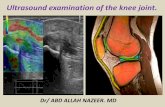
Examination of knee
-
Upload
drsiddique-h-ranna -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
73 -
download
2
Transcript of Examination of knee

PRESENTER:-Dr. Baharul Islam Choudhury
PGT
MODERATOR:-Dr. M. Gayan
Asst. Proff.
Date- 04 /11 / 2015


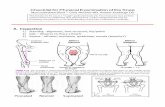
Bony structures-
> Condyles of femur
> Condyles of Tibia
> Patella

JOINT CAPSULE

Ligamentum Patellae


Oblique Popliteal
ligament

Ant & Post Cruciate ligament

Medial & Lateral Meniscus

Transverse ligament
Connects the ant. ends of
med & lat
meniscus.

MUSCLES CONTROL MOVEMENT OF KNEE
Movement Principal Muscle Accessory Muscle
Flexion 1. Biceps Femoris2. Semimembranosus3. Semitendinosus
1. Gracilis2. Sartorious3. Popliteus
Extension 1. Quadriceps Femoris 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae
Med Rotation of flexed leg 1. Popliteus2. Semimembranosus3. Semitendinosus
1. Gracilis
Lat Rotation of flexed leg 1. Biceps Femoris


NERVE SUPPLY OF KNEE JOINT
> Femoral nerve, through its branches to the vasti, especially vast med.
> Sciatic nerve, through the genicular branch of the tibial & common peroneal nerve.
> Obturator nerve, through its posterior division.


Occurs during last stage of extension.
Medial rotation of femur takes place.
All the ligaments are taut in locking position.
Quadriceps Femoris acts on locking mechanism.

PAIN
SWELLING
STIFFNESS
MECH. DISORDER ( locking, giving way, click)
LIMP
LOSS OF FUNCTION

Position during examination
Standing
Sitting
Supine
prone

Inspection
Palpation
Deformity and R.O.M
Measurements
Special tests

INSPECTION
Gait
Attitude

Inspc. Cont..
Swelling
Muscle Wasting

Inspc. Cont..
Sinus
Scar

Inspc. Cont..
Skin condition
Venous prominence

PALPATION Temperature-
Tenderness-
> Bony tenderness
> Joint line tenderness

PALP CONT… Retropatellar Tenderness
>Patellar Grind test-
Patient supine & knee extended
Med & lat pressure over the prox patella
Press it into intercondylar groove
Ask to contract quadriceps

PALP. CONT…
Retropatellar Tenderness
> Facet tenderness test-

PALP.. CONT….
Retropatellar Tenderness
> Friction test-
Patient supine > Knee extended > Compress the patella > Glide the patella from med to lat & sup to inf.

Swelling


Normally when knee is gradually flexed a hollow
appears & then disappears just lateral to the
patellar tendon. In the presence of fluid when
compared to the opposite knee refilling of the
hollow occurs at a lesser angle of flexion.



Other Test For Swelling
Transillumination Test.
+ive- on enlarged bursa, cystic swelling.
-ive-on swelling containing blood, pus.
Compression Test.
+ive in Baker’s cyst, popliteal aneurysm.

PALP. CONT…
Palpation of patella
Palpation of lower end of femur
Palpation of upper ends of Tibia & Fibula
Palpation of popliteal fossa
Palpation of muscle
Palpation for any crepitus
Palpation of Lymph Nodes

MOVEMENTS
Flexion – 0 to 150 degree or till the heel touches the buttock
Extension- till the thigh & leg form a straight line
Abduction & Adduction– absent on extension but slight degree is possible on semiflexion.
Rotation – absent on extension but some degree is possible when hip & knee are flexed to 90 degree

Wasting of Quadriceps
Q- Angle
Indicates the direction of pull of patella by Quadriceps
In male- 14 degree
In female – 17 degree

STABILITY TEST
TESTS FOR ACL.
Lachman test
* Patient on supine.
* Knee on 15-20 deg flex.
* Femur is stabilized.
* Thumb on other hand
on jnt line.
*Anteriorly directed lift
ing force applied.
* Ant. Translation with
soft or mushy end point indicate +ive result.

Lachman Test
Modification I

Stable Lachman Test
Modification II

Drop leg Lachman Test ( Modification III)

Lachman Test ( Modification IV)

Active Lachman Test

ACL test cont..
Anterior Drawer Test-
* Patient is on supine.
* Hip flexed to 45 deg &
knee 90 deg.
* Sits on Patient’s foot.
* Gentle & repeated pull
& push on prox leg.
* Displacement 6-8 mm
Greater than opposite knee +ive result.

Rotary Test For ACL Insufficiency
Lateral Pivot Shift Test Of Macintosh

Rotary Test For ACL Insufficiency
Jerk Test
+ive result when
Lat tibia spontaneously uslysubluxes forward
with sudden
Jerk at about 30 deg
of flexion.

Sag sign

Post. Drawer Test-

Quadriceps active Test

Slocum Test

External Rotation
Recurvatum Test

Jacob Test ( Reverse Pivot Shift Sign )

Mc,murray’sTest

Apley’ Grinding Test-

Thessaly Test-

Squat TestSeveral repetition of full squat with feet & leg
alternately internally & externally rotated.Pain on medial or lateral joint line corresponding
to the side of the torn meniscus.pain in the internally rotated position suggests lat
meniscus inj & pain in externally rotated position
suggests med meniscus inj.

TEST FOR MCL & LCL STABILITY
Valgus & Varus stress test-

Valgus & Varus stress Test

Apley’s Distraction Test For MCL & LCL

TEST FOR RECURRENT PATELLAR DISLOCATION
Apprehension Test-
Pressing patella laterally
Flexing knee slowly
Induce anxiety & resistant
to further movement.

Examination Of Popliteal Fossa.
Examination Of Hip.

THANKING YOU