The importance of artificial coastal structures (tetrapods ...
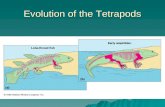
Evolution of the Tetrapods. The Origin of Tetrapods The first vertebrates on land were amphibians in...
-
Upload
ambrose-wilcox -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of Evolution of the Tetrapods. The Origin of Tetrapods The first vertebrates on land were amphibians in...

Evolution of the Tetrapods

Evolution of the Tetrapods

The Origin of Tetrapods• The first vertebrates on land were
amphibians in the _________(400 mya)• Arose from the rhipidistian (a family of
lobed finned fish) (based on morhpology) or a lungfish (DNA)

Origin of Tetrapods

Classification
• Phylum: Chordata• Subphylum: Vertebrata• Superclass: Gnathostomata• Class: Amphibia
– Order: Urodela (Salamanders)– Order: Anurans (Frogs and Toads)– Order: Apodans (Caecilians)

Class: Amphibia• Two lives
– refers to metamorphosis of many frogs• Skin smooth and moist (cutaneous
respiration)• _____ chambered heart with a double
circulation system

Order: Urodela
• 400 species• Salamanders• Retain their tail as
adults• Limbs are at right
angles to the body• Carnivorous• Most have internal
fertilization using a _____________
• Axolotl - paedomorphosis

Order: Anurans• 3500 species• Frogs and Toads• Lose their tail as
adults• Hind limbs are
adapted for jumping• Tongue connected to
front of mouth• Secrete mucus• __________ Fertilization

Order: Apodans
• 150 species• Caecilians• Legless and blind• Mostly Tropical• __________
Fertilization• Usually give birth
to live young.

Gas Exchange

Conditions for Respiratory Surfaces
• Large surface area• Thin• Moist

Aquatic vs. Terrestrial• Less than ____%
oxygen• Oxygen amounts
decrease as the temperature increases
• Aquatic animals use large amounts of energy to obtain oxygen (____%)
• About _____% oxygen
• Developed invaginations to increase surface area and decrease evaporation
• Terrestrial animals may use only 1% - 2% of its energy to obtain oxygen

Gills• Found in echino-
derms, mollusks, annelids, arthropods, some vertebrates
• Countercurrent Gas Exchange

Countercurrent Gas Exchange• Maintains gradient over the whole length of
the capillaries• Extracts ____% of the oxygen from the
water

Tracheal Systems

Diffusion Lungs
• Found in invertebrates• Gas moved primarily by diffusion
– may be increased by body movement
• Modifications– snails - cavity with gill modified into lung– scorpions and spiders - invaginations of
the abdomen

Ventilation Lungs
• Found in amphibians, reptiles, mammals and birds
• Pharynx• Larynx• Trachea• Bronchi• Bronchioles• Alveoli

Alveoli

Ventilating The Lungs
• _______ Pressure Breathing– pushes air down
trachea– seen in frogs and
other amphibians
• ________ Pressure Breathing– suction created
by diaphragm– seen in
mammals

Negative Pressure Breathing

Evolution of the _________ Egg
• Allows animals to complete their entire life cycle on land
• Has shell that retains water (or is lost when kept inside mammals)
• Specialized extraembryonic membranes (not part of the animal)

The Amniotic Egg

Evolution of the Amniotic Egg
• Amnion - Protects from dehydration and mechanical shock
• Yolk Sac - Nutrient storage• Albumin (egg white) - Nutrient
storage• Allantois - stores waste, gas
exchange• Chorion - gas exchange• *** Good Essay….

Amniotes

How Reptiles differ from Amphibians
• Tough, dry skin• Amniotic egg• Crushing or
gripping jaws• Copulatory organs• More efficient
circulatory system with a higher blood pressure
• More developed lungs (thoracic breathing)
• Better water conservation
• Better body support and limbs
• Better nervous system

Classification
• Phylum: Chordata• Subphylum: Vertebrata• Superclass: Gnathostomata• Class: Reptilia (not real)
– Class: Testudines (Turtles and Tortoises)
– Class: Spenodontia (Tuataras)– Class: Squamata (Lizards and Snakes)– Class: Crocodilia (Crocodiles and
Alligators)

Reptile Radiation
• Synapsids (therapsids) - led to mammals
• Sauropsids– _________
(turtles)– _________ (all
others)

Class: Testudines (Chelonia)• Protective Shell
– Carapace (top)– Plastron (bottom)
• Land and Sea -Evolved on land and returned to water (lay eggs on land) Largest,
Leatherback Sea Turtle (2,000 lbs!)

