Hoye cold war
Transcript of Hoye cold war

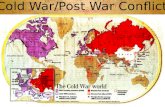
The Cold WarMs. Hoye
U.S. History AP/Reg

The BeginningSuperpowers – US & Soviet UnionDifferences led to Cold WarWeapons used
–Threat of force–Propaganda–Military and economic aid for weaker
nations

Types of Governments
Democracy
Government by the people; citizens hold the power
Communism
Totalitarian system of government in which a single party controls state-owned means of production; a society without class distinctions or private property

EconomicsA study of choices of people trying to
satisfy their wants in a world of scarcity.
The way in which a society decides what goods to produce, how to produce them, and for whom goods will be produced.
Economic System

2 Types of Economic Systems
Free Enterprise
Individuals own most of the resources used and control their use; government plays very small role in the economy.
Socialism
Government owns and controls most of the resources; government plays major role in the economy.

ORIGINS OF THE COLD WAR WWII Alliance of Britain and U.S. with
Soviet Union was pragmatic “marriage of convenience” to defeat Germany
1. Lack of trust of Stalin.• unified wartime command• atomic bomb
2. Soviets believed western allies not sharing load
3. Soviet mistreatment of eastern Europeans during WWII

ORIGINS OF THE COLD WAR: Wartime Diplomacy
“Big Three” Allied leaders were consistently unable to resolve their basic disagreements over the structure of post-war Europe
Tehran Conference (November 1943)
– U.S. and Britain would open a second front within six months– Allies would create a post-war international organization
Stalin, Roosevelt & Churchill at Tehran, 1943

ORIGINS OF THE COLD WAR : Wartime Diplomacy
Yalta Conference (January-February 1945) – Loose set of principles that avoided the most divisive issues. – Division of Germany (and Berlin) into four “zones of occupation”; Reunification of Germany at a future date; process not specified – Soviets would enter Pacific war within 3 months after Germany had been defeated– United Nations – Poland – free elections at some unspecified date after the war
Churchill, Roosevelt and Stalin at Yalta, February 1945
“the holding of free and unfettered elections as soon as possible on the basis of universal suffrage and secret ballot"

ORIGINS OF THE COLD WAR : Wartime Diplomacy
San Francisco Conference - United Nations Formed (April 1945) – Security Council
• 11 members • Permanent seats with veto power for U.S., Britain,
France, China and USSR
– General Assembly – Secretariat
• Secretary-General – International Court of Justice

ORIGINS OF THE COLD WAR : Wartime Diplomacy
Potsdam Conference (July-Aug. 1945)
– Reparations: Stalin allowed to take 25% of West German industry
– Nazi leaders: to be tried as war criminals at Nuremberg
– Poland: Free elections– Japan: Unconditional
surrender– Korea: to be temporarily
divided Churchill, Truman and Stalin at Potsdam

ORIGINS OF THE COLD WAR: Causes of Cold War
Soviets the main cause (Original U.S. view)– Aggressive policies of expansion (in eastern Europe) and
violation of Yalta agreements
U.S. the main cause (Revisionist interpretation)– By insisting that entire world be open to American trade and
influence (capitalist expansionism & internationalism)
Neither/Both the cause (post-revisionist interpretation) – Two most powerful nations in world bound to clash– Through ignorance and misconceptions, both countries helped
to create an atmosphere of tension and suspicion that touched off the Cold War
Could the Cold War have been avoided? How?

Iron CurtainSpeech
Churchill used phrase March 1946 Represents the Soviet-made barrier
splitting Europe into non-Communist Western Europe and Communist Eastern Europe
Became symbol of the Cold War

Marshall Plan
Massive aid package to Europe Billions of dollars spent to speed recovery
measures Stalin thought it was trick Western European economies thrived Helped stop spread of communism

Marshall Plan On June 5, U.S.
Secretary of State George Marshall – proposes a massive aid
program to rebuild Europe from the ravages of World War II.
Nearly $13 billion in U.S. aid was sent to Europe from 1948 to 1952. – The Soviet Union and
communist Eastern Europe decline U.S. aid, citing "dollar enslavement."

Truman Doctrine
March 12, 1947 Greece and Turkey
in danger of falling to communist insurgents
Truman requested $400 million from Congress in aid to both countries.
Successful effort

Truman Doctrine
Made clear intentions to resist Soviet expansion in Europe and elsewhere
Took on international responsibilities as leader of Western world
Aid to Greece and Turkey Stalin saw containment policy as
“encirclement” by capitalist world to isolate Soviet Union

Containment Policy
George F. Kennan, Senior State Department official, posted to USSR during war.
Containment was a United States policy using military, economic, and diplomatic strategies to stall the spread of communism, enhance America’s security and influence abroad, and prevent a "domino effect".

Berlin Airlift Blockade of Berlin
began on June 24, ’48
From June 1948 to May 1949, U.S. and British planes airlift 1.5 million tons of supplies to the residents of West Berlin.
After 200,000 flights, the Soviet Union lifts the blockade.

1949 – Fall of China
In June, Jiang Jieshi defeated by Mao– Flee to island of Taiwan
Oct 1, Mao proclaims People’s Republic of China (PRC)
Two months later, Mao travels to Moscow,– negotiates the Sino-
Soviet Treaty of Friendship, Alliance and Mutual Assistance.

