Chapter 26 The Thoracic Spine. Overview In the thoracic region, protection and function of the...
-
Upload
hailey-okeefe -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
4
Transcript of Chapter 26 The Thoracic Spine. Overview In the thoracic region, protection and function of the...

Chapter 26Chapter 26
The Thoracic SpineThe Thoracic Spine

OverviewOverview
In the thoracic region, protection In the thoracic region, protection and function of the thoracic and function of the thoracic viscera take precedence over viscera take precedence over segmental spinal mobilitysegmental spinal mobility
The thoracic complex can be a The thoracic complex can be a significant source of local and significant source of local and referred pain referred pain

AnatomyAnatomy
The thoracic spine forms a kyphotic curve The thoracic spine forms a kyphotic curve between the lordotic curves of the cervical between the lordotic curves of the cervical and lumbar spinesand lumbar spines
The curve begins at T 1-2 and extends down The curve begins at T 1-2 and extends down to T 12 with the T 6-7 disc space as the apexto T 12 with the T 6-7 disc space as the apex
The thoracic kyphosis is a structural curve, The thoracic kyphosis is a structural curve, which is present from birthwhich is present from birth
Unlike the lumbar and cervical regions, which Unlike the lumbar and cervical regions, which derive their curves from the corresponding derive their curves from the corresponding differences in intervertebral disc heights, the differences in intervertebral disc heights, the thoracic curve is maintained by the wedge-thoracic curve is maintained by the wedge-shaped vertebral bodies, which are about 2 shaped vertebral bodies, which are about 2 mm higher posteriorly than anteriorlymm higher posteriorly than anteriorly

AnatomyAnatomy
The thoracic vertebrae consist of the The thoracic vertebrae consist of the usual elements: the vertebral body usual elements: the vertebral body (centrum), transverse processes, (centrum), transverse processes, neural arch, and spinous processneural arch, and spinous process
As elsewhere in the spine, the thoracic As elsewhere in the spine, the thoracic vertebrae are designed to endure and vertebrae are designed to endure and distribute the compressive forces distribute the compressive forces produced by weight bearing, most of produced by weight bearing, most of which is borne by the vertebral bodies which is borne by the vertebral bodies

AnatomyAnatomy
The thoracic vertebral body is The thoracic vertebral body is roughly as wide as it is long so roughly as wide as it is long so that its anterior-posterior and that its anterior-posterior and medial-lateral dimensions are of medial-lateral dimensions are of equal lengthequal length

AnatomyAnatomy
The height, end-plate cross-sectional The height, end-plate cross-sectional area, and bone mass of the vertebral area, and bone mass of the vertebral bodies increases cranial to caudal, bodies increases cranial to caudal, particularly in the lower levelsparticularly in the lower levels
Progressive wedging of the thoracic Progressive wedging of the thoracic vertebral bodies occurs with increasing vertebral bodies occurs with increasing age in the majority of individuals, with age in the majority of individuals, with disc space narrowing at multiple levels disc space narrowing at multiple levels occurring from the third decade of lifeoccurring from the third decade of life

AnatomyAnatomy
The transverse processes of the The transverse processes of the thoracic vertebrae differ from those of thoracic vertebrae differ from those of the cervical and lumbar spines due to the cervical and lumbar spines due to the presence of a costal articular facet the presence of a costal articular facet on the transverse processon the transverse process
The costotransverse joint is formed by The costotransverse joint is formed by an oval facet on the lateral aspects of an oval facet on the lateral aspects of all of the transverse processes to all of the transverse processes to which the rib attaches, except for T 11 which the rib attaches, except for T 11 and T 12 to which no ribs are attached and T 12 to which no ribs are attached

AnatomyAnatomy
The thoracic vertebrae are The thoracic vertebrae are classified as typical or atypical classified as typical or atypical with reference to their morphologywith reference to their morphology– The typical thoracic vertebrae are The typical thoracic vertebrae are
found at T 2-9, although T 9 may be found at T 2-9, although T 9 may be atypical in that its inferior costal facet atypical in that its inferior costal facet is frequently absentis frequently absent
– The atypical thoracic vertebrae are The atypical thoracic vertebrae are the first, tenth, eleventh and twelfththe first, tenth, eleventh and twelfth