Class: Testudines (Chelonia)
• No _____• Most move legs
to breathe • TDS (low:male
high:female)

Class: Sphenodontia• ___________
– Two living species(New Zealand)
– Not a True Lizard (no external ears, different teeth)
– Very Primitive (similar to mesozoic reptiles
– Well developed eye below skin?

Class: Squamata• Lizards
– geckos, iguanas, skinks, chameleons
• terrestrial, burrowing, aquatic, arboreal
• moveable eyelids (in most)
• Paired copulatory organs

Class: Squamata• Tongue usually not
bifurcated• Lower jaw loosely
connected to skull• TSD (female to male)• ______________

Class: Squamata

Class: Squamata

Class: Squamata
Gila MonsterGila Monster – –
• One of three One of three poisonous lizardspoisonous lizards
• Protein in saliva Protein in saliva studied to treat studied to treat diabetes.diabetes.

Class: Squamata• Snakes• Lack limbs• Lack moveable
eyelids

Class: Squamata
• Bifurcated tongue • _________ organ• Pit Vipers (Loreal
Pits)

Class: Squamata
• Venom– Viperidae (Folding
Fangs)• Rattlesnakes
– Elapidae (Fixed Front Fangs)
• Cobras, Sea Snakes, Coral Snakes
– neurotoxic– hemotoxic

Class: Squamata

Feeding Adaptations
• Teeth curved and pointed inward• Hinged __________ bone• Bones of jaw are attached by
muscles and ligaments• Moveable palate• Elastic skin• No sternum

Class: Crocodilia• Largest living reptiles
• Most closely related to dinosaurs
• Complete secondary ________
• Four chambered heart (?)
• Nest temperature (female/male)

Dinosaurs and Pterosaurs
• Dinosaurs – Ornithischian– Saurischian– Pterosaurs– flying reptiles

Animal Structure and Function
(4th exam)

Animal Nutrition

Nutritional Requirements
• Undernourished– not enough
calories
• Overnourished– too many calories
• ____________– missing one or
more essential nutrients

Essential Nutrients
• Essential Amino Acids• Essential Fatty Acids• Essential Vitamins• Essential Minerals

Essential Amino Acids
• Found in proteins– 20 different types
• 8 essential in adult humans (9 infants)
• all in animal proteins• vegetarians need to
eat grains and beans

__________ – Essential in infantsHistidine

Essential Fatty Acids
• Unsaturated fatty acids– used to make phospholipids for
membranes

Essential Vitamins
• Fat Soluble– stored in fat– ___________
• Water Soluble– excreted in urine– B complex and C

Essential Minerals
• Inorganic nutrients– Calcium & Phosphorous
• bones
– Iron• anemia
– Iodine• thyroid hormones
– Sodium, Chlorine, & Potassium• nerve function, water regulation

Food Types
• Heterotrophic– Herbivores– Carnivores– Omnivores– Insectivores

Feeding Adaptations
• Suspension Feeders

Feeding Adaptations
• Substrate Feeders

Feeding Adaptations
• Fluid Feeders

Feeding Adaptations
• Bulk Feeders

Intracellular Digestion
• Inside cells• All animals• Exclusive in:
– Protista– Porifera

Extracellular Digestion
• Outside cells• All animals above the sponges• Two Types
– _________________– _________________

Gastrovascular Cavity
• One opening• Found in
Cnidaria and Platyhelminthes

Alimentary Canal
• Two openings• Allows for
specialization– Mouth– Pharynx– Esophagus– Crop– Gizzard– Stomach– Intestine– Anus


Mammalian Digestion• Accessory Glands
– salivary glands– pancreas– liver (emulsification)– gallbladder
• Peristalsis • Sphincters• “Food”
– bolus– acid chyme– feces

Macromolecule Digestion
Carbo Protein NucleicAcids
Fat
Mouth Initial
Stomach Initial
Intestine Main Main InitialMain
InitialMain


Dentition and Diet• Nonmammal
vertebrates• Carnivores
– canines (grasping/puncturing)
– incisors (tearing)– molars and premolars
• (crushing and grinding)
• Herbivores• Omnivores

Digestive Tracts
• Carnivores– ________
digestive system
– small cecum
• Herbivores– ________
digestive system
– large cecum