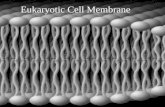
Cell Membrane Every cell is surrounded by a protective membrane called a cell membrane. This...
-
Upload
karin-townsend -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
1
Transcript of Cell Membrane Every cell is surrounded by a protective membrane called a cell membrane. This...

Cell Membrane• Every cell is surrounded by a protective
membrane called a cell membrane.• This membrane is flexible & protects the inside
of the cell from the environment outside of the cell.
• Mostly made up of two different types of macromolecules- proteins and a type of lipid called phospholipids.

Cell Wall• Plant cells, fungal cells, bacteria and
some types of protists have cell walls.• Cell wall is a stiff structure outside the
cell membrane & protects a cell from attack by viruses and other harmful organisms.
• In plant & fungal cells, a cell wall helps to provide structural support in order to maintain the cell’s shape.

Cell Appendages
• Cell appendages are used for movement• Flagella are long, tail-like appendages that
whip back & forth and move a cell• Cells can also have cilia which are short
hair like structures. Cilia can move a cell or move molecules away from a cell.

Cytoplasm & Cytoskeleton• Most of the water in cells is in the
cytoplasm.• Cytoplasm is the fluid inside a cell that
contains salts & other molecules.• The cytoplasm also contains the cell’s
cytoskeleton which is a network of threadlike proteins that are joined together.
• The cytoskeleton is made up of proteins. The cytoskeleton helps give the cell its shape & helps it move.

Prokaryotic Cells• Is one of the two types of cells• The genetic material in a prokaryotic cell
is not surrounded by a membrane (this is most important feature in prokaryotic cells)
• Missing many other cell parts • Most prokaryotic cells are unicellular
organisms

Eukaryotic Cells• Plant, animal, fungi and protists are made
of eukaryotic cells.• Most eukaryotic cells have genetic material
that is surrounded by a membrane.• Eukaryotic cells have cell structures called
organelles, which have special jobs.• Eukaryotic cells are usually larger than
prokaryotic cells.

The Nucleus• The largest organelle inside most eukaryotic cells• The nucleus directs cell activities & contains genetic
information stored in DNA.• Chromosomes is where the DNA is stored inside the
nucleus• Also the nucleus contains the nucleolus which looks
like a dark spot in a cell. The nucleolus makes ribosomes, which make proteins.
• The nucleus is surrounded by two membranes that forms structure called the nuclear envelope. Nuclear envelope has many pores. Certain molecules move in & out of the nucleus through these pores.

Manufacturing Molecules• Proteins are important molecules in cells. • Proteins are made on small structures called
ribosomes. • Ribosomes do not have cell membranes & are
in the cell’s cytoplasm. They also attach to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
• Rough ER is where protein is made.• Smooth ER has no ribosomes and is where
lipids like cholesterol is made. Smooth ER is important because it helps remove harmful substances from a cell.

Processing Energy• All living things require energy to in order to survive.
Cells process some energy in special organelles.• Two organelles that process energy through chemical
reactions are: mitochondria and chloroplasts (in plant cells only).
• In mitochondria the energy made is stored in molecules called ATP. ATP is the fuel for cell jobs such as: growth, cell division & material transport.
• Plant cells & some protists like algae contain organelles called chloroplasts. Chloroplasts use light energy & make food (sugar called glucose) through a process called photosynthesis. The sugar contains stored chemical energy & releases it when the cell needs it.

Processing, Transporting & Storing Molecules
• The golgi apparatus (looks like a stack of pancakes) is near the ER in a cell. It prepares proteins to do their jobs in the cell and then puts the proteins in little packages called vesicles.
• The vesicles then transport substances from one area in the cell to other areas. In animal cells these vesicles are called lysosomes.
• Some cells haves have saclike structures called vacuoles. Vacuoles store food, water & waste material. A typical plant cell usually has one large vacuole (central vacuole). Some animal cells have many small vacuoles.