Digestion, Absorption, and Transport Chapter 3. Chapter 3 Objectives 1.Explain how foods move...
-
Upload
violet-miles -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
2
Transcript of Digestion, Absorption, and Transport Chapter 3. Chapter 3 Objectives 1.Explain how foods move...

Digestion, Digestion, Absorption, and Absorption, and
TransportTransport
Chapter 3Chapter 3

Chapter 3 ObjectivesChapter 3 Objectives
1. Explain how foods move through the digestive system, describing the actions of the organs, muscles, and digestive secretions along the way. a. List the segments of the digestive tract in order from the mouth to the colon.b. Explain the mechanical processes of digestion in order of occurrence in the
digestive tract.c. List the five organs and their secretions which assist in the breakdown of food.d. List the secretions that break down carbohydrates.e. List the secretions that break down protein.f. List the secretions that break down fat.
2. Describe the anatomical details of the intestinal cells that facilitate nutrient absorption.
3. Explain how nutrients are routed in the circulatory systems from the GI tract into the body and identify which nutrients enter the blood directly and which must first enter the lymph.
4. Describe how bacteria, hormones, and nerves influence the health and activities of the GI tract.a. Identify the hormones involved in digestive and absorptive processes.
5. Outline strategies to prevent or alleviate common GI problems.a. Apply the concepts presented in the chapter to explain common digestive tract
problems.

DigestionDigestion
• Breaking down foods into nutrients• Prepare for absorption
• Challenges of digestion• Tasks of the mouth (eat, breathe, drink)• Diaphragm (blockade)• Steady movement (pacing)• Lubrication of food (fluidity)• Digestive enzyme functions (surface area)• Excretion of waste (periodic)

Anatomy of the Digestive TractAnatomy of the Digestive Tract
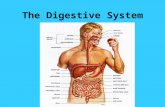
• Gastrointestinal (GI) tract• Flexible and muscular tube• Path
• Mouth → esophagus → stomach → small intestine → large intestine → rectum → anus
• Lumen = inner space within the GI tract)• Continuous
• Not “inside” the body

The Gastrointestinal TractThe Gastrointestinal Tract
Fig 3-1 (pg 71)

Anatomy of the Digestive TractAnatomy of the Digestive Tract
• Mouth• Process of digestion begins
• Mastication
• Four basic taste sensations• Sweet, sour, bitter, salty (savory/umami)
• Aroma (75-95%), texture, and temperature
• Must be in solution
• Pharynx – digestion and respiratory tube• Bolus – swallowed food

Anatomy of the Digestive TractAnatomy of the Digestive Tract
• Esophagus• Two sphincters (each end)
• Upper esophageal sphincter
• Lower esophageal sphincter
• Stomach• Movement of bolus• Chyme – semiliquid mass• Pyloric sphincter

Anatomy of the Digestive TractAnatomy of the Digestive Tract
• Small intestine• Common bile duct
• Pancreas and gall bladder
• Three segments (duodenum, jejunum, ileum)
• Large intestine (colon)• Ileocecal valve • Withdrawal of water• Rectum and anus

Transverse colon
Ascending colon
Descending colon
Sigmoid colonAnus
Rectum
Appendix
Opening from small intestine to large intestine
End of small intestine
Stepped Art
Figure 3-2 p72


Muscular Action of DigestionMuscular Action of Digestion
• Peristalsis• Circular and longitudinal muscles working
together• Rate and intensity of contractions vary• Stress, meds, conditions may interfere with
peristalsis
• Stomach action• Strongest, thickest muscles – circular,
longitudinal, and diagonal muscles• Timing the release of chyme (3x/min)

Stomach MusclesStomach Muscles

Muscular Action of DigestionMuscular Action of Digestion
• Segmentation• Contraction of circular muscles in small
intestine• Mix chyme
• Promote contact with absorption cells
• Sphincter contractions• Periodically open and close• Control pace of GI tract contents

An Example of a Sphincter An Example of a Sphincter MuscleMuscle

Secretions of DigestionSecretions of Digestion
• Five organs1. Salivary glands2. Stomach3. Pancreas4. Liver (gall bladder)5. Small intestine
• Secretions• Water• Enzymes

Secretions of DigestionSecretions of Digestion
• Enzymes• Protein that facilitates a chemical reaction• A catalyst – remains unchanged• Facilitate hydrolysis – addition of water to
breakdown molecules• Look for –ase in the name

Secretions of DigestionSecretions of Digestion
1. Salivary glands = Saliva• Moisten food for easy passage• Protective role• Carbohydrate digestion
2. Stomach = Gastric juice• HCl, along with water and enzymes• Protein digestion• Mucus to protect• pH units

The Salivary Glands

The pH ScaleThe pH Scale

Secretions of DigestionSecretions of Digestion
3. Pancreas = Pancreatic juice • Released via ducts into duodenum• Enzymes act on all three energy nutrients• Sodium bicarbonate
4. Small Intestine = Intestinal enzymes• Enzymes act on all three energy nutrients
5. Liver/Gallbladder = Bile• Liver produces• Gallbladder excretes• Bile = emulsifier, not enzyme

Summary of Digestive Secretions & Their Major Actions

The Final StageThe Final Stage
• Undigested residues• Fiber carries some minerals, bile acids,
additives, contaminants out of the body• Exercise intestinal muscles• Fiber retains water stool consistency
• Colon• Intestinal bacteria ferment some fibers gas• Recyclable materials retrieved
• Water and dissolved salts



