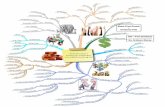
Ccna 1 Mind Map
Transcript of Ccna 1 Mind Map

[Type text]
7. Application
6. Presentation
5. Session
4. Transport
3. Network
2. Data Link
1. Physical PDU: bits
Notes: different media (copper, fiber, wireless)
advantages/disadvantages of each kind. When to use ST/Cross?
And how to tell the difference between them.
Protocols:
TCP UDP
OSI Reference
Model
• This layer serves as the source and destination of
communications across data networks.
• Directly accessing the underlying processes that
manage and deliver communication to the human
network.
• Enabling users to interact with the data network in a
way that is meaningful and effective.
Dividing data received from an application into segments
Adding a header to identify and manage each segment
Using the header information to reassemble the segments
back into application data
Passing the assembled data to the correct application
Enabling data to be directed to the correct application
running on end devices using port numbers.
Carrying data from one host to another regardless of
the type of data.
Layer 3 IP routing does not guarantee reliable
delivery or establish a connection before data is
transmitted. This connectionless and unreliable
communication is fast and flexible, but upper layers
must provide mechanisms to guarantee delivery of
data if it is needed.
Preparing Network layer packets for
placement onto the physical media that
transports data.
Encoding the bits for transmission and decoding them at the
destination.
Describing the physical, electrical, and mechanical
characteristics of the physical media and connectors that
interconnect network devices.
Various media and Physical layer protocols have different
data-carrying capacities. Raw data bandwidth is the theoretical
upper limit of a bit transmission. Throughput and goodput are
different measures of observed data transfer over a specific
period of time.
PDU: Data Stream
Protocols:
DNS: used to resolve Internet names to IP addresses.
HTTP: used to transfer files that make up the
Web pages of the World Wide Web.
SMTP: used for the transfer of mail messages
and attachments (MUA MTA, MTA MTA)
POP: mail delivery protocols. They deliver e-
mail from the e-mail server (MDA) to the client
(MUA)
Telnet: terminal emulation protocol used to
provide remote access to servers and
networking devices.
PDU: Segment
PDU: Packet Protocols: IPv4, IPv6
Notes:
L3 uses logical addresses to
identify and route traffic from one
network to another.
Network/subnet address.
Broadcast address. Host address.
Subnet mask.
Public vs. private addresses
Default Gateway
Purpose of the routing table
PDU: Frame
Notes:
L2 uses physical addresses to identify nodes and deliver
frames in the local network/segment.
Ethernet is the most widely used LAN technology.
CSMA/CD, CSMA/CA, Token passing