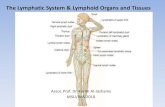
Definition The tissues and organs that produce, store, and carry white blood cells that fight...
-
Upload
shannon-skinner -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of Definition The tissues and organs that produce, store, and carry white blood cells that fight...


DefinitionThe tissues and organs that produce, store, and
carry white blood cells that fight infections and other diseases.
This system includes the Bone Marrow SpleenThymus

Development Development starts by the end of the fifth week
of embryonic life. The lymphatic system begins as a series of
sacs 108 at the points of junction of certain of the embryonic veins.
The lining walls of its vessels are always endothelial.
These lymph-sacs are developed by the confluence of numerous venous capillaries, which at first lose their connections with the venous system, but subsequently, on the formation of the sacs, regain them.

Development in Human EmbryoIn human embryo the lymph sacs from which the
lymphatic vessels are derived are six in number.
Two paired Jugular Lymph sac At the junction of the internal jugular and
subclavian veins.
Retroperitoneal Lymph sac
At the root of the mesentery of the intestine. develops from the primitive vena cava and mesonephric veins
Posterior Lymph sacs Develop from the iliac veins

Lymphatic System ComponentsLymphatic system components includes :
LymphLymph OrgansLymph VesselsLymph Tissues

LymphLymph means clear water and it is basically
the colorless fluid and protein that has been squeezed out of the blood.
Lymph is a fluid similar in composition to blood plasma.
Changes in plasma composition will change lymph composition.
Protein concentration of lymph is lower than in plasma and varies inversely proportional to rate of formation that varies from tissue to tissue.

Lymph flow rate Lymph flow rate is usually low. It is
influenced primarily by the rate of lymph formation.
The flow rate is affected by compression of lymphatics by negative intrathoracic pressure (breathing).
Valves in the lymph vessels prevent retrograde flow similar to those in veins.


Formation of lymph ISF forms at the arterial (coming from the
heart) end of the capillaries because of higher pressure of blood,
Most of it returns to its venous ends and venules; the rest (10—20%) enters the lymph capillaries as lymph.
Thus lymph formed is a watery clear liquid with the same composition as the ISF.
As it flows through the lymph nodes, however, it comes in contact with blood and tends to accumulate more cells (particularly lymphocytes) and proteins.


Lymphatic OrgansAn organ that is characterized by clusters of
lymphocytes and other cells, such as macrophages, enmeshed in a framework of short, branching connective tissue fibers.
Formation: The lymphocytes originate in the red bone
marrow with other types of blood cells and are carried in the blood from the bone marrow to the lymphatic organs.

Types of Lymphatic organs
Primary lymphatic organs Thymus gland Bone marrow
Secondary lymphatic organs Encapsulated diffuse lymphoid tissue
includes the spleen and lymph nodes.
Unencapsulated diffuse lymphoid tissue includes gut-associated lymphoid tissues and the tonsils.

Lymph nodes One of a number of small swellings found at
intervals along the lymphatic system. They are widely distributed throughout the
body along the lymphatic pathways. Lymph nodes are not present in the central
nervous system.Composed of lymphoid tissue.

Structure of lymph nodesSmall bean-shaped structuresUsually less than 2.5 cm (1 inch) in length. Three superficial regions where lymph nodes
tend to cluster 1. Inguinal nodes in the groin2. Axillary nodes in the armpit3. Cervical nodes in the neck


Function of Lymph nodesFilter the lymph before it is returned to the
bloodPreventing foreign particles from entering
the bloodstreamThey also produce lymphocytes

Waxing, Waning of Lymph NodesWaxing and waning terms used to describe
transient or short-term fluctuations in the size of lymph nodes that could be accounted
Response to treatmentImmune activation against lymphomaCollapsing of necrotic areas in lymph nodes
may explain a sudden decrease in a large lymph node.
Lymph nodes may enlarge when immune cells react to pathogen such as virus or bacteria.

Swollen Lymph Glands

TonsilsCluster of lymphatic tissue just under the
mucous membranes that line the nose, mouth, and pharynx (throat) called tonsils.
There are three groups of tonsils. 1. Pharyngeal tonsils 2. Palatine tonsils 3. Lingual tonsils
Provide protection against harmful substances and pathogens that may enter the body through the nose or mouth.


Enlarge Tonsil

Spleen

Function of SpleenFilters bloodStores blood

Thymus Primary lymphatic organ in the body; it is
located over the heart and/or in the neck area, anterior to the ascending aorta and posterior to the sternum.
The thymus consists of two lobes enclosed in a capsule and is further divided internally
Function of the thymus is the processing and maturation of special lymphocytes (white blood cells) called T-lymphocytes or T-cells, which are associated with antibody production.



LymphaticsTubular vessels transport back lymph to the
blood ultimately replacing the volume lost from the blood during the formation of the interstitial fluid.
Lymph capillariesLymph vesselsLymphatic trunksLymphatic ducts

The two main lymph ducts are: Right lymphatic ductThoracic duct
Structure of lymphatics is based on that of blood vessels.
Inner lining of single flattened endothelial cells
Smooth muscles arranged in a circular fashion around endothelial cells
Outermost layer consists of fibrous tissue


Lymphoid TissuesSpecialized form of reticular connective tissue
that contains various types of white blood cells enmeshed In it, most numerous being the lymphocytes.
Lymphoid tissue can be of three types depending upon the stage of lymphocyte development and maturation.
Primary(central) lymphoid tissueSecondary(peripheral) lymphoid tissueTertiary lymphoid tissue

Function of Lymphoid Tissues Makes up the spleen, the thymus, and the
tonsils, as well as visceral nodes, and lacteals which are all associated with mucous membranes of the gastro-intestinal tract.
Concerned with immune functions in defending the body against the infections and spread of tumors.

Functions of Lymphatic System Draining fluid into the bloodstream Filtering lymph Filtering the bloodhelps fight infection in many ways such as Helping to make special white blood cells
(lymphocytes) that produce antibodies
Having other blood cells called macrophages inside the lymph nodes which swallow up and kill any foreign particles,

Draining Fluid into Bloodstream