AbsorptionAbsorption
• Small intestine• Majority of absorption• Ten feet long
• Surface area – villi, microvilli
• Absorption techniques• Simple diffusion – with gradient
• Facilitated diffusion – carrier cell
• Active transport – against gradient

Carrier loads nutrient on outside of cell . . .
Carrier loads nutrient on outside of cell . . .
Outside cell
Cell membrane
. . . and then releases it on inside of cell.
. . . and then releases it on inside of cell.Inside
cellFACILITATED
DIFFUSION
Some nutrients (such as the water-soluble vitamins) are absorbed by facilitated diffusion. They need a specific carrier to transport them from one side of the cell membrane to the other. (Alternatively, facilitated diffusion may occur when the carrier changes the cell membrane in such a way that the nutrients can pass through.)
ACTIVE TRANSPORT
Some nutrients (such as glucose and amino acids) must be absorbed actively. These nutrients move against a concentration gradient, which requires energy.
Stepped Art
Some nutrients (such as water and small lipids) are absorbed by simple diffusion. They cross into intestinal cells freely.
SIMPLE DIFFUSION
Figure 3-8 p77

Anatomy of the Absorptive Anatomy of the Absorptive SystemSystem
• Villi• Select and regulate nutrients absorbed
• Microvilli• Enzymes and “pumps”
• Crypts• In the “valleys”• Secretion of intestinal juices
• Goblet cells• Mucus secretion


A Closer Look at the Intestinal A Closer Look at the Intestinal CellsCells
• Villi cells• Regulate nutrient absorption based on needs
• Microvilli• Enzymes and ‘pumps’
• Specialized cells • Duodenum not the same as ileum
• Food combining• Enhanced use in the body• Ex: vit C and iron

A Closer Look at the Intestinal Cells
• Once in villus, divergent transport pathways1. Bloodstream
• Water-soluble nutrients and smaller products of fat digestion
• Liver
2. Lymphatic system• Larger fats and fat-soluble vitamins
• Chylomicrons (ch 5)
• Bypass liver at first


The Vascular SystemThe Vascular System
• Closed system of vessels• Heart pump
• Blood• Delivers oxygen and nutrients• Removes carbon dioxide and wastes• Blood flow
• Special routing for digestive system
• Liver

The Vascular SystemThe Vascular System

The LiverThe Liver

The Lymphatic SystemThe Lymphatic System
• One-way route• No pump• Circulation between cells
• Entry into bloodstream• Subclavian vein (near heart)
• Nutrients in lymphatic vessels• Bypass liver at first


Health and Regulation of the GI Health and Regulation of the GI TractTract
• Gastrointestinal bacteria – flora • Most are not harmful
• Benefits of gastrointestinal bacteria
• Factors influencing bacteria presence• Diet – probiotics
• Prebiotics
• Digestion of fibers and complex proteins• Vitamin production

Gastrointestinal Hormones and Gastrointestinal Hormones and Nerve PathwaysNerve Pathways
• Homeostatic regulation• Endocrine system• Nervous system• Feedback mechanisms
• Examples • GI hormones
• Gastrin stimulates HCl secretion• Secretin stimulates bicarb secretion• Cholecystokinin (CCK) stimulates bile
secretion

An Example of a Negative An Example of a Negative Feedback LoopFeedback Loop

The Primary actions of The Primary actions of Selected GI Hormones Selected GI Hormones

The System at Its BestThe System at Its Best
• Sensitive and responsive to environment• Immunity against intestinal diseases• Defense against foreign invaders
• Health of digestive system• Healthy supply of blood• Lifestyle factors• Types of foods eaten
• Balance, moderation, adequacy, and variety


Common Digestive Common Digestive ProblemsProblems
Highlight 3Highlight 3

ChokingChoking
• Food slips into trachea• Cuts off breathing
• International sign for choking• Heimlich maneuver
• Foods commonly associated with choking• Prevention of choking

Normal Swallowing and Normal Swallowing and ChokingChoking

First Aid for ChokingFirst Aid for Choking

VomitingVomiting
• Vomiting• Adaptive mechanism of the body• Medical treatment
• Dehydration
• Self induced

Diarrhea
• Diarrhea• Symptom of medical conditions & treatments
• Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
• Colitis
• Treatment

Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Colitis
• Irritable bowel syndrome• Characterization• Cause
• Unknown
• Triggers
• Colitis• Inflammation of large intestine

Celiac Disease
• Autoimmune disease• Inflammation of small intestine
• Gluten-containing foods• Symptoms• Treatment
• Rehydration

ConstipationConstipation
• Not a disease• Symptoms of constipation• Causes
• Lifestyle• Side effect of medications
• Prevention• Fiber and water• Physical activity

Constipation
• Hemorrhoids• Diverticulosis• Laxatives• Harmful practices
• Colonic irrigation

Belching and GasBelching and Gas
• Belching• Swallowed air• Prevention
• Intestinal gas• Consumption of certain foods
• Individually determined

Heartburn and Heartburn and ““Acid Acid IndigestionIndigestion””
• Gastroesophageal reflux (heartburn)• Causes• Prevention
• Indigestion• Causes• Antacids and acid controllers
• Damage to esophagus• Barrett’s esophagus

Gastroesophageal Reflux

UlcersUlcers
• Peptic ulcers• Gastric ulcers• Duodenal ulcers
• Causes• Bacterial infection• Anti-inflammatory drugs• Excessive gastric acid secretion
• Ulcer treatment regimen

Strategies to Prevent or Alleviate Common GI Problems