AnatomyAnatomy
The common spinal ligaments are The common spinal ligaments are present at the thoracic vertebrae, and present at the thoracic vertebrae, and they perform much the same function they perform much the same function as they do elsewhere in the spineas they do elsewhere in the spine
The anterior longitudinal ligament in The anterior longitudinal ligament in this region is narrower but thicker this region is narrower but thicker compared to the rest of the spinecompared to the rest of the spine
The posterior longitudinal ligament, is The posterior longitudinal ligament, is wider here at the intervertebral disc wider here at the intervertebral disc level, but narrower at the vertebral level, but narrower at the vertebral body than in the lumbar region body than in the lumbar region

AnatomyAnatomy
The zygapophyseal joints of the The zygapophyseal joints of the thoracic spine function to restrain thoracic spine function to restrain the amount of flexion and anterior the amount of flexion and anterior translation of the vertebral translation of the vertebral segment, and to facilitate rotationsegment, and to facilitate rotation
They appear to have little influence They appear to have little influence on the range of side bendingon the range of side bending

AnatomyAnatomy
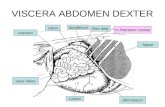
The bony thoracic cage is formed The bony thoracic cage is formed by twelve pairs of ribs, the by twelve pairs of ribs, the sternum, the clavicle and the sternum, the clavicle and the thoracic spine vertebraethoracic spine vertebrae
All of the ribs are different from All of the ribs are different from each other in size, width, and each other in size, width, and curvature, although they share curvature, although they share some common characteristicssome common characteristics

AnatomyAnatomy
The ribs are divided into two The ribs are divided into two classifications: (1) true/false and (2) classifications: (1) true/false and (2) typical/atypicaltypical/atypical– Ribs 1 through 7 are named true ribs Ribs 1 through 7 are named true ribs
because their cartilage attaches directly to because their cartilage attaches directly to the sternumthe sternum
– Ribs 3 through 9 are typical ribs. The Ribs 3 through 9 are typical ribs. The typical rib is characterized by a posterior typical rib is characterized by a posterior end, which is comprised of a head, neck end, which is comprised of a head, neck and tubercle and tubercle

AnatomyAnatomy
The costovertebral articulation also The costovertebral articulation also forms an intimate relationship forms an intimate relationship between the head of the rib and the between the head of the rib and the lateral side of the vertebral body lateral side of the vertebral body
The radiate ligament connects the The radiate ligament connects the anterior aspect of the rib head to the anterior aspect of the rib head to the bodies of two adjacent vertebrae and bodies of two adjacent vertebrae and their intervening disc, in a fan-like their intervening disc, in a fan-like arrangement arrangement

AnatomyAnatomy
The costotransverse joint is a The costotransverse joint is a synovial joint between an synovial joint between an articular facet on the posterior articular facet on the posterior aspect of the rib tubercle and an aspect of the rib tubercle and an articular facet on the anterior articular facet on the anterior aspect of the transverse process, aspect of the transverse process, which is supported by a thin which is supported by a thin fibrous capsule fibrous capsule

AnatomyAnatomy
The sternum consists of three The sternum consists of three parts: the manubrium, the body, parts: the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process.and the xiphoid process.
The manubrium is broad and thick The manubrium is broad and thick superiorly, and narrower and superiorly, and narrower and thinner inferiorly, where it thinner inferiorly, where it articulates with the body articulates with the body

AnatomyAnatomy
The first, sixth and seventh costal The first, sixth and seventh costal cartilages are each linked to the cartilages are each linked to the sternum by a synchondrosissternum by a synchondrosis
The second to fifth ribs are each The second to fifth ribs are each connected to the sternum through a connected to the sternum through a synovial joint, whereby the cartilage synovial joint, whereby the cartilage of the corresponding rib articulates of the corresponding rib articulates with a socket-like cavity in the with a socket-like cavity in the sternum sternum

