ECOLOGISTS STUDY ENVIRONMENTS AT DIFFERENT LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION. Population Ecology Organism ...
-
Upload
andrew-fleming -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of ECOLOGISTS STUDY ENVIRONMENTS AT DIFFERENT LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION. Population Ecology Organism ...

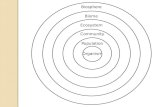
ECOLOGISTS STUDY ENVIRONMENTS AT DIFFERENT LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION.
Population Ecology
Organism Population Community Ecosystem Biome

Population Ecology
Population:all the organisms that both belong to the same group or species and live in the same geographical area
Specific species at the same place at the same time
Example:1,738 trout in Kentucky Lake in 1986

Population Size
The size of a population is always changing!
Four factors affect the size of a population:Immigration (coming in)BirthsEmigration (leaving)Deaths

Population Density
Population Density:The number of individuals that live in
a defined areaHelps scientists determine how
crowded an area is
Formula:# of individualsArea
(units2)
= population density

Population Growth
Population growth is based on available resources.
FOOD
WATER
SHELTER

Population Growth
Exponential Growth (J curve)Rapid population increase due to an abundance of resources.

Population Growth
Logistic Growth (s curve)Due to a population facing limited resourcesNo more will fit!!!

Population Growth
Carrying CapacityThe maximum number of individuals that the environment can support
When resources run out the population cannot keep growing

Population Growth
Ecological Factors limit population
growth.
Limiting Factors:Something that keeps the size of a population down

Limiting Factors
Density-dependent limiting factors:Depend on the number of individuals in a given area.
Examples: Predation Competition (competing for resources)
Parasitism & diseaseHave a larger effect in densely populated areas

Limiting Factors
Density-independent limiting factors:Limit a population’s growth regardless of the number of individuals
Examples: Unusual weather Natural disasters Human activities