DNA Basics. The Structure of DNA A VERY long polymer of repeating units called nucleotides A VERY...
-
Upload
eric-wells -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
0
Transcript of DNA Basics. The Structure of DNA A VERY long polymer of repeating units called nucleotides A VERY...

DNA BasicsDNA Basics

The Structure of DNAThe Structure of DNA
A VERY long A VERY long polymerpolymer of repeating units of repeating units called nucleotidescalled nucleotides
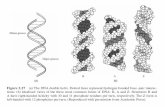
Double-stranded helixDouble-stranded helix Sugar-phosphate backboneSugar-phosphate backbone
sugar is sugar is DDeoxyriboseeoxyribose Four bases hang off the backboneFour bases hang off the backbone
AAdenine, denine, TThymine, hymine, GGuanine, uanine, CCytosineytosine Order of the bases is key to genetic functionOrder of the bases is key to genetic function

The DNA Double HelixThe DNA Double Helix

TerminologyTerminology
Chromosomes contain genes which are Chromosomes contain genes which are made up of DNA and proteinmade up of DNA and protein Humans have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs)Humans have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) 23 from mother, 23 from father23 from mother, 23 from father
DNA = long string of A,T,G,C’sDNA = long string of A,T,G,C’s Gene = short section of DNAGene = short section of DNA
contains recipe for one proteincontains recipe for one protein less than 10% of DNA is genes, 90% “junk”less than 10% of DNA is genes, 90% “junk” approx 25,000 genes in humansapprox 25,000 genes in humans

Base PairingBase Pairing
Everything about the function of DNA Everything about the function of DNA is due to is due to base pairingbase pairing Nitrogen bases from one strand of DNA Nitrogen bases from one strand of DNA
form weak hydrogen bonds with form weak hydrogen bonds with complementary bases of other strandcomplementary bases of other strand
A always bonds to T, G always bonds A always bonds to T, G always bonds to Cto C

A to T Base PairingA to T Base Pairing

C to G Base PairingC to G Base Pairing

DNA ReplicationDNA Replication DNA is double-strandedDNA is double-stranded Strands are connected by the basesStrands are connected by the bases
A on one strand double hydrogen bonds to T on A on one strand double hydrogen bonds to T on the other strandthe other strand
C on one strand triple hydrogen bonds to G on the C on one strand triple hydrogen bonds to G on the other strandother strand
Strands are coiled in a Strands are coiled in a double helixdouble helix Strands are unzipped by enzyme helicaseStrands are unzipped by enzyme helicase New bases hydrogen bond to exposed New bases hydrogen bond to exposed
bases on parent strands, creating 2 new bases on parent strands, creating 2 new double helixesdouble helixes

DNA ReplicationDNA Replication
Before a cell divides:Before a cell divides:

The Central Dogma of The Central Dogma of BiologyBiology
DNA makes RNA makes ProteinDNA makes RNA makes Protein Proteins make you what you areProteins make you what you are
eye color, diabetic, etc…eye color, diabetic, etc… DNA is sacred, can’t leave nucleus (too DNA is sacred, can’t leave nucleus (too
big)big) Cell makes messenger RNA copy of DNA’s Cell makes messenger RNA copy of DNA’s
instructions that can leave the nucleusinstructions that can leave the nucleus Copying mRNA from DNA is called Copying mRNA from DNA is called
TranscriptionTranscription

The Central DogmaThe Central Dogma
DNA DNA RNA RNA ProteinProtein

Transcription AnimationsTranscription Animations“DNA makes RNA”“DNA makes RNA”
AnimationAnimation

Differences between DNA Differences between DNA and RNAand RNA
DNA is double stranded; RNA is single DNA is double stranded; RNA is single stranded – relevance?stranded – relevance?
DNA has deoxyribose; RNA has ribose DNA has deoxyribose; RNA has ribose sugarsugar
DNA has bases adenine, thymine, guanine, DNA has bases adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine; RNA has bases adenine, and cytosine; RNA has bases adenine, URACIL, guanine, and cytosineURACIL, guanine, and cytosine
Many types of RNA – main ones are:Many types of RNA – main ones are: rRNA, tRNA, and mRNArRNA, tRNA, and mRNA

RNA makes ProteinRNA makes Protein
mRNA codes for protein in a process mRNA codes for protein in a process called called TranslationTranslation
Occurs at the cell’s ribosomesOccurs at the cell’s ribosomes Proteins are long strings of Proteins are long strings of amino amino
acidsacids tRNA molecules bring amino acids to tRNA molecules bring amino acids to
the mRNA molecule and link up by the mRNA molecule and link up by base pairingbase pairing

Translation Translation PracticePractice
Use the table of Use the table of Codon Triplets to Codon Triplets to translate this bit translate this bit of mRNAof mRNA


Translation PracticeTranslation Practice mRNA codons (a codon is a set of mRNA codons (a codon is a set of
three mRNA basesthree mRNA bases GCU ACG GAG CUU CGG AGC GCU ACG GAG CUU CGG AGC
UAGUAG Order of amino acids according to Order of amino acids according to
sequence abovesequence above _____ _________________________________ ____________________________

When The Process Goes When The Process Goes WrongWrong
Genetic disease – Sickle Cell AnemiaGenetic disease – Sickle Cell Anemia A single base is wrong in the DNA A single base is wrong in the DNA
There is an A where a T belongsThere is an A where a T belongs This causes a single amino acid to be wrong in This causes a single amino acid to be wrong in
the hemoglobin protein (452 amino acids big)the hemoglobin protein (452 amino acids big) Valine goes where glutamate belongsValine goes where glutamate belongs Hemoglobin is slightly mis-shapen as a resultHemoglobin is slightly mis-shapen as a result

Applications of DNA Applications of DNA TechnologyTechnology
Recombinant DNA - inserting genes Recombinant DNA - inserting genes into DNA strandsinto DNA strands Transgenics – a genetically altered Transgenics – a genetically altered
organism (bacteria producing human organism (bacteria producing human insulin)insulin)
Gene therapyGene therapy DNA fingerprintingDNA fingerprinting

Complete the following w/sComplete the following w/s Quick reviewQuick review DNA basicsDNA basics DNA technologyDNA technology Practice transcription and translationPractice transcription and translation