THE JOURNEY OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM - YOUTUBE THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM.
Digestive System
-
Upload
olive-harvey-college -
Category
Education
-
view
3 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Digestive System

Anatomy and PhysiologyDigestive System

Gastrointestinal System (GI)
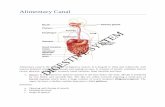
• 30 ft of muscular tube called gut or alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract( stretches between the mouth and anus)
• Sections Include: Oral Cavity, Pharynx, Esophagus, Stomach, Small Intestine, Colon
• The accessory organs are: Liver, gallbladder, Pancreas, Salivary Gland

Three Main Functions
• Digesting Foods • Absorbing Nutrients• Eliminating Waste

Oral Cavity
• Food enters the mouth, where it is broken down by the teeth.
• The tongue mixes the food with saliva, to make it easier to swallow.
• Saliva contains enzymes that breakdown carbohydrates and contains a slippery lubricant that makes food traveling down the esophagus easier.
• The tongue has taste buds that help distinguish: Bitter, sweet, sour, or salty foods
• Palate is the roof of the mouth

Oral Cavity (Continue)
• Uvula hangs from the flexible posterior portion, serves two functions: Speech production and gag reflex
• Swallowing cause the epiglottis to cover the larynx to prevent food from entering the lungs
• The cheeks and lips are the anterior opening.

Oral cavity (Teeth)
• First stage of digestion • Front Teeth: bite, tear,
cut food into smaller pieces
• Cutting teeth: Incisors, Cuspids, Canines
• Grinding teeth: Bicuspids, premolars, molars; these teeth crush and grind food into finer pieces
• The tooth has two parts• The Crown (visible to
the teeth) covered by enamel; under the enamel is the dentin
• The root ( below the gums); constructed of cementum ( bony socket) and tiny periodontal ligaments
• Humans have two sets of teeth: Deciduous teeth( baby teeth) and Permanent teeth

Pharynx
• When swallowing food, food enters the oropharynx, then through the laryngopharynx
• Epiglottis flap close to cover the larynx and trachea, so food do not enter the respiratory tract
• Food continues down the esophagus by peristalsis ( wavelike muscular contractions) push food through the gastrointestinal tract

Stomach
• J-Shape muscular organ • Acts as a sac that collect and churn food with digestive juices• Three Regions :Fundus ( upper region), Body ( main region),
Antrum ( lower region)• Hydrochloric Acid secretions that come out of the mucus
membranes of the rugae ( lining of the stomach). Food mixes with this to form a liquid mixture called Chyme.
• Sphincters controls the entry and exit of food, to ensure the food moves forward.
• Lower esophageal sphincter keeps food from flowing backwards
• Pyloric sphincter regulates the passage of food into the small intestine

Small Intestine
• Small Bowel• Absorbs nutrients
from food• Major site of
digestion • 20 ft in length• Three Sections:
Duodenum(10-12in long), Jejunum( 8 ft long), Ileum (12 ft Long)

Colon
• Fluid left over after digestion, enters the colon• Feces exits through the colon during bowel movements• 5 ft long• The cecum is the first three inches of the colon• The sections to the colon: Ascending colon, transverse colon,
descending colon, sigmoid colon• Rectum, where feces is stored, leads to the anus• Anal Sphincter controls the evacuation of feces; defecation

Accessories of the Digestive system
• Salivary glands: which is located in the oral cavity.
• Liver: process nutrients absorbed by the small intestine and detoxifies harmful substances in the body
• Gallbladder: Bile produced by the liver is stored here.
• Pancreas: Produces secretions for digestion, Buffers and Pancreatic enzymes. Produces hormones insulin and glucagon; regulates the levels of glucose in the blood

Pathology
• Aphthous ulcers• Herpes Labialis• Esophageal Varices• Gastric Carcinoma• Peptic ulcer Disease• Anal Fistula• Crohn’s Disease• Polyposis• Volvulus• Inguinal Hernia

Diagnostic Therapeutic and Procedures
• Intravenous Cholecystography• Bite-wing x-ray• Upper gastrointestinal series• Lower gastrointestinal series• Bariatric Surgery• Colostomy

Conclusion
• The Digestive system helps the human body absorb nutrients, and rid the body of waste.
• With the use of the digestive system, our food we ingest can be use to help growth development, healthy eye site and skin complexion