AnatomyAnatomy
A large number of muscles arise A large number of muscles arise from and insert on the thoracic from and insert on the thoracic spine and ribsspine and ribs
The muscles of this region can be The muscles of this region can be divided into those that are divided into those that are involved in spinal or extremity involved in spinal or extremity motion, and those that are motion, and those that are involved in respiration involved in respiration

AnatomyAnatomy
The blood supply to this region is The blood supply to this region is mainly provided by the dorsal mainly provided by the dorsal branches of the posterior intercostal branches of the posterior intercostal arteries, while the venous drainage arteries, while the venous drainage occurs through the anterior and occurs through the anterior and posterior venous plexusesposterior venous plexuses
The spinal cord region between T 4 The spinal cord region between T 4 and T 9 is poorly vascularized and T 9 is poorly vascularized

AnatomyAnatomy
In the thoracic region there is great In the thoracic region there is great variability in the topography of the variability in the topography of the nerves, and the structures that they nerves, and the structures that they serveserve
Typically, the spinal root arises from the Typically, the spinal root arises from the lateral end of the spinal nerve but, in lateral end of the spinal nerve but, in 25% of cases, the spinal root is made up 25% of cases, the spinal root is made up of two parts that arise from the superior of two parts that arise from the superior border of the spinal nerveborder of the spinal nerve
The thoracic spinal nerves are The thoracic spinal nerves are segmented into dorsal primary and segmented into dorsal primary and ventral primary divisions ventral primary divisions

BiomechanicsBiomechanics
The thoracic spinal segments possess The thoracic spinal segments possess the potential for a unique array of the potential for a unique array of movementsmovements
However, there is very little agreement However, there is very little agreement in the literature with regards to the in the literature with regards to the biomechanics of the thoracic spine and biomechanics of the thoracic spine and most of the understanding is based most of the understanding is based largely on the ex vivo studies and a largely on the ex vivo studies and a variety of clinical modelsvariety of clinical models

BiomechanicsBiomechanics
Flexion of the thoracic spine in Flexion of the thoracic spine in weight bearing is initiated by the weight bearing is initiated by the abdominal muscles and, in the abdominal muscles and, in the absence of resistance, is continued absence of resistance, is continued by gravity, with the spinal erector by gravity, with the spinal erector muscles eccentrically controlling the muscles eccentrically controlling the descent. Flexion may also occur descent. Flexion may also occur during bilateral scapular protractionduring bilateral scapular protraction

BiomechanicsBiomechanics
Extension of the thoracic spine is Extension of the thoracic spine is produced principally by the lumbar produced principally by the lumbar extensors, and results in an inferior extensors, and results in an inferior glide of the superior facet of the glide of the superior facet of the zygapophyseal jointzygapophyseal joint
1-2º of extension is available at each 1-2º of extension is available at each thoracic segment, giving an overall thoracic segment, giving an overall average of 15-20º of thoracic average of 15-20º of thoracic extension for the entire thoracic spine extension for the entire thoracic spine

BiomechanicsBiomechanics
Side bending of the thoracic spine is Side bending of the thoracic spine is initiated by the ipsilateral abdominals, initiated by the ipsilateral abdominals, and erector muscles, and then and erector muscles, and then continued by gravitycontinued by gravity
A total of 25-45º of side bending is A total of 25-45º of side bending is available in the thoracic spine, at an available in the thoracic spine, at an average of about 3-4º to each side per average of about 3-4º to each side per segment, with the lower segments segment, with the lower segments averaging slightly more, at 7º to 9º each averaging slightly more, at 7º to 9º each

