Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]
-
Upload
deepasridhar -
Category
Documents
-
view
131 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]
![Page 1: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/1.jpg)
17th NATIONAL SAHODAYA
CONFERENCE19th - 21st DECEMBER,
2010Vineet Joshi
Chairman, CBSE
![Page 2: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/2.jpg)
Section I - OVERVIEW
Section II- MANAGING CHANGE FOR BETTER LEARNING
Section III- INITIATIVES
Section IV- ROAD AHEAD
![Page 3: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/3.jpg)
SECTION I –
OVERVIEW
![Page 4: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/4.jpg)
4
41 School Boards in India3 National Boards• 2 formal education sector• 1 non formal education sector
CBSE – 11,040 school 24 countries
▪Private ▪Kendriya Vidyalayas ▪State Government ▪Navodaya Vidyalayas
▪ CTSA ▪Others
CBSE : National Board
a) Kendriya Vidalayas - 940b) JNV - 543c) Govt. School - 1857d) Independent Schools - 7641e) CTSA - 59
![Page 5: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/5.jpg)
5
CBSE SCHOOLS-11,040
665
504
615
34703
98
173
853
330
198
1299330
181
288168
280
165
388
842
313
49
19
29
182
252
24
242
07
09
08
1773
140
Andhra Pradesh 284Arunachal Pradesh 244Assam 169Bihar 362Chhattisgarh 362Goa 9Gujarat 209Haryana 912Himachal Pradesh 177Jammu & Kashmir 100Jharkhand 294Karnataka 408Kerala 845Madhya Pradesh 646Daman & Diu 5Delhi 1800Lakshadweep 4
Maharashtra 348Manipur 50Meghalaya 19Mizoram 8Nagaland 30Orissa 192Punjab 682Rajasthan 544Sikkim 183Tamil Nadu 258Tripura 24Uttar Pradesh 1358Uttarakhand 338West Bengal 169A&N 100Chandigarh 140D&N Haveli 3Puducherry 11
![Page 6: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/6.jpg)
6
SCHOOLS ABROAD157 SCHOOLS IN 23 COUNTRIES
• Bangladesh 01
• Bahrain 06
• Burma 01• Ethiopia 02• Iran 01• Saudi Arabia
25• Kuwait 16• Libya 02• Oman 11• Afghanistan 01• Nepal
12• Qatar
07• Tanzania 01• Nigeria
01• Uganda 01• Malaysia 02• Japan 02
• West Africa 01• U.S.S.R.
01• Yemen
01• Indonesia 01• Singapore 04• United Arab Emirates 57
![Page 7: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/7.jpg)
CHANGING PARADIGMS – SIR KEN ROBINSON
![Page 8: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/8.jpg)
GLOBAL CHALLENGES
![Page 9: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/9.jpg)
CONTEXT OF LEARNERS AND TEACHERS
![Page 10: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/10.jpg)
![Page 11: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/11.jpg)
CHANGING LEARNER PROFILE
![Page 12: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/12.jpg)
21ST CENTURY WORKFORCE
![Page 13: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/13.jpg)
CHANGING EMPLOYABILITY SKILLS
![Page 14: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/14.jpg)
▪
▪
CHANGING EMPLOYABILITY SKILLS
![Page 15: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/15.jpg)
JOBS IN THIS NEW MILLENNIUM REQUIRE A
STUDENT TO BE AN EFFECTIVE:
Adapted from Tom Friedman’s book: The World Is Flat (2006)
![Page 16: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/16.jpg)
WOMB TO TOMBLife long Learning
Both formal and non-formal institutions
SCHOOLS FORMAL
DISSOLVING BOUNDARIES Canteens
PlaygroundCorridors
Labs
Non-formal institutions
Media Electronic
• TV
• Movies
• Internet
Print• Newspaper• Journals • Magazine
Peer Learning•Frie
nds
•Homes
•Siblings
•Seniors
•School
•play
Elders
Nuclear
Parental time
Monitoring
Social Network sites
Classrooms
Travel
Home
Annual/
Sports Day
WHEN???AND
WHERE???
