipid bilayer

Phospholipid bilayer
• when placed in H2O, phospholipids form 2 layers – the polar heads
(hydrophilic) face out and the non-polar tails (hydrophobic) face in
The Cell Membrane

C. STEROIDS (lipids)Structure:Structure:•4 fused rings 4 fused rings of carbon with “stuff” attached (called functional groups)•E.g. Testosterone, estrogen, cholesterol and vitamin D


STEROIDS (lipids)
Structure (cont`d):•Non-polar so can easily pass through cell membranes•Are water insoluble (it is a lipid)

STEROIDS (lipids)Function:Function:•used as sex hormone (e.g. estrogen & testosterone)

Emulsification•Needed to mix fats/oils into water•e.g. soap and bile (produced by gallbladder)

Review of Carbs & Lipids Quiz
1. Review sheet #s 1-7
2. Inquiry Into Life (12th ed.) online quiz