Experiment No 3
description
Transcript of Experiment No 3

Experiment No 3
Preparation of Phosphate Buffers and calculation of pH values by changing volume of the solution

5
Experiment
Material and Chemicals
Overview
Introduction
Procedure
Objective
1
2
3
4

Introduction

A buffer is an aqueous solution that has a highly stable pH. If acid or base is added to a buffered solution, its pH will not change significantly.
When hydrogen ions are added to a buffer, they will be neutralized by the base in the buffer. Hydroxide ions will be neutralized by the acid.
Neutralization reactions will not have much effect on the overall pH of the buffer solution.
Buffer

Most commonly used phosphate buffers, consist of a mixture of monobasic di hydrogen phosphate and dibasic mono hydrogen phosphate.
By varying the amount of each salt, a range of buffers can be prepared.
Phosphates have a very high buffering capacity and are highly soluble in water.
Phosphate Buffer

Phosphates inhibit many enzymatic reactions and procedures that are the foundation of molecular cloning, including cleavage of DNA by many restriction enzymes, ligation of DNA, and bacterial transformation.
Phosphates precipitate in ethanol, it is not possible to precipitate DNA and RNA from buffers that contain significant quantities of phosphate ions.

Experiment

Two Potassium salts, KH2PO4 and K2HPO4Distilled H2OpH MeterFlasksBeakersAnalytical BalanceSpoonPaperPencilMeasuring Cylinder
Apparatus and Chemicals

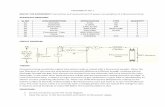
Layout and protocol of the Experiment

2.72 grams KH2PO4
200 mlDist H2O
0.1 M solution
3.40 grams K2HPO4
200 mlDist H2O
0.1 M solution
10 ml A0 ml B
9 ml A1 ml B
0 ml A10 ml B
Measurement of pH using pH meter
A B

Prepare 0.1 M solution of KH2PO4 , 2.72 grams of KH2PO4 is dissolved in 200 ml of distilled water and shake well in beaker. (A)
In another beaker Prepare 0.1 M solution of K2HPO4 , 3.46 grams of K2HPO4 is dissolved in 200 ml of distilled water and shake well . (B)
The solutions are mixed together in such away that 10 ml of A and 0 ml of B in separate beaker, 9 ml of A and 1 ml of B, 0 ml of A and 10 ml of B and so on.
Protocol

pH of every beaker containing mixed solutions are measured with the help of pH meter.
pH values are put in the table.

Thank You