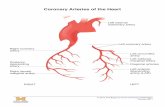
Blood supply of the heart. Tow coronary arteries arise from the aortic sinuses : The right...
-
Upload
elisabeth-pitts -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of Blood supply of the heart. Tow coronary arteries arise from the aortic sinuses : The right...


Blood supply of the heart . Tow coronary arteries arise
from the aortic sinuses :
The right coronary artery . The left main coronary artery .


The right coronary artery branches into :
Right marginal artery . Posterior descending artery .
The right coronary artery supplies right atrium ,right ventricle and bottom portion of both ventricles and back of the septum .

The left main coronary artery quickly branches into two large arteries :
Circumflex artery . Left anterior descending artery .
The left coronary artery supplies left atrium, left ventricle and the front of the septum.

Coronary artery disease (CAD) Coronary artery disease is one of the most
common and serious effects of aging.
Atherosclerosis narrow the passageway for the movement of blood.
This stenosis often leads to eventual
blockage of the coronary arteries and a “heart attack” .


Risk factors
Uncontrollable :
gender
Hereditary
Race
Age
controllable : hypertension
Diabetes
hyperlipidemia
Smoking
Physical activity
Obesity
Stress and anger

Presentation of patient with CAD :
Asymptomatic (silent CAD). Stable angina . Unstable angina . Myocardial infarction .

Asymptomatic CAD
It may not be diagnosed until a person shows signs and symptoms of a heart attack, heart failure, or an arrhythmia .
It is usually associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus .

Stable angina
Coronary ischemia is due to imbalance between blood supply and oxygen demand .
It occurs when oxygen demand exceeds blood supply .

Clinical features
Chest pain or substernal pressure lasts less than 10-15 minutes .
brought on by exertion or stress .
relived by rest or nitroglycerin .

Diagnosis Stress tests .a. Stress ECG : recording ECG before, during, and after
exercise on a treadmill . Positive findings include ST segment depression, chest pain, hypotension or ventricular arrhythmias .
b. Stress ECHO : performed before and immediately after exercise . It is positive if there is wall motion abnormality not present at rest .
c. Pharmacologic stress test : IV adenosine or dobutamine can be used to induce cardiac stress instead of exercise and combined with ECG, ECHO or nuclear perfusion imaging .

Cardiac catheterization with coronary arteriography .
most accurate method of identifying the presence and severity of CAD .
Main purpose is to identify patients with significant CAD to determine the need of revascularization .

Treatment
Risk factor modification :
Quit smoking . Control hypertension . Control diabetes . Control hyperlipidemia . Weight loss and exercise . Reduce intake of saturated fat and
cholesterol .

Medical therapy .
Aspirin. Beta blockers . Nitrates . Calcium channel blockers . ACE inhibitors and diuretics if heart
failure present .

Revascularization .
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) .
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) .

Unstable angina
Blood supply is decreased secondary to reduced resting coronary flow .
In contrast to stable angina , oxygen demand is unchanged .

Clinical features
Angina at rest . Chronic angina with increasing
frequency, duration or intensity of the chest pain .
New onset angina that is sever and worsening .

Diagnosis
History . Stress tests . Cardiac catheterization with
coronary arteriography . Diagnostic workup to exclude
myocardial infarction .

Treatment Hospital admission Medical therapy : Oxygen Morphine Nitrates Aspirin Beta blockers
Catheterization/Revascularization .

After the acute treatment
Continue aspirin, beta blockers and nitrates .
reduce the risk factors .

Myocardial infarction
Necrosis of the myocardium as a result of an interruption of blood supply .
Most patients with MI have a history of CAD or arrhythmias .

Clinical features
Asymptomatic . Chest pain . substernal crushing pain radiating to
the neck, jaw or left shoulder and arm .
Other symptoms like dyspnea, weakness, syncope, nausea and vomiting .

Diagnosis
ECG . Cardiac enzymes ( CK-MB and
Tropnins ).

Treatment Admission to the CCU . Medical therapy : Oxygen Morphine Nitrates Aspirin Beta blockers ACE inhibitors Statins Heparin

Revascularization .
Benefit is highest if performed early .
Should be considered in all patients .
Two forms of revascularization : thrombolysis or PCI .

Angioplasty
a non-surgical treatment used to open narrowed coronary arteries to improve blood flow to the heart.
It can be performed during a diagnostic cardiac catheterization when a stenosis is identified, or it may be scheduled after a catheterization has confirmed the presence of coronary artery disease.

Once the catheter is in place, one of these interventional procedures is performed to open the artery:
balloon angioplasty . Balloon angioplasty with stenting. Drug-eluting stents (DES) . rotablation . cutting balloon.

Balloon angioplasty (PTCA)
a small balloon at the tip of the catheter is inserted near the stenosed area of the coronary artery.
When the balloon is inflated, the plaque is compressed against the artery walls and the diameter of the blood vessel is widened to increase blood flow to the heart .
sometimes complicated by vessel recoil and restenosis .

Balloon angioplasty with stenting (PCI) balloon angioplasty is performed in
combination with the stenting procedure. stent is a small, metal mesh tube that
acts as a scaffold to provide support inside the coronary artery.
the balloon is inflated and the stent expands to the size of the artery and holds it open.
The balloon is deflated and removed, and the stent stays in place permanently.

Drug-eluting stents (DES)
Drug-eluting stents contain a medication that is actively released at the stent implantation site.
Drug-eluting stents have a thin surface of medication to reduce the risk of restenosis.

Rotablation (Percutaneous Transluminal Rotational Atherectomy or PTRA) A special catheter, with an acorn-shaped,
diamond-coated tip, is guided to the point of narrowing in the coronary artery.
The tip spins around at a high speed and grinds away the plaque on the arterial walls.
This process is repeated as needed to treat the blockage and improve blood flow.
microscopic particles are washed safely away in your blood stream and filtered out by your liver and spleen.

Cutting balloon
The cutting balloon catheter has a balloon tip with small blades.
When the balloon is inflated, the blades are activated. then, the balloon compresses the plaque into the arterial wall.

Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)Indication for surgery :
Left main artery disease or equivalent . Triple vessel disease . Abnormal Left Ventricular function . Failed PCI . Immediately after Myocardial Infarction (to help
perfusion of the viable myocardium). Life threatening arrhythmias caused by a previous
myocardial infarction. Occlusion of grafts from previous CABGs.

Most common arteries bypassed:
Right coronary artery
Left anterior descending coronary artery
Circumflex coronary artery

Conduits used for bypass :
Saphenous vein used for bypassing right coronary artery and circumflex coronary artery .
Internal mammary artery (IMA) used for bypassing left anterior descending coronary artery .

Steps of the procedure
Harvesting the grafting vessle . Median sternotomy . Heparin administered to minimize
clotting Cardiopulmonary bypass . Cannulation of:
Ascending aortaRight atriumFemoral artery

o Cold potassium cardioplegia .o Bypass of arteries by making
Incision in the target artery .o Anastamosis of graft with artery .o On completion of the vascular
anastomoses, the aorta is unclamped.
o anticoagulation is reversed by giving protamine.


Advantages
Relief of angina in 90% of patients
80% angina free after 5 years
Survival about 95% after 1 year
Low chance of restenosis

Disadvantages
2-3 days in ICU, 7-10 day total hospital stay .
3-6 month full recovery time .5-10% have post-op
complications .High cost .

Thank you !