Cell Membrane
Transcript of Cell Membrane

Cell Membrane and Transport
Ariel Sacco
Ashlee Heidgerd Sidney Hardie

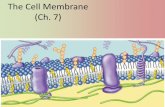
Cell Membrane• It is composed of lipids, proteins, and
carbohydrates.• It is a bilayer of phospholipids molecules.• The water soluble phosphates are the
heads on the membrane.• The water insoluble fatty acids are the tails
inside the membrane.• Proteins function as receptors on the
surface and form passageways for ions and molecules.
• It is the outermost layer of the cell.

Fluid Mosaic Membrane Model
Hydrophobic Region
Hydrophilic Region
Carbohydrate Side Chain
Glycoprotein
Integral Protein
Phospholipid
Hydrophobic Region
Hydrophilic Region
Transmembrane Protein

Diffusion• In the body, diffusion exchanges
oxygen and carbon dioxide.• It’s the movement of molecules
of ions from higher concentration to lower concentration


Facilitated Diffusion
• Special carrier molecules move substances through the membrane.
• It moves substances from higher concentration to lower concentration


Osmosis• The diffusion of water molecules
from higher water concentration to lower water concentration through a permeable membrane.
• The osmotic pressure increases as the number of particles are dissolved.
• Cells lose water when in hypertonic solutions and gain water in hypotonic solutions.


• The Na K pump is an example of endocytosis and exocytosis because during this process potassium ions are diffusing out of the cell and the sodium ions are diffusing in to the cell.
PUMP


Endocytosis• It conveys relatively large particles into a cell.• It occurs in three forms which are pinocytosis,
phagocytosis, receptor mediated endocytosis.– Pinocytosis – cells take in tiny droplets of
liquid from their surroundings– Phagocytosis – the cell takes in solids from
their surroundings– Receptor mediated endocytosis – protein
molecules are drawn into the cell by receptors


Exocytosis• It releases substances that were
stored in the cell.• Transcytosis – it combines
endocytosis and exocytosis to transport a particle across the cell.

The End