Chemical Bonding 1. Covalent bonding 2. Ionic bonding All elements and atoms need stability.
-
Upload
bryce-norton -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
1
Transcript of Chemical Bonding 1. Covalent bonding 2. Ionic bonding All elements and atoms need stability.

Chemical Bonding
1. Covalent bonding
2. Ionic bonding
All elements and atoms need stability.

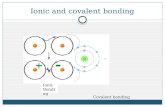
Ionic Bonding
This occurs when electrons are transferred.
Reacting sodium (Na) with chlorine (Cl):



Ionic Bonding
This occurs when electrons are transferred.
Metal atoms lose the electron, or electrons, in their highest energy level and become positively charged ions. Non-metal atoms gain an electron, or electrons, from another atom to become negatively charged ions.
The force of attraction between these oppositely charged particles keeps them together. This occurs between metals and non-metals.

Patterns
Group 1 +1 Na+
Group 2 +2 Mg2+
Group 3 +3 Al +
Group 4 Share electrons
Group 5 -3 N-3
Group 6 -2 O-2
Group 7 -1 Cl-3
Group 0 Unreactive
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/add_aqa_pre_2011/atomic/
Group 1 elements react with elements in group 7.
Group elements lose an electron and group 7 elements gain an electron.

Covalent bonding
This occurs when electrons are shared. These occur between non-metals.

Example 1
Water

Example 2
Oxygen
Oxygen AtomOxygen Atom Oxygen AtomOxygen Atom
Oxygen Molecule (O2)

Example 3
Chlorine

Use your periodic tables and knowledge of electron arrangements to answers the following questions:
1. Why are group 7 elements (halogens) so reactive?
2. Why are group 0 elements (noble gases) so un-reactive?

3. Draw the ions that would be formed for the following:
Aluminium (Al) Potassium (K) Fluorine (F) Oxygen (O)
For each state whether electrons had been lost of gained.

4. Complete the following table:Atomic number
Atom Electronic structure of
atom
Ion Electronic structure of ion
8 O [2,8]2-
19 2,8,8,1 K+
17 Cl Cl-
20 2,8,8,2
5. Draw dot and cross diagrams to show how the following to form ions together:- lithium and chlorine- calcium and oxygen- aluminium and chlorine

6. Draw diagrams to show the covalent bonds between the
following atoms:
- 2 hydrogen atoms- 2 chlorine atoms- a hydrogen and a fluorine atom