Virtual Interaction
![Page 17: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/17.jpg)
1. Personal awarenessSelf-concept, identity,realistic self-esteem,
self-direction, autonomy
3. Task awarenessUnderstanding,
using, constructing, communication skills in context
2. Process awareness:
learningMonitoring, reflection,
cooperation, critical self-assessment
Experientiallearning
Teacher’s professional awareness
Professional autonomy, communicative action,commitment to learning
Culture of learning institution and society
Quality of learning environment, culture of learning community, collaboration between participants
Experience
ReflectApply
Conceptualize
How??
![Page 18: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/18.jpg)
SECTION – II
MANAGING CHANGE FOR BETTER LEARNING
![Page 19: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/19.jpg)
MANAGING CHANGE FOR
BETTER LEARNING
SCHOOL BASED ASSESSMENT
ADDRESSING RESISTANCE TO
CHANGE
SUPPORTING TEACHERS IN
IMPLEMENTING CCE
TEACHING EMPOWERMENT
EMBEDDING TECHNOLOGY IN
CCE ENVIRONMENTSTRENGTHENING
FORMATIVE LEARNING
DIMENSIONS OF CO-SCHOLASTIC
SKILLS
APTITUDE AND PROFICIENCY – GOING BEYOND ACHIEVEMENT
RESPONDING TO DIVERSITY
THROUGH CCE
LIFE SKILLS EDUCATION
![Page 20: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/20.jpg)
Examination Reforms - CCEA Historical Perspective
Hunter Commission 1882
Sadler Commission 1917
Hartog Commission 1929
Sargeant Plan 1944
Mudaliar Commission 1952,53
National Policy on Education 1979
Review 1986
NCF 2000 NCF 2005
Position Paper NCERT 2006
Central Board Of Secondary Education Introduces Continuous Comprehensive Evaluation
2009 Class X Board Exam Optional 2011
![Page 21: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/21.jpg)
Scheme - CCE-3 partsPart - I
Scholastic Assessment
1A 1B
Formative Assessment (FA) Summative Assessment (SA)
Part - 2
Co-scholastic Areas
2B2A
Work Experience, ArtEducation, Health Education
Ist Term(April-Sept) IInd Term
(Oct-March)
10% marks10% marks10% marks10% marks
At the end of Ist Term
20% marks
At the end of IInd Term
40% marks
Life SkillsAttitudes and Values
Part - 3
Co-scholastic Activities
3B3A
Literary and Creative Activities
Health and Physical Education
![Page 22: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/22.jpg)
ViolencesNPE – 1986, POA – 1992
NCF - 2005PURPOSE
Improve teaching learningDevelop learning abilities through
activities rather then exams
CCE
FEATURESCovers all aspects
Continuous – Continual Comprehensive Personal
Scholastic Curricular + Co-scholastic Social LS
TechniquesObservationOral
ToolsObservation scheduleOral questionsDiagnostic test
TechniquesOralWritten
ToolsOral questionsQuestion paperAssignmentprojectDiagnostic test
TechniquesOralWrittenPractical
ToolsOral questionsQuestion paperAssignmentProjectDiagnostic testActivity/experiment
TechniquesWrittenPracticalViva voce
ToolsQuestion paperAssignmentProjectPractical (activity / experiment)Oral questions
TechniquesWrittenPracticalViva voce
ToolsQuestion paperAssignmentProjectPractical (activity / experiment)Oral questionsPortfolio
Classes I & II
Classes III,IV & V
Classes VI to VIII
Classes IX & X
Classes XI & XII
5-point gradingA* Outstanding 90-100A Excellent 75-89B Very Good 56-74C Good 35-55D Scope for improvement Below 35
Classes I - V
Classes VI – XII
5-point grading
Tools•Questions•ObservationSchedule•Interview schedule•Checklist•Rating scale•Anecdotal records•Document analysis•Tests andInventories•Portfolio analysis
Co-scholastic AreasLife SkillsWork EducationVisual & Performing ArtsAttitudes & Values
![Page 23: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/23.jpg)
![Page 24: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/24.jpg)
![Page 25: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/25.jpg)
![Page 26: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/26.jpg)
![Page 27: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/27.jpg)
GRADING SCALE FOR SCHOOL ASSESSMENT
Assessment areas:
Part 1 A : Scholastic 9Part 1 B : Scholastic 5
Part 2 : Co-Scholastic Part 2 A : Life Skills 5Part 2 B : Attitudes & Values 3
Part 3 : Co-Scholastic Part 3 A: Co-curricular Activities 3Part 3 B :Health & Physical Education 3
GRADING SCALE (Point)
![Page 28: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/28.jpg)
ADDRESSING
RESISTANCE
TO CHANGE
![Page 29: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/29.jpg)
RESISTANCE TO CHANGE
![Page 30: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/30.jpg)
