Decalcification of bone
-
Upload
burnett-d-justus -
Category
Business
-
view
7.424 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Decalcification of bone

HENRY MOORE
NO ONE EVER KNOWS WHAT EACH DAY IS GOING TO BRING. THE IMPORTANT THING IS TO BE OPEN AND READY FOR IT.

UNIVERSITY FOR DEVELOPMENT
STUDIES
UNIVERSITY FOR DEVELOPMENT
STUDIES

BONE DECALCIFICATION.
• Presented by;
• Group three
• Nursing(LEVEL 100)

Calcium ions found in the bones are responsible for its rigid posture and without it, bones may be flexible and most of time unable to carry their body weight. Diseases such as osteomalacia and rickets are as a result of lack of calcium in the bones of those areas.De-calcification of bones as our topic is about the removal of these calcium from the bones. As such, we are going to look at the following about the topic:•The definition of decalcification of bones•The purpose of decalcification of bones•The principle of bone decalcification•The method of decalcification of bonesHow to test for the completion of decalcification

INTRODUCTION
Decalcification Loss of calcium salts from a bone or tooth. OR The process of removing calcareous
matter.
Bone decalcification Removal of calcium ions from the bone
through histological process thereby making the bone flexible and easy for pathological investigation.

PURPOSE OF BONE DECALCIFICATION
• The purpose is to make the bone flexible and easy for pathological investigation. This is necessary in order to obtain soft sections of the bone using the microtome
• Failure to decalcification results in torn, ragged sections and damage to the cutting edge of the microtome knife

PRINCIPLE OF DECALCIFICATION
• Insoluble calcium salt are converted into soluble calcium salts by the action of decalcifying agent so that the tissue become soft.
• Chelating agent binds to calcium ions present in the bone and decalcification is carried out.

Methods of decalcification
• Traditional method
• Acid decalcifying agents.
• Ion exchange resins with acid and decalcifying fluids.
• Electrolytic decalcification.
• Chelating agents.

TRADITIONAL METHOD
• There is a traditional method of handling hard tissues such as bones ,but it posses problems to both pathologists and histotechnologists.
• This is because ,it involves a lot of cutting of the tissue and keeping them for long periods in decalcifying solutions and this makes it difficult to get the cellular details intact.

Acid decalcifying agent
• Acids are further divided into two namely : weak acids and strong acids.
• Weak ( Picric, Acetic and Formic acid)
• Strong (Nitric and Hydrochloric acid)

Nitric acid
MEHTODThin slices of fixed tissue are placed in
a freshly prepared 5-10% solution of nitric acid in distilled water.
Decalcification through this should not extend beyond 48 hours.
Formalin is added to nitric acid to protect the tissue against maceration and swelling.

Formic acid
• Formic acid is widely used as a decalcifying agent.
• For routine 10% of formic acid in distilled water is recommended and higher concentration gives more rapid decalcification.
• A large volume of fluid is used and renewed every 48 hours.

Ion exchange resins with acid decalcifying fluids
It is an advanced system that quickly remove calcium from bone while leaving superior cellular details intact.
Electrolytic DecalcificationIt is the speedier decalcification without
damage to cytological features and staining.
Drawback:
Heat produced in the process may cause the charring of specimen in the process

Chelating Agents
• EDTA is a chelating agent, it is a white crystalline powder soluble in distilled water to about 20%.
• As a decalcifying agent it combines with calcium ions to form soluble, non ionized compounds.
• The volume of solution for decalcifying should be 150 times that of the tissue.
• The solution should be renewed every
5 to 7 days during decalcification.

Advantages of EDTA
• Deposits of iron and other metals may also be removed by EDTA.
• Tissue is not hardened after decalcification.
• It can be good for Bone ,Teeth and any calcified tissue.
• This is also the preferred solution for
decalcifying bone material for transmission electron microscopy .

Test for completion of Decalcification
There are three methods for determining the completion of progress of decalcification.
By X-ray examination.
By Ammonia method(chemical method).
By Physical method

X-ray Examination
• The most reliable method for determining decalcification.
• But as this facility is not present in all the laboratories

Ammonia Method
• In this method ammonia is added drop by drop in the decalcifying solution cloudiness indicate the presence of calcium.
• The specimen is then placed in a fresh solution of decalcifying fluid and test is repeated after a suitable interval of time.

PHYSICAL METHOD
• This include bending the specimen or inserting a pin, razor or scalpel directly into the tissue.
• The disadvantage of inserting a pin is introduction of tears and pinhole or artifacts.
• Slightly bending is less disruptive but will not conclusively determine if all calcium salts have been removed.
• After checking for rigidity, wash thoroughly prior to processing.

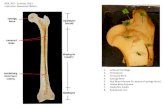
DIAGRAM OF A DECALCIFIED BONE.

SUMMARYSUMMARY

BONE DECALCIFICATION Removal of calcium ions from the bone through
histological process thereby making the bone flexible and easy for pathological investigation.
Methods; Acid decalcifying agents Traditional method Ion exchange resins with acid and decalcifying fluids.
Electrolytic decalcification Chelating agents

QUOTE :
THE ONLY WAY TO DISCOVER THE LIMIT OF THE POSSIBLE IS TO GO BEYOND THEM INTO THE IMPOSSIBLE.