Korean War, 1950-1953 On June 25, North
Korean communist forces cross the 38th parallel and invade South Korea.
On June 27, Truman orders U.S. forces to assist the South Koreans
The U.N. Security Council condemns the invasion and est’d a 15-nation fighting force.
Chinese troops enter the conflict by year's end.
Cease fire eventually brings war to close by 1953

Dien Bien Phu, Vietnam After a long siege,
Vietnamese communists under Ho Chi Minh defeat French colonial forces at Dien Bien Phu on May 7.
In July, the Geneva Accords divide the country at the 17th parallel, creating a North and South Vietnam.
The United States assumes the chief responsibility of providing anti-communist aid to South Vietnam.

General Vo Nguyen Giap.

1959 - Castro takes power January 1, 1959
communist forces under Fidel Castro takeover in CUBA
Castro nationalizes the sugar industry and signs trade agreements with the Soviet Union.
The next year, Castro seizes U.S. assets on the island.

1961 - Bay of Pigs
U.S.-organized invasion force of 1,400 Cuban exiles is defeated by Castro's government forces on Cuba's south coast at the Bay of Pigs.
Launched from Guatemala in ships and planes provided by the United States, the invaders surrender on April 20 after three days of fighting.
Kennedy takes full responsibility for the disaster.
Captured Cubans

1960 - The U-2 Affair
On May 1, an American high-altitude U-2 spy plane is shot down on a mission over the Soviet Union.
After the Soviets announce the capture of pilot Francis Gary Powers, the United States recants earlier assertions that the plane was on a weather research mission.

• Mad Magazine makes fun of the Cold War with their Spy vs. Spy column.
• CIA vs. KGB

Sputnik On October 4, the Soviet
Union launches Sputnik, the first man-made satellite to orbit the Earth.
In 1958, the U.S. creates the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, and the space race is in full gear.
***Significant because it shows that Soviets have technological advancements that USA has not mastered***

Sputnik I (1957)
The Russians have beaten America in space—they have the technological edge!

Effects on the United States
•Americans fear a Soviet attack with missile
technology
Effects on the United States
•Americans fear a Soviet attack with missile
technology
• Americans resolved to regain technological superiority over the Soviet Union
• In July 1958, President Eisenhower created NASA or National Space and Aeronautics Agency• 1958 --> National Defense Education Act
• Americans resolved to regain technological superiority over the Soviet Union
• In July 1958, President Eisenhower created NASA or National Space and Aeronautics Agency• 1958 --> National Defense Education Act
1957 Russians launch SPUTNIK I1957 Russians launch SPUTNIK I

Atomic Anxieties:
• “Duck-and-Cover Generation”
Atomic Anxieties:
• “Duck-and-Cover Generation”
Atomic Testing:• Between July 16, 1945 and Sept. 23,
1992, the United States conducted 1,054 official nuclear tests, most of them at the Nevada Test Site.
Atomic Testing:• Between July 16, 1945 and Sept. 23,
1992, the United States conducted 1,054 official nuclear tests, most of them at the Nevada Test Site.
Americans began building
underground bomb shelters and cities had underground fallout shelters.
Americans began building
underground bomb shelters and cities had underground fallout shelters.
Effects of Sputnik on United StatesEffects of Sputnik on United States


McCarthyism Claimed 205 communists
working for State Department
Attacked wealthy & privileged—popular appeal
Even Eisenhower wouldn’t challenge him
Army hearings in 1954 televised– McCarthy exposed as a
bully (“reckless cruelty”

• Red Scare was Americans response to the fear of
Communism
• Senator Joseph McCarthy accused 205 US Govt.
officials of being Communist.
• McCarthyism to destroy or assassinate one’s
character without proof and it ruined the careers
of many Americans.
red scare
Became a witch hunt that led to Americans pledging a “loyalty oath” to the United
States…….

1961 - Berlin Wall
On August 15, communist authorities begin construction on the Berlin Wall to prevent East Germans from fleeing to West Berlin.

JFK in Berlin
http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=5359589

1962 - Cuban Missile Crisis After Bay of Pigs
invasion, the Soviet Union installed nuclear missiles in Cuba.
After U-2 flights Kennedy ordered a naval blockade of Cuba on October 22 until the Soviet Union removed its missiles.
On October 28, the Soviets agreed to remove the missiles, defusing one of the most dangerous confrontations of the Cold War.


Copyright 2007 unimaps.com, used with permission


1972 – Nixon visits China Nixon becomes the first U.S. president
to visit China, meeting with Mao Tse-tung on February 21.
The two countries issue a communique recognizing their "essential differences" while making it clear that "normalization of relations" was in all nations' best interests.
The rapprochement changes the balance of power with the Soviets.

1985 - Gorbachev comes to power On March 11, Mikhail Gorbachev came
to power in the Soviet Union. Gorbachev ushered in an era of reform.
– perestroika • Economic reform- restructuring
– glasnost– means openness, allowed greater free
expression and criticism of Soviet policies

1987 - INF
On December 8, 1987, Reagan and Gorbachev signed the Intermediate Range Nuclear Forces Treaty
Started the trend of“DISARMAMENT”… which is the destruction of nuclear weapons around the globe.

1989 - Berlin Wall falls
Gorbachev renounced the Brezhnev Doctrine, which pledged to use Soviet force to protect its interests in Eastern Europe.
On September 10, Hungary opened its border with Austria, allowing East Germans to flee to the West.
After massive public demonstrations in East Germany and Eastern Europe, the Berlin Wall fell on November 9.
Signified the END of the Cold WAR.

Fall of Berlin Wall

1990 – German unification At a September 12 meeting in
Moscow, the United States, Soviet Union, Great Britain, France and the two Germanys agreed to end Allied occupation rights in Germany.
On October 3, East and West Germany united as the Federal Republic of Germany.