• Emotional• Cognitive• Intentional• Imagined• Healthy resistance• Insidious resistance – placid and acceptable
on the surface but instigate others behind the back
TYPES OF RESISTANCE
![Page 31: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/31.jpg)
• Habit
• Inertia
• Fear of the unknown
• Absence of the skills required to tackle the
change, diligence and hard work
CAUSES OF RESISTANCE
![Page 32: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/32.jpg)
ADDRESSING RESISTANCE
• Addressing the concerns- firmly and quickly• Open communication channels• Active listening• Evidences, facts and research support• Using media-both print and electronic• Positive and reinforcing messages
![Page 33: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/33.jpg)
TEACHER
EMPOWERMENT
![Page 34: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/34.jpg)
![Page 35: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/35.jpg)
Let’s talk about Empowerment
The definition of Empower is:
To Enable or PermitTo Authorize or AllowTo Sanction
Empowerment has to start with someone and that is usually a Leader. But TOP DOWN management is not what we’relooking for. A Leader must have a Visionbut must be able to Give that Vision tothose who can make it happen – the staff!
Vision Articulate
Disseminate
Goal
![Page 36: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/36.jpg)
Training And Empowerment
• In-service Teacher Training programme through Sahodayas.
• Empowerment of Heads of Institutions in collaboration with top business schools and also with NUEPA.
• Theme based regional and national level Sahodaya conferences.
![Page 37: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/37.jpg)
INDUCTION PROGRAMMES FOR THE PRINCIPALS OF NEWLY AFFILIATED
SCHOOLS -2010
S. No. Dates Venue No. of Participants
1. 14.9.10 Delhi Public School, Ghaziabad, Vasundhara 27
2. 22.9.10 Kothari International School, Noida 37
3. 28.9.10 Centre Point School, Nagpur 60
4. 12.10.10 Delhi Public School, Bhilai, Chhatisgarh 31
5. 21.10.10Scholars Home Senior Secondary School, Dehradun 30
6. 25.10.10 B. B. U. L. Jain Vidyalaya, Bangalore 67
7. 08.11.10 Cambridge International School, Jalandhar 42
8. 15.11.10 Delhi Public School, Guwahati 17
9. 22.11.10 Indore Public School, Indore 29
10. 29.11.10 Delhi Public School, Patna 18
TOTAL 358
![Page 38: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/38.jpg)
CAPACITY BUILDING PROGRAMMES FOR THE
PRINCIPALS• Indian Institute of Management, Ahmedabad – 10 years• National University of Educational Planning and Administration, New
Delhi – 10 years • Indian Institute of Management, Bangalore – 9 years • Indian Institute of Management, Lucknow – 5 years• Indian Institute of Management, Kolkata – 3 years
First time this year• Indian Institute of Management, Kozhikode • Indian Institute of Foreign Trade• Educational Technology and Management Academy, Gurgaon• Management Development Institute, Gurgaon• International Confederation of Principals, Victoria, Australia
![Page 39: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/39.jpg)
BENEFITS OF TEACHER EMPOWERMENT
Enhanced participation in school decision making
Enhance teachers' commitment
Enhanced expertise
Enhanced student achievement
Enhanced student performance
Improvement in instruction and pedagogical quality
![Page 40: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/40.jpg)
Road map of Teacher competences for a
Knowledge Based Secondary School
1.Ac
ting
ethi
cally
and
resp
onsi
bly
in th
e pe
rfor
man
ce o
f fun
ction
s
2.Bec
oming i
nvolve
d in an
individual
and co
llecti
ve
projec
t of p
rofes
sional
develo
pmen
t
3. Acting critically as a
professional, interpreting the
objects of knowledge or
culture in performing
one’s functions
4. Designing teaching-learning situations for the subject matter to be learned5. Directing teaching-learning
situations for the content to be
learned
6. Evaluating the progress of learning
7. P
lann
ing,
org
anizi
ng a
nd
supe
rvisi
ng th
e w
ay th
e
grou
p-cla
ss w
orks
8. Adapting te
aching to th
e
students d
iversity
9. Integrating new technologies
into the preparation and
development of teaching-learning
10. Communicating clearly and
correctly in the teaching language
11. Co-operating with the school
staff, with parents, and with
the various social agents
12. Working in co-operating
with the other m
embers
of the pedagogical team
Level - III
Level-II
LEVEL - I
LEVEL l : INITIAL TEACHER EDUCATIONLEVEL II: TEACHER INDUCTIONLEVEL III: PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT
![Page 41: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/41.jpg)