BiomechanicsBiomechanics
Axial rotation is produced either Axial rotation is produced either by the abdominal muscles and by the abdominal muscles and other trunk rotators, or by other trunk rotators, or by unilateral elevation of the armunilateral elevation of the arm
Pure axial rotation (twisting) can Pure axial rotation (twisting) can only occur at two points in the only occur at two points in the spine: at the thoracolumbar and spine: at the thoracolumbar and cervicothoracic junctions cervicothoracic junctions

BiomechanicsBiomechanics
Because the anterior end of the ribs is lower Because the anterior end of the ribs is lower than the posterior, when the ribs elevate than the posterior, when the ribs elevate they rise upwards while the rib neck drops they rise upwards while the rib neck drops downdown
In the upper ribs, this results in an anterior In the upper ribs, this results in an anterior elevation (pump handle) which increases the elevation (pump handle) which increases the anterior-posterior diameter of the thoracic anterior-posterior diameter of the thoracic cavity cavity
In the middle and lower ribs (excluding the In the middle and lower ribs (excluding the free ribs), this results in a lateral elevation free ribs), this results in a lateral elevation (bucket handle), which increases the (bucket handle), which increases the transverse diameter of the thoracic cavitytransverse diameter of the thoracic cavity

ExaminationExamination
Differential diagnosis of thoracic Differential diagnosis of thoracic pain can be difficult. This is due pain can be difficult. This is due to the complicated biomechanics to the complicated biomechanics and function of the region, the and function of the region, the proximity to vital organs, and the proximity to vital organs, and the many articulationsmany articulations

ExaminationExamination
Pain arising from inflammation of Pain arising from inflammation of the axial spine can mimic a variety the axial spine can mimic a variety of serious conditions, including of serious conditions, including cardiac/pulmonary pathology, renal cardiac/pulmonary pathology, renal colic, fracture, a tumor, or colic, fracture, a tumor, or numerous visceral and numerous visceral and retroperitoneal abnormalities, retroperitoneal abnormalities, including abdominal aortic including abdominal aortic aneurysm aneurysm

ExaminationExamination
HistoryHistory– The clinician must determine if the The clinician must determine if the
pain is provoked or alleviated with pain is provoked or alleviated with movement or posture movement or posture (musculoskeletal pain), respiration (musculoskeletal pain), respiration (rib dysfunction or pleuritic pain), (rib dysfunction or pleuritic pain), eating or drinking (gastric pain), or eating or drinking (gastric pain), or exertion (rib dysfunction or cardiac exertion (rib dysfunction or cardiac pain)pain)

ExaminationExamination
Systems ReviewSystems Review– Thoracic pain may originate from just Thoracic pain may originate from just
about all of the visceraabout all of the viscera– Both visceral and somatic afferent nerves Both visceral and somatic afferent nerves
transmit pain messages from a peripheral transmit pain messages from a peripheral stimulus and converge on the same stimulus and converge on the same projection neurons in the dorsal hornprojection neurons in the dorsal horn
– The thoracolumbar outflow of the The thoracolumbar outflow of the autonomic nervous system has its location autonomic nervous system has its location here. Stimulation of this outflow can lead here. Stimulation of this outflow can lead to the presence of facilitated segments, to the presence of facilitated segments, and trophic changes in the skin of the and trophic changes in the skin of the periphery periphery

ExaminationExamination
ObservationObservation– The clinician should observe:The clinician should observe:
The relationship of the bony structuresThe relationship of the bony structures Smoothness of the thoracic curveSmoothness of the thoracic curve The degree of thoracic kyphosis The degree of thoracic kyphosis The amount of lateral curvature of the The amount of lateral curvature of the
thoracic spinethoracic spine Chest wall shapeChest wall shape Asymmetry in muscle bulk, prominence, Asymmetry in muscle bulk, prominence,
or length or length

