mind map 6
-
Upload
jalan-batu-tiga-dua -
Category
Documents
-
view
2.243 -
download
4
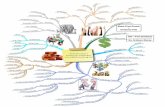
Transcript of mind map 6

INVESTIGATINGTHE
LIVING THINGSYEAR 6

1.1 Understanding that some animals live in groups and others live in solitary
ANIMALS
GROUPSEg:
lions, elephants,ants
SOLITARYEg:
turtles, eagles
Reasons
food safety
Reasons
Avoid competition-Food
- space
Interaction among animals cooperation
competition

1.2 Understanding that competition is a form of interaction among living things
INTERACTION AMONG LIVING THINGS
Cooperation- living together
factors reasons
competition
PLANTS
- Food- Water- Mate- shelter-Territory (space)
- limited food and water- mate for breeding- defending shelter- Defending territory
competition
factors reasons
- Sunlight- Water- Nutrient- Space
LIMITED
-sunlight-water- space- nutrient
ANIMALS



INVESTIGATINGINVESTIGATINGFORCE AND ENERGYFORCE AND ENERGY
YEAR 6YEAR 6

Force and EnergyForce and Energy
1.2 Understanding the effects of a force
1.2.1 Force can move a stationary object
1.2.2 Force can change the motion of an object
1.2.3 Force can change the shape of an object
1.1.2 State that force cannot be seen but its effects can be observed
1.1.1 State push and pull are forces
FORCE1.1 Understanding
that push andpull are forces

FRICTION
1. Definition
2. Effects
3. Ways to reduce/increase
4. Advantages and disadvantages
5. Design a fair test

FRICTION
definitionIs a type of force
(slows down a moving object)
WaysEffects
Produce heat
Opposes motion
Causes wear and tear
reduce increase
Advantages DisadvantagesHandlings objects
Movements
Sharpening knives
Lighting matches
Wear and tear
Heat
Slow down movements
Designing a fair test

INVESTIGATING FORCE INVESTIGATING FORCE AND ENERGYAND ENERGY
FORCEFORCE
1.3 Analysing friction
1. State that friction is a type of force
2. Describe the effects of friction
3. Describe ways to reduce friction
4. Describe ways to increase friction
5. State the advantages of friction
6. State the disadvantages of friction7. Conclude that friction occurs when two surfaces are in contact
8. Design a fair test to find out how different types of surfaces affect the
distance a trolley moves (variables)

An object which moves faster travels a longer distance in a given time
An object that moves faster takes a shorter time to travel a given distance
Problem solving
Which object moves faster?
State what SPEED is
Understanding Speed
A measurement of how fast an object moves
Speed = Distance / Time (Unit of speed : m/s, km/h)

INVESTIGATINGINVESTIGATINGMATERIALMATERIAL
YEAR 6YEAR 6

THEME: INVESTIGATING MATERIAL
FOOD SPOILAGE
Food spoilt
State the condition for
microorganisms to grow
microorganism can spoil food
Characteristic-unpleasant smell--unpleasant taste--changed colour--changed texture--mouldy
-Food cannot be eaten-Food unsafe to eat
-Air-Water-Nutrient-Suitable temperature-Suitable acidity
whatIdentify
FOOD PRESERVATION
-The food will last longer-The food is easy to store-To reduce wastage of food-Slow down the growth of microorganisms.-Retain freshness
Reason Why
importants

Food Preservation
Salting•Egg•Fish
Pasteurising•Milk
Freezing•Meat•Fish
Vacuum packing•Potato
•Peanuts
Drying•Fish
•prawn Boiling•CurrySmoking
•Fish•Banana
BottlingOr
Canning•Fruits
Cooling•Fruits
•vegetables
Waxing•Fruits
Pickling•Fruits
•Vegetables

2.1Waste ManagementEffects of improper
disposal of waste on the environment
Types
Sources
Disposal in a local area
Disposal
Decay
Non decay
proper
Throwing into the river, open
burning, littering,burying
Factories, food stalls, market, residential
Village-Throwing into the river,
open burning, littering,bury
Air pollution, water pollution, sickness, diseases, acid rain,
flash-flood
Daily collection of waste
Compost, recycle,
Incinerator, reuse
Town- collection of waste
in alternate days
Organic wasteWays
How
improper
Harmful effects
Improve Ways

LO. 2.2Understanding thatSome waste can decay
waste thatdo not decay
Advantages of waste decaying.
Disadvantages of waste decaying.
Predict what will happen tohuman and the environment
if waste do not decay.
Biodegradable
Organic Waste
State
Give examplescertain waste can decay
Microorganisms can cause waste materials to decay.
Materials
Plastic
Glass
Chemical waste

INVESTIGATINGINVESTIGATINGTHE EARTH AND THE THE EARTH AND THE
UNIVERSEUNIVERSEYEAR 6YEAR 6

what
MOON ECLIPSEMOON ECLIPSE SUN ECLIPSESUN ECLIPSE
ECLIPSEECLIPSE
Partial and total eclipse
Position of earth ,sun and moon and moonPosition of earth ,sun and moon and moon
How
Draw
Why it occurs?evolution , simulation
Predict the scenario of the Earth during the eclipse of the sun

INVESTIGATINGINVESTIGATINGTHE IMPORTANT OF THE IMPORTANT OF
TECHNOLOGYTECHNOLOGYYEAR 6YEAR 6

MACHINE
1.1 UNDERSTANDING SIMPLE MACHINE
1.2 ANALYSING A
COMPLEX MACHINE1.3
APPRECIACING THE INVENSION OF
MACHINES THAT MAKE LIFE EASIER
what
Identify
Predict
DEFINE SIMPLE MACHINE
SIMPLE MACHINES IN A
COMPLEX MACHINE
Observing a bicycle

MACHINE
SIMPLE MACHINE COMPLEX MACHINE
APPRECIACING THE INVENSION OF
MACHINES THAT MAKE LIFE EASIERPredict
Types• WHEEL AND AXLE• LEVER• WEDGE• PULLEY• GEAR• INCLINED PLANE• SCREW
device that allows us to use less force to make work
easier or fasterA COMPLEX MACHINE
IS MADE UP OF MORE THAN ONE SIMPLE MACHINE
EXAMPLESWheel barrow
Tin openerBicycle
conclusion
MACHINES CAN MAKE OUR LIVES
EASIER
HOWEXPLAIN
HOW LIFE IS WITHOUT MACHINES