THE MASTER
It is related by a sufi master that, when he was a youth, he wanted to attach himself to a teaching master. He sought the sage, and asked to become his disciple.The teacher said: “You are not yet ready.” Since the young man was insistent, the sage said:” Very well, I will teach you something. I am going on a pilgrimage to Mecca. Come with me.” The disciple was overjoyed. “Since we are traveling companions,” said the teacher,” one must lead, and the other obey. Choose your role.” “I will follow, you lead,” said the disciple. “If you know how to follow,” said the master.The journey started and it started to rain. The master got up and held a covering over the disciple, protecting him. “But this is what I should be doing for you,” said the disciple.“I command you to allow me to protect you thus.” Said the sage.When it was day the young man said:” Now it is a new day. Let me be the leader, and you follow me.” The master agreed. “I Shall now collect brushwood, to make a fire,” said the youth.“You may do no such thing; I shall collect it,” said the sage.“I command you to sit there while I collect the brushwood!” said the young man.“You may do no such thing, “said the teacher,” for it is not in accordance with the requirements of discipleship for the follower to allow himself to be served by the leader.”And so, on every occasion, the Master Showed the Student what discipleship really meant, by demonstration.
![Page 42: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/42.jpg)
SUPPORTING TEACHERS IN
IMPLEMENTING CCE
![Page 43: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/43.jpg)
CCE : System of school-based evaluation of students that
covers all aspects of
Continuous Comprehensive
Learning Assessment periodic
Scholastic aspectsScholastic aspects include curricular areas or subject specific areasas
Co-scholastic aspectsCo-scholastic aspects include life skills,Co-curricular, attitudes and values
Students’ Development
![Page 44: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/44.jpg)
Website for disseminating Information
![Page 45: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/45.jpg)
![Page 46: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/46.jpg)
![Page 47: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/47.jpg)
CCE- SUPPORT MATERIAL
![Page 48: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/48.jpg)
![Page 49: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/49.jpg)
SUPPORT MATERIAL ONLINE
![Page 50: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/50.jpg)
DISASTER MANAGEMENT
Class - X
Class - IX
Class - VIII
![Page 51: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/51.jpg)
CBSE – Support – CENBOSEC - Quarterly Journals
51
![Page 52: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/52.jpg)
Report Book for Class IX
![Page 53: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/53.jpg)
CCE - CERTIFICATE OF SCHOOL-BASED ASSESSMENT
![Page 54: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/54.jpg)
![Page 55: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/55.jpg)
![Page 56: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/56.jpg)
![Page 57: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/57.jpg)
![Page 58: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/58.jpg)
![Page 59: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/59.jpg)
![Page 60: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/60.jpg)
![Page 61: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/61.jpg)
![Page 62: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/62.jpg)
EMBEDDING
TECHNOLOGY IN CCE
ENVIRONMENT
![Page 63: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/63.jpg)
ICT IN SCHOOLS
Introduction
• ICT - crucial resource in education.
• Children use computers from an early age and continue to university level.
• Children taught practical ICT skills that are transferable into the work place.
![Page 64: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/64.jpg)
Objectives of the ICT in schools
• Establish an enabling environment to promote the usage of ICT in schools.
• Enhance the learning levels of students in Mathematics, Pure Sciences, Social Sciences, Language and numerous Extra- Curricular activities
• Promote critical thinking and analytical skills by developing self –learning
• Enable students to acquire skills needed for the digital world for higher studies and gainful employment.
• Build capacity in teachers to upgrade their learning and teaching skills by using ICT tools.