ExaminationExamination
PalpationPalpation– The areas of spinous process obliquity The areas of spinous process obliquity
may be divided into four regions by the so-may be divided into four regions by the so-called ‘rule of three’ called ‘rule of three’
1st group of 3 spinous processes (T 1-3) are 1st group of 3 spinous processes (T 1-3) are level with vertebral body of the same levellevel with vertebral body of the same level
2nd group of 3 spinous processes (T 4-6) are 2nd group of 3 spinous processes (T 4-6) are level with the disk of the inferior levellevel with the disk of the inferior level
3rd group of 3 spinous processes (T 7-9) are 3rd group of 3 spinous processes (T 7-9) are level with the vertebral body of the level belowlevel with the vertebral body of the level below
The 4th group of 3 spinous processes reverse The 4th group of 3 spinous processes reverse the obliquitythe obliquity

ExaminationExamination
Active Motion TestingActive Motion Testing– Active range of motion tests are used to determine Active range of motion tests are used to determine
the osteokinematic function of two adjacent the osteokinematic function of two adjacent thoracic vertebrae during active motions, to thoracic vertebrae during active motions, to determine which joints are dysfunctional, and the determine which joints are dysfunctional, and the specific direction of motion lossspecific direction of motion loss
– Active range of motion is initially performed Active range of motion is initially performed globally, looking for abnormalities, such as globally, looking for abnormalities, such as asymmetrical limitations of motionasymmetrical limitations of motion
– A specific examination is then performed on any A specific examination is then performed on any region that appeared to have either excessive or region that appeared to have either excessive or reduced motionreduced motion

ExaminationExamination
For those clinicians heavily For those clinicians heavily influenced by the muscle energy influenced by the muscle energy techniques of the osteopaths, techniques of the osteopaths, position testing is used to determine position testing is used to determine which segment to focus onwhich segment to focus on
Other clinicians omit the position Other clinicians omit the position tests and proceed to the combined tests and proceed to the combined motion and passive physiological motion and passive physiological tests tests

ExaminationExamination
Costal examinationCostal examination– It is well worth postponing the It is well worth postponing the
costal, or rib, examination until after costal, or rib, examination until after the thoracic spinal joints have been the thoracic spinal joints have been examined and treated, or the testing examined and treated, or the testing of which proved negative of which proved negative

ExaminationExamination
A neurological deficit is very difficult to A neurological deficit is very difficult to detect in the thoracic spinedetect in the thoracic spine
In this region, one dermatome may be In this region, one dermatome may be absent with no loss of sensationabsent with no loss of sensation
Sensation should be tested over the Sensation should be tested over the abdomen; the area just below the xiphoid abdomen; the area just below the xiphoid process is innervated by T 8, the umbilicus process is innervated by T 8, the umbilicus by T 10, and the lower abdominal region, by T 10, and the lower abdominal region, level with the anterior superior iliac spines, level with the anterior superior iliac spines, by T 12by T 12
Too much overlap exists above T 8 to make Too much overlap exists above T 8 to make sensation testing reliablesensation testing reliable

InterventionIntervention
Acute phase goals include:Acute phase goals include:– Decrease pain, inflammation, and muscle spasmDecrease pain, inflammation, and muscle spasm– Promote healing of tissuesPromote healing of tissues– Increase pain-free range of vertebral and costal Increase pain-free range of vertebral and costal
motionmotion– Regain soft tissue extensibilityRegain soft tissue extensibility– Regain neuromuscular controlRegain neuromuscular control– Initiate postural educationInitiate postural education– Promote correct breathingPromote correct breathing– Educate the patient about activities to avoid and Educate the patient about activities to avoid and
positions of comfort.positions of comfort.– Allow progression to the functional stageAllow progression to the functional stage

InterventionIntervention
Functional phase goalsFunctional phase goals– To significantly reduce or to completely To significantly reduce or to completely
resolve the patient’s painresolve the patient’s pain– The restoration of full and pain-free The restoration of full and pain-free
vertebral and costal range of motionvertebral and costal range of motion– Full integration the entire upper and lower Full integration the entire upper and lower
kinetic chainskinetic chains– Complete restoration of respiratory functionComplete restoration of respiratory function– The restoration of thoracic and upper The restoration of thoracic and upper
quadrant strength and neuromuscular quadrant strength and neuromuscular controlcontrol