CELLS Structure. Cell Membrane Surrounds the cell to separate it from its external environment...
-
Upload
kathlyn-stone -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
2
Transcript of CELLS Structure. Cell Membrane Surrounds the cell to separate it from its external environment...

CELLS
Structure

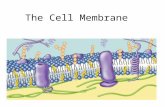
Cell Membrane Surrounds the cell to separate it from its external
environment Composed of a phospholipid bilayer that has proteins
embedded in it Cholesterol is also an important component of cell
membranes since it keeps the membrane intact yet fluid The membrane acts as a selective barrier by controlling
what substances enter and leave the cell

Membrane Structures Microvilli (microvillus):
extensions of the cell membrane used to increase the surface area of the cell
Cilia (cillium): short, hair-like extensions on the cell membrane used for movement
Flagella (Flagellum): long, whip-like structures used for movement

Cell Interior
Cytoplasm: A semi-fluid substance in which all of
the cell’s organelles are suspended Located between the nucleus and the
cell membrane Contains the cytoskeleton
Cytoskeleton: a network of microtubules that support the cell and give it shape

Nucleus Nucleus: the control center of the cell
and where the cell’s DNA is located Nuclear Membrane:
Separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm Contains pores so that substances may enter
or leave the nucleus Nucleolus: structure within the nucleus
that is responsible for making rRNA Nucleoplasm: similar to the cytoplasm, it
is a semifluid substance in which the DNA and nucleolus are suspended

Organelles Endoplasmic reticulum (ER):
Extensive network of membranes There are 2 types:
Rough ER: contains ribosomes that make proteins destined to leave the cell
Smooth ER: makes lipids, steroids, and is involved in detoxification; important in cells that are responsible for ridding the body of toxic substances (i.e. liver)

Organelles (cont.) Ribosomes:
Structures involved in protein synthesis
Found attached to the RER or suspended in the cytoplasm
Mitochondria: structures used to make ATP (energy compound)
Golgi complex (apparatus): Series of flat membrane-bound sacs Packages proteins made from the
RER and sends them in membrane-bound vesicles to their destination

Organelles (cont.)
Vacuole: Membrane-bound compartment that
serves many functions (i.e. absorbs water, stores proteins, stores wastes, etc.)
Plant cells have one large central vacuole whereas animal cells contain several small vacuoles

Organelles (cont.) Lysosome:
Membrane-bound organelles filled with hydrolytic enzymes
These enzymes are used to break down substances (i.e. carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, old organelles, etc.)