![Page 65: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/65.jpg)
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES& CHALLENGES
rewriting the rules of engagement
![Page 66: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/66.jpg)
PhoneChannel http://www.digitalopportunity.org/article/archive/1072/
Interactive textbookshttp://www.phschool.com/social_studies/
Tablet PCs
http://www.communities.hp.com/online/blogs/highered/archive/2007/09/28/HPPost4561.aspx
Computerised tutor http://in.youtube.com/watch?v=lxUzKoIt5aM http://www.boloji.com/mahabharata/index.htm www.culturalindia.net/indian-folktales/panchatantra-tales/index.html http://www.harappa.com/gandhi.html
MEDIA – PRINT – ELECTRONIC CHALLENGES
Values and Violence
![Page 67: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/67.jpg)
EVOLUTION OF ICT IN EDUCATION
Master Plans
MP 1 : ICT literacy MP 2: Promotion and stabilization of ICT use in Education
PM 3: Advances ICT use in Education
MP 4: Utilization based ICT
Goal Establish ICT infrastructure
Promotion of use of ICT in Education
Advances in Education and research
Creative ICT based Education/Learning
ICT Develop-ment
•Infrastructure building•ICT literacy education•Internet portal service through CBSE website
•Development and distribution of content•National system for sharing educational contents•Digital Library System•Improving teaching methods•Teaching / Learning center•Cyber Home Learning System
•Customized learning•Develop digital textbooks•U-Learning pilot projects•National Teacher Training Information Service
•Create digital ecosystem for learning and research•Intensify ICT use•Focused on side effects of ICT•Data and evidence based on policy making•Encourage state holder’s participation and communication•Promote internal ICT use in educationFocus on ICT literacy ICT use ICT Leadership Creative HRD
using ICTTraining Directio
n
![Page 68: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/68.jpg)
DIGITAL CONTENT
Interactionactivities
Multi-media
Hyperlinkyou tube
Teacher TV
Data Searching
Learning Modules/LessonPlans
Connection ofcontents ownedby social/cultural
Institutions
Assessmenttools
LearningManagement
System
Connectionto national/
Internationalknowledge
Textbook
![Page 69: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/69.jpg)
Encourage students and teachers to improve their ability to develop and apply new teaching/learning models and methods that are appropriate for the changing educational environment
Encourage students and teachers to improve their ability to develop and apply new teaching/learning models and methods that are appropriate for the changing educational environment
Social Networking Software
WIKI
Open Education Resource
Cloudcomputing
Digital Textbook,
e-Book
Leveraging Resources to make Education/Learning
Creative
Semantic Web
Simulation Technologies
CloudService
3D : Second Life, AR, VR
OCW
CloudApp.
ICT: OPEN SOURCES
![Page 70: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/70.jpg)
STRENGTHENING
FORMATIVE LEARNING
![Page 71: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/71.jpg)
• Formative assessment is thus carried out during a course of instruction for providing continuous feedback to both the teachers and the learners for taking decisions regarding appropriate modifications in the transactional procedures and learning activities.
![Page 72: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/72.jpg)
• Summative assessment is carried out at the end of a course of learning. It measures or 'sums-up' how much a student has learned from the course. It is usually a graded test, i.e., it is marked according to a scale or set of grades
![Page 73: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/73.jpg)
![Page 74: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/74.jpg)
FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT
• Informs teacher where the
need/problem lies. • Focus on problem area.
• Helps teacher give specific feedback
• Provide relevant support • Plan the next step
For the Teacher
For the Student Helps student identify
the problem areas Provides feedback and
support.
Helps to improve performance
Provides opportunity to improve performance
Remedial
Diagnostic
![Page 75: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/75.jpg)
METHODS OF ASSESSMENT
1. Observation2. Assignment
3. Projects
4. Portfolio
5. Checklist
6. Rating scale
7. Anecdotal records
![Page 76: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/76.jpg)
TECHNIQUES FOR EFFECTIVE ASSESSMENT
• Conversational skills• Assignments• Verbal skills• Subject wise academic quiz• Project/ research• Intellectual activity (on the spot
activities)• Presentations.• Group discussions• Computer skills.• Activities for better understanding of
the concept.• Observation and evaluation through
practice .
![Page 77: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/77.jpg)
RESPONDING TO
DIVERSITY THROUGH CCETHE MASTER
![Page 78: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/78.jpg)
Inclusive education is an evolving practice. It is a means, not an end; a journey, not a destination; a process, not a product. It may start without waiting for discourses to close and policy to change, for children of today cannot wait, and their education cannot stop.
