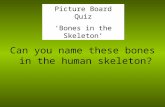
Can you name these bones in the human skeleton? Picture Board Quiz ‘Bones in the Skeleton’
Bones, Muscles and Skin Chapter 1...muscles and are attached to the bones of your skeleton and...
Transcript of Bones, Muscles and Skin Chapter 1...muscles and are attached to the bones of your skeleton and...

BELL RINGER
• Welcome Back!
• Please take out your new
packet of notes (Bones,
Muscles and Skin)
• Once you find your new seat
put your card on my front desk.
• Pick up a Body System Text
book by the emergency
window and tell Ms. Mello your
textbook number

BONES, MUSCLES AND SKIN
CHAPTER 1

BODY ORGANIZATION
•The human body is organized by the different components that work together to
perform all of the functions your body does.
•Going from the smallest to the largest, put these terms in order:
_____ Organs
_____ Tissues
_____ Cells
_____ Organ systems
1. The _____________ is the basic unit of structure and function in a living thing.
2. ______________ are a group of similar cells that perform the same function. There are four types:
• _______________________ composed of muscle cells and can contract or shorten
• _______________________ directs and controls electrical messages between the brain and body
• _____________________ provides support for the body and connects all its parts (ex. Bone & fat)
• _____________________ covers the surfaces, inside & out of your body for protection
1
2
3
4
Cell
Tissues
Muscle tissue
Nervous tissue
Connective tissue
Epithelial tissue

BODY ORGANIZATION
•The human body is organized by the different components that work together to
perform all of the functions your body does.
•Going from the smallest to the largest, put these terms in order:
_____ Organs
_____ Tissues
_____ Cells
_____ Organ systems
3. An ____________ is a structure that is composed of different kinds of tissue.
An organ performs a specific job. (ex. Heart, lungs, brain, stomach, skin etc…)
4. An ______________________ is a group of organs that work together to
perform a major function. For example your esophagus, stomach, intestines, and
colon are parts of the Digestive System.
1
2
3
4
Organ
Organ system

ORGAN SYSTEMSOn your white boards write down what organ system matches each number
Digestive =
Nervous =
Skeletal =
Respiratory =
Muscular =
Endocrine =
Excretory =
Circulatory =
1 23
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8

ORGAN SYSTEMS
Digestive- Breaks down food and absorbs nutrients
Nervous- Detects information from the environment and controls body functions.
Skeletal- Supports and protects the body.
Respiratory- Takes in oxygen and eliminates carbon dioxide.
Muscular- Enables movement of the body and internal organs.
Endocrine- Controls many body processes by means of chemicals.
Excretory- Removes wastes.
Circulatory- Transports materials to and from cells.
Brain pop bodysystems

HOMEOSTASIS
•All of the body systems work together to maintain homeostasis which is the
body’s tendency to keep an internal balance.
•Homeostasis is the process by which an organisms internal environment is kept
stable in spite of changes in the external environment.
•What examples of homeostasis can you think of that your body does?
Brain pop homeostasis

BELL RINGER
-Good morning, please take out your body
system homework, note packet and science
journal
-Answer the following questions in your science
journal
1. Put the following in order from smallest to
largest:
Tissues, cells, organelles, organ systems,
organs, nucleus, chromosome, gene
2. Which organ system matches this definition:
“Transports materials to and from cells”.
3. How is exercise an example of homeostasis?
4. How do you think the skeletal and muscular
system works together?

THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
•What is the purpose of the skeletal system?
1. To provide shape and support
2. Allow you to move
3. Protects your organs
4. Produces blood cells
5. Stores minerals and other materials for when your body needs them
• A newborn has about 275 bones while an
adult has 206 bones
• Where do these bones go?
• As we grow some of the bones in our bodies fuse
together like our skull

JOINTS OF THE SKELETON•Joints allow bones to move in different ways. There are immovable
and movable joints.
•Immovable joints- connect bones in a way that allows little to no
movement
•Moveable joints are held together by connective tissues called
ligaments and cartilage. Cartilage covers the ends of bones and
keep them from rubbing against each other.
• Types of Moveable joints
1. Hinge- forward and backward motion
2. Ball-and-Socket- greatest range of motion, can swing freely
3. Pivot- allows for one bone to rotate around another
4. Gliding- one bone to slide over another
Joints

TRY THESE MOVEMENTS!
1.Move your arm in a circle =
2.Lift a book from your desk =
3.Kneel down =
4.Wave your hand =
5.Twist your head from side to side =
Ball-and socket joint
Hinge jointHinge joint
Hinge and gliding joint
Pivot joint

BONE INJURIES1.Fracture- a break in the bone. Simple fractures the bone may be cracked
or completely broken into two or more pieces. Complex fractures is when
the bone sticks out through the skin.
2.Dislocation- When the end of a bone comes out of its joint.
3.Sprain- when ligaments are stretched too far and tear in places. Ankle
sprains are most common. Swelling may occur.
4.Osteoporosis- Mineral loss in the bones as people age which makes the
bones weak and easily broken. More common in women than in men. A
calcium rich diet can help avoid mineral loss.

THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
There are about 600 muscles in
your body. Muscles are divided into
those that are involuntary and those
that are voluntary.
•Involuntary muscles are ones that
we are not in conscious control of.
Some examples are the involuntary
muscles that control breathing and
digesting food.
•Voluntary muscles are ones that we
are in conscious control of. For
instance smiling and standing up
use voluntary muscles.

BELL RINGER
-Good morning, please take out your note packet and science journal-Answer the following questions in your science journal
1. Put the following in order from smallest to largest:
Tissues, cells, organelles, organ systems, organs, nucleus, chromosome, gene
2. Which organ system matches this definition:“Controls many body processes by means of chemicals.”
3. Give an example of voluntary muscle?
4. Where is cardiac muscle found?

7TH PERIOD BELL RINGER
-Good afternoon please take out your note packet
-Answer the following questions on a scrap piece of paper found at your squad.
When you are done make sure your name is on it and turn it into the bin. These
will be graded!
1. Put the following in order from smallest to largest:
Tissues, cells, organelles, organ systems, organs, nucleus, chromosome, gene
2. Which organ system matches this definition:
“Controls many body processes by means of chemicals.”
3. Give an example of voluntary muscle?
4. Where is cardiac muscle found?

THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
Your body has three types of muscle
tissue.
1. Skeletal Muscle- these are voluntary
muscles and are attached to the bones
of your skeleton and provides the force
that moves your bones.
• Muscle cells contract when they receive messages from the nervous
system. Muscles work with skeleton to allow movement and coordination
2. Smooth Muscle- these are
involuntary muscles and work
automatically. They react more slowly to
control the movements of internal
organs and blood vessels
3. Cardiac Muscle – this is involuntary
muscle found only in your heart.

THE SKIN!What is the largest organ in the human body?
• If your skin was stretched out flat it would cover an area larger than 1.5 m^2
which is about the size of a twin mattress.
Functions of the skin
• Covers and protects the body from injury, infection and water loss
• Regulates body temperature (blood vessels enlarge when hot and get smaller
when cold. Also through sweating)
• Eliminates wastes (through sweating)
• Gathers information about the environment (nerves detect pain, pressure, and
temperature).
• Produce vitamin D (when absorbing sunlight, required for Calcium absorption).

THE EPIDERMIS•The first layer of skin is called the epidermis and is the outermost layer.
•There are no nerves of blood vessels in this layer.
•Many of the cells on the epidermis are dead and every time you rub your hands
together, you lose thousands of dead skin cells and any bacteria on them.
•Some cells in the epidermis produce melanin, the pigment or colored
substance that give skin its color. Melanin protects the skin from burning.

THE DERMIS
•The dermis is the inner and second layer of the skin. It is below the epidermis but
above a layer of fat.
•The dermis contains nerves and blood vessels, sweat glands, hairs, and oil glands.
•Sweat glands produce perspiration, which reaches the skins surface through
openings called pores. Strands of hair grow within the dermis in structures called
follicles.

2 POINT DISCRIMINATION
-You are going to test the sensitivity of your skin on your inner arm and hands!
- You will take two paper clips and move one away slowly by picking it up and putting
it down again on the skin. When you finally feel two different “points” you will use a
ruler to measure the distance

CHAPTER 2
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM

BELL RINGER
How does your teeth and saliva work together to digest food.

THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
1.Break down food into
molecules the body can
use
2.The molecules are
absorbed into the blood
and carried throughout the
body
3.Wastes are eliminated
from the body
TC
There are three primary
functions for the
digestive system
Metabolism- the sum of all of the chemical
processes in the human body

THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM•Digestion- the process by which
your body breaks down food into
small nutrient molecules. There are
two kinds of digestion
• How do you digest food?
TC
•Mechanical Digestion- when
you bite and chew food
•Chemical Digestion –
chemicals produced by the
body break foods into smaller
chemical building blocks
• Absorption- is the process by which nutrient
molecules pass through the wall of your
digestive system into your blood

THE DIGESTIVE JOURNEY
•The mouth- both mechanical and
chemical digestion begin in the mouth.
•Mechanical digestion in the mouth is
performed by your
____________________
•Chemical digestion in the mouth is
performed by your
______________________.
•Saliva is an enzyme which are proteins
that speed up chemical reactions in
the body.
Teeth
Saliva
TC

THE DIGESTIVE JOURNEY
•As you swallow the epiglottis
closes off your windpipe,
preventing food from entering.
•The food then enters the
esophagus which is a muscular
tube that connects the mouth to
the stomach. Food remains in
the esophagus for only about 10
seconds.
•After food enters the
esophagus, it pushes the food
toward the stomach.
TC

THE DIGESTIVE JOURNEY
•In the stomach mechanical
and chemical digestion occur
•Mechanical digestion-
the smooth muscle in the
stomach contracts to
produce a churning
motion and mixes the
food with fluids
•Chemical digestion- The
stomach contains
digestive juice that
contains the enzyme
pepsin and hydrochloric
acid
TC

FINAL DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION
•After the liquid leaves the
stomach it enters the small
intestine where most
chemical digestion takes
place.
•Almost all chemical
digestion and absorption of
nutrients takes place in the
small intestine and the
nutrients from food will
eventually enter the
bloodstream.
•This is completed with the
help from the liver,
gallbladder and pancreas. Dr Bionics Digestive System
TC

THE LARGE INTESTINE
•Once the liquid food
material reaches the end of
the small intestine most of
the nutrients have been
absorbed. The remaining
material moves into the
large intestine
• The water from the food material is absorbed into the bloodstream and the remaining material is readied for elimination from the body.
• The large intestine ends at the rectum where waste material is compressed into solid form and is then eliminated from the body through the anus.
TC
Dr Bionics Digestive System

PUT THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TERMS IN ORDER
•Esophagus
•Mouth
•Small intestine
•Large intestine
•Stomach
•Bloodstream
TC

BELL RINGERYou want to have a snack. You can either have one large
apple or three twix minis. Which one will provide more
energy?
Calories = 130
Total Fat = 0 g
Total Carbohydrate = 34 g
Protein = 1g
Calories = 150
Total Fat = 7 g
Total Carbohydrate = 20 g
Protein = 1g

FOOD & ENERGY
•Nutrients are the substances in the food that provide the
body with everything it needs to carry out all of its
essential processes.
TC
Food provides your body with the needed materials for
growing, repairing tissues and the energy to live.
• There are six groups of nutrients necessary for human health• Carbohydrates• Fats• Proteins• Vitamins• Minerals• Water

FOOD & ENERGY
When nutrients are used the amount
of energy they released are
measured in units called calories.
Calorie- the amount
of energy needed to
raise the temperature
of one gram of water
by one degree
Celsius
Calorie Ted-ed
You need to eat a certain number of Calories a day to meet your body’s energy needs. Your daily energy requirements depends on many factors• Level of physical activity• Age • Gut bacteria• Length of digestive track• Medical conditions• Gender• Metabolism

6 TYPES OF NUTRIENTS
1. Carbohydrates- Provide short acting energy and the raw materials to
make cell parts
2. Fats- Provide long-lasting energy as well as form part of the cell
membrane and supports your internal organs and insulates your body.
3. Proteins- needed for tissue growth and repair. Also they plan an important role in chemical reactions with cells
4. Vitamins- are helpers in a variety of chemical reactions in the body.
Example Vitamin K helps your blood to clot.
5. Minerals- nutrients that are not made by living things. They are present in soil and are absorbed by plants through their roots… Then we eat the plants.Example calcium is needed for strong teeth and bones.
6. Water- most important nutrient because the body’s vital processes such as the breakdown of nutrients take place in water.
Vitamins Ted-ed

FOOD LABELSBy law every food item must have listed specific nutritional information on it. This information are called food labels.
Food Labels allow you to evaluate a single food as well as to compare the nutritional value of two different foods. There are 4 important parts to a food label.
1. Serving Size- The size of a single serving AND the number of servings in the container.
1.
2.
2. Calories- How much energy you get from one
serving of this food including how many calories
from fat.
3. Percent Daily Value- How the nutritional
content of one serving fits into the recommended
diet for a person following 2,000 calories a day
3.

FOOD LABELS
By law every food item must have listed specific nutritional information on it. This information are called food labels.
Food Labels allow you to evaluate a single food as well as to compare the nutritional value of two different foods. There are 4 important parts to a food label.
4.
4. Ingredients- are listed in order by
weight, starting with the main ingredient.
Here you can find if substances that you
are allergic to or do not want to eat are in
the food item

1. FOOD LABEL
1. How many servings of this
food are there in the entire
container?
2. How many calories are
there in two servings of this
food?
3. How many servings of this
food would a person need
to eat to get 50% of the
recommended daily value
of total fat?
8 servings
460 calories
5 servings