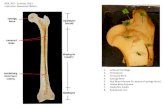
Bone - Academic Computer Centeracademic.pgcc.edu/~aimholtz/AandP/LectureNotes/ANP1_Lec/Bone... ·...
Transcript of Bone - Academic Computer Centeracademic.pgcc.edu/~aimholtz/AandP/LectureNotes/ANP1_Lec/Bone... ·...
Endosteum
Endosteum
Osteoprogenitorcell
Osteoblasts
Nuclei
Osteoclast
Osteocyte
Spongy bone
Medullary cavity
Spongy bone
Medullary cavity
Endosteum lining bony canals and covering trabeculae
Perforating canal
Perforating fibers
Periosteal blood vesselPeriosteum
Osteon
Centralcanal
Lamellae
Compactbone
Spongy bone
Osteon Concentric layers of bone matrix
Surrounding a central canal
Lamellae
Microscopic Structure of Long Bone
Centralcanal
Osteon
Collagenfiberorientation
Concentriclamellae
Nerve
Vein Artery
Bone Matrix
⅓ Osteoid
Collagen + Ground substanceProvides flexibility & Resists tension
⅔ Hydroxyapatite -CaP0
4 and Ca(OH)
2
Provides hardness & Resists compression
Cartilagegrows here.
Cartilageis replacedby bone here.
Long Bone – Growth in LengthInterstitial growth
Calcified cartilagespicule
Osseous tissue(bone) coveringcartilage spicules
Resting zone
Osteoblast depositingbone matrix
Proliferation zoneCartilage cells undergo mitosis.
Hypertrophic zoneOlder cartilage cells enlarge.
Ossification zoneNew bone formation is occurring.
Calcification zoneMatrix becomes calcified; cartilage cells die; matrix begins deteriorating.
1
2
3
4
Childhood Growth Hormone
Stimulates epiphyseal plate activity - cartilage production and cartilage conversion to bone
Sex Hormones Estrogen/TestosteroneStimulates epiphyseal plate activity. It causes FAST conversion of cartilage to bone and SLOW production of new cartilage.
Articular cartilage
Epiphyseal plate
Bone isresorbed here.
Bone isresorbed here.
Bone is addedhere.
Bone Remodeling (Appositional Growth)
Bone Deposition/Resorption depends on Blood [Ca2+]
↓ Blood [Ca2+]
Increased intestinal Ca2+ absorption
Parathyroid glands release PTH
Decreased urinary Ca2+ excretion
Increased osteoclast activity