Madan Mohan Jha(School Without Walls)
![Page 79: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/79.jpg)
Inclusive, Learning-Friendly Environment in Schools
Inclusive, Learning-Friendly
Environmentbased on shared vision and values
Culturally sensitive, celebrates differences and
attempts learning opportunities
to create for ALL children
Promotes participation, cooperation, and
collaboration
Promotes healthy lifestyles and Life Skills
Learning is relevant to children’s daily lives;
children take responsibility for their learning
Promotes opportunities for
teachers to learn and benefit from that learning
Safe; protects ALL children from harm, violence and abuse
Includes ALL children: girls and boys: those from
different cultural or linguistic backgrounds;
those with special abilities or
learning needs
Families, teachers and communities are
involved in children’s learning
Gender fair and
Non-discriminatory
![Page 80: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/80.jpg)
Inclusive, Learning-Friendly Classroom
Traditional classroom Inclusive,learning-friendly classroom
Relationships
Distant (the teacher addresses students with her back towards them)
Friendly and warm. The teacher sits next to and smiles at the child with a hearing impairment. The parent-helper praises this child and assists other children.
Who is in theclassroom?
The teacher as well as students with quite similar abilities
The teacher, students with a wide range of backgrounds and abilities, and others such the parent-helper
Seatingarrangement
Identical seating arrangements in every classroom (all children seated at desks in rows; girls on one side of the room, boys on the other)
Different seating arrangements, such as girls and boys sitting together on the floor in two circles or sitting together at tables
Learningmaterials
Textbook, exercise book, chalkboard for teacher
Variety of materials for all subjects such as math materials made from newspapers, or posters and puppets for language class
Resources The teacher is interacting with children without using any additional teaching materials.
The teacher plans a day in advance for the class. She involves the children in bringing learning aids to the class, and these aids do not cost anything.
Evaluation Standard written examinations Authentic assessment; Observations; Samples of children’s work over time such as portfolios (see Booklet 5)
![Page 81: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/81.jpg)
CBSE Manuals - PSP
Poor School Performance
![Page 82: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/82.jpg)
PSP – Extracts
Poor School Performance
![Page 83: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/83.jpg)
PSP – Extracts
Poor School Performance
CBSE Manual on InclusionUnder Revision
![Page 84: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/84.jpg)
CBSE – QuarterlyCENBOSEC
Inclusive Practices
![Page 85: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/85.jpg)
ACCESSIBLE RAMPS
ACCESSIBLE RESOURCESACCESSIBLE PLAYGROUNDS
Inclusive Education Schools have: ACCESSIBLE FURNITURE
![Page 86: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/86.jpg)
Gender Sensitivity
![Page 87: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/87.jpg)
Future Plan of ActionRoad Ahead
• Revise PSP as ‘Inclusion”• Teacher Empowerment• Introduction of Human Rights as
an Elective• Further Reforms for Differently
Abled• In Examinations• Credit for Schools Mainstreaming
![Page 88: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/88.jpg)
APTITUDE AND
PROFICIENCY
- GOING BEYOND
ACHIEVEMENT
![Page 89: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/89.jpg)
Aptitude Test:Student Global Aptitude Index (SGAI)
• Online Aptitude test• Optional • May also be used as a tool along with
the grades obtained in the CCE to help students decide the choice of subjects in Std XI.
• Proposed to be available twice -end of std IX. -end of std X .
Humanities
Science Commerce
![Page 90: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/90.jpg)
• battery of Aptitude Tests which also combines Interest profile of a student.
• customized to suit the Indian context and variety of student population in Private, Government and Aided Schools affiliated to CBSE.
• should be taken only as an indicator or a facilitator
Aptitude Test:Student Global Aptitude Index (SGAI)
![Page 91: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/91.jpg)
SGAI DESCRIPTION
• simple paper and pencil test • 2 – 2½ hours duration• MCQ, Negative marking • Broadly indicates:
– Scientific Aptitude– Numerical Aptitude– Social Aptitude– Behavioral Science Aptitude– Art Aptitude, and – Interest areas
![Page 92: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/92.jpg)
• act as a benchmark in testing of skills and higher mental abilities of students
• provide motivation to students for academic excellence in the respective subject
• provide feedback to students and parents
• Assess students on – abilities and skills to apply concepts and principles of the
subject to everyday life situations.– skills to create and devise methods for solving subject
related problems.– abilities to analyse, synthesise and evaluate a given
situation on the basis of learning in the subject.
(Circular No