Do Now
description
Transcript of Do Now

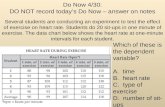
DO NOWIndependently answer the following
questions in your spiral.
1. What is the difference between a population and a sample?
2. What is the purpose of a sample?3. True or False: A survey that only polls 15% of a
population has an undercoverage bias because 85% of the population is not included.
4. Defend your answer to #3.

HOMEWORK• Continue brainstorming your project
ideas.
• Finish your “Wandering Proposal” if not done during class.

AGENDA• Sampling Concepts Review• Return Chapter 12 Quizzes• Project Intro!! Get Excited!!! • Project Wandering Proposal•Due @ end of class

DO NOWIndependently answer the following
questions in your spiral.
1. What is the difference between a population and a sample?
2. What is the purpose of a sample?3. True or False: A survey that only polls 15% of a
population has an undercoverage bias because 85% of the population is not included.
4. Defend your answer to #3.

SAMPLING

POPULATION OF INTEREST: MINT CHOCOLATE CHIP
Simple Random Sample

POPULATION OF INTEREST:ALL 6 FLAVORS
Stratified Sample

POPULATION OF INTEREST:BOX OF NEAPOLITAN
ICE CREAM SANDWICHES
Cluster Sample

Slide 12 - 9
VOLUNTARY RESPONSE BIAS• Sample Badly with Volunteers:• In a voluntary response sample, a large group
of individuals is invited to respond, and all who do respond are counted. • Voluntary response samples are almost always biased, and
so conclusions drawn from them are almost always wrong.• Voluntary response samples are often biased
toward those with strong opinions or those who are strongly motivated.
• Since the sample is not representative, the resulting voluntary response bias invalidates the survey.

Slide 12 - 10
CONVENIENCE BIAS
• Sample Badly, but Conveniently:• In convenience sampling, we simply include the
individuals who are convenient. • Unfortunately, this group may not be
representative of the population.
• Convenience sampling is not only a problem for students or other beginning samplers.• In fact, it is a widespread problem in the
business world—the easiest people for a company to sample are its own customers.

EXAMPLE• You want to know what Muchin senior think about the
prom theme.
• Convenience Sample: Your friends.
• Bias: You friends may all think alike or may just agree with you because you are their friend.

Slide 12 - 12
UNDERCOVERAGE BIAS• Sample from a Bad Sampling Frame:• An SRS from an incomplete sampling frame
introduces bias because the individuals included may differ from the ones not in the frame.
• Undercoverage:• Many of these bad survey designs suffer from
undercoverage, in which some portion of the population is not sampled at all or has a smaller representation in the sample than it has in the population.
• Undercoverage can arise for a number of reasons, but it’s always a potential source of bias.

EXAMPLE• You want to know what Muchin students (9-12th
grades) think about the senior/junior off-campus lunch policy.
• You stop every 5th student who comes off of the elevator between 7:00 – 7:30 am.
• Which group is under-represented here?

Slide 12 - 14
NONRESPONSE BIAS
• Watch out for nonrespondents.• A common and serious potential source
of bias for most surveys is nonresponse bias.
• No survey succeeds in getting responses from everyone. • The problem is that those who don’t
respond may differ from those who do.• And they may differ on just the
variables we care about.

EXAMPLE• You want to find out what percentage of people who
walk downtown feel stressed / busy.
• Who will stop to talk to you?
• Will you be able to account for the busy people?

Slide 12 - 16
RESPONSE BIAS
• Work hard to avoid influencing responses.• Response bias refers to anything in the
survey design that influences the responses. • For example, the wording of a question can
influence the responses:• “You agree with me, right?”

EXAMPLE• The survey can be biased (wording of questions,
answer choices, etc.)• The circumstances can influence people’s answers.• Ms. Neal gives you a survey with the following
circumstances:• You have to put your name on it.• You have to fill it out in front of her.• It asks you various questions about cheating, skipping,
and complaining about teachers.• Will these circumstances affect your response?

UNIT 3 PROJECTExperiments and Surveys

GET CREATIVE!• Work individually.
• Connect it to your senior project.
• Survey and / or experiment.
• Next two weeks – calendar of process / deadlines tomorrow.