Important MACROMOLECULES (“Large Molecules”) Used in Biological Systems:
description
Transcript of Important MACROMOLECULES (“Large Molecules”) Used in Biological Systems:

Important
MACROMOLECULES(“Large Molecules”)
Used in Biological Systems:
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids

What Are They???
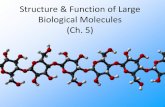
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids are the 4 major classes of organic compounds in cells.
Because these are very large molecules and very important in Biological Systems, we refer to these 4 classes of organic compounds as the MACROmolecules of Life.

Important Terminology
Compound: Two or more DIFFERENT molecules combined.
Example: Water molecules bound together with hydrogen bonds are NOT compoundsExample: Sucrose (table sugar) is a compound. (More than one type of molecule present.
Mixture: Two or more DIFFERENT compounds combined.
Organic: Any molecule that contains a carbon atom.
**All of the macromolecules discussed in this presentation are organic**

Monomer: Simplest single-carbon component of a compound or macromolecule.
Dimer:Two monomers combined.
Polymer:Many monomers combined to form a large “macro” molecule
Important Terminology (cont.)

Composition of MacromoleculesElements Involved:
CarbonHydrogenOxygenNitrogenPhosphorous
Formulas:Carbohydrates = CH2OLipids = CHOProteins = CHONNucleic Acids = CHONP
ALL OF THESE MACROMOLECULES ARE ORGANIC

Monomers Involved:1. Carbohydrates: monosaccharides
2. Lipids: glycerol and fatty acids
3. Proteins: Amino AcidsThere are 20 Amino Acids used to make proteins in mammals.
4. Nucleic Acids: NucleotidesNucleotides consist of a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group and a ribose sugar. There are 5 known nucleotides.
Composition of Macromolecules(continued)

CARBOHYDRATES (CH2O)
Monomers of carbohydrates: Monosaccharides
Carbon Water (C6H12O6 ==> CH2O)
Carbohydrates are Sugars!Saccharide = greek word for sugar
Where saccharin (artificial sweetener) got its name
Carbohydrates Carbohydrates usuallyusually end with the end with the ––ose suffixose suffix

One saccharide moleculeaka Simple sugarsmonomers that comprise carbohydrates
Examples: Glucose – used in Cellular RespirationFructose – fruit sugar Galactose – part of Milk sugarRibose – part of DNA and RNA molecules
Classification (Forms) of Carbs
Monosaccharide

Disaccharide Two monosaccharides combined
Examples: » Sucrose = Glucose + Fructose (table sugar)
» Maltose = Glucose + Glucose
(malted milk balls, ice cream malts)
» Lactose = Glucose + Galactose (milk sugar; lactation)
Classification (Forms) of Carbs (cont.)

Polysaccharide Many monosaccharides combined
Very large molecules
Complex Carbohydrates
Examples:»Glycogen – NRG storage in mammals»Starch – NRG stored in plants; Pasta»Cellulose – Paper; humans can’t digest
Long chains of glucose
Classification (Forms) of Carbs (cont.)

Uses of carbohydrates
Used as a primary source of NRG in humans.Strength and Rigidity in plantsSweetenerPaperThickenersExample of Medical use:
Heparin (polysaccharide) » (Hep-lock)
• Used to prevent excessive blood clotting when administering IV fluids in hospitals

LIPIDS (CHO)Monomers of Lipids:
Fatty Acids and glycerol
Lipids are Fats!
Basic Elements:CHO
Some Lipids are called “saturated” and some are called “Unsaturated.”
Saturated: All 4 of Carbon’s possible binding sites are bound by atoms. These are solids at room temperature. (Examples: Vaseline, Wax, Shortening)
Unsaturated: Not all of Carbon’s possible binding sites are bound by other atoms. Carbon will then form double bonds with other Carbon atoms. These are liquids at room temperature (Examples: Cooking Oil, gasoline)

Forms of LipidsTriglyceride = glycerol + fatty acid chains
Lipids are stored in humans as triglyceridesFatty acids have two regions
» Hydrocarbon chain» Carboxyl group (COOH)
SteroidsCholesterolBile saltsMale and female sex hormones
– Estrogen and Progesterone– Testosterone
Wax Phosopholipid – Part of Cell membrane
ProstaglandinsRaise and lower blood pressureContract smooth muscle (blood vessels, intestines)

Uses of Lipids
Used as a Secondary source of energy in humansConstruction of Cell MembranesHelps to maintain Homeostasis (prostaglandins)Protective Coatings
Waterproofing agents; Car Wax
CookingPetroleum Products
Gasoline; Paint Thinner; Vaseline
Candles

PROTEINS (CHON)Monomers of proteins: Amino Acids
Basic Elemental Components: CHON
20 Amino Acids found in MammalsExample of amino acids:
GlycineLeucine
Amino acids Amino acids usuallyusually end in –INE end in –INE

PROTEINS & AMINO ACIDS• Single carbon amino acids = Peptides
– Peptides are bound together to make DIPEPTIDES (2 peptides) or POLYPEPTIDES, (more than 2).
• The covalent bond between 2 peptides is called a Peptide BOND.
• Proteins are chains of amino acids AND
Polypeptides are chains of amino acids!•PROTEINS = POLYPEPTIDES!!!
Leu
Phe
Trp
Met
Lys

More on ProteinsProteins are Temperature dependent!
High temperatures will “Denature” proteins, which means they will break down, lose their shape, and cease to function
Low Temperatures cause proteins such as enzymes to function less efficiently. The Optimal temperature for Protein function is body temperature.
Body temperature is 98.6F or ~32CExample:
Fevers are dangerous because proteins such as enzymes will stop functioning if temperature goes to high
Fresh vs. Canned Pineapple in Gelatin» Enzyme (Bromelain) found in fresh pineapple breaks down
protein» Gelatin is a Protein.» Mix fresh pineapple in Gelatin: Gelatin won’t set» Use canned pineapple: Gelatin will set. Why?
• Pineapple is heated during process of canning, which denatures bromelain

Forms of Proteins
Enzymes = ProteinsAct as catalysts for bodily reactions, which help reactions occur easier, faster, and with less energy.
Plant Proteins: Gluten Example: Whey and Soy Protein
Enzyme and Substrate
Muscle tissue:Proteins are stored in the body as muscle tissueLast energy reserve but can be used as an NRG source if
neither Carbohydrates nor Lipids are available.

Uses and Examples of Proteins
Tertiary Energy Source in HumansFacilitate Reactions (Enzymes)Aid in Digestion (Enzymes)Coded for by DNA and RNAExamples (Forms):
Insulin» Some diabetics don’t produce this
Lactase» People who are Lactose Intolerant don’t produce this
Amylase» Found in saliva; breaks starch into individual glucose» Makes potatoes sweet if you keep them in your mouth long
enough

NUCLEIC ACIDS (CHONP)Monomers of Nucleic Acids: NucleotidesElements: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorous
Five nucleotides; Four in each of the nucleic acids DNA and RNA
CytosineThymineAdenineGuanineUracil(replaces thymine in RNA)
FORMS: DNA and RNAWhat does DNA and RNA stand for?
DNA= Deoxyribonucleic AcidRNA= Ribonucleic Acid
FUNCTION: Stores Genetic information that codes for all the proteins in your body.
Used as a template or blue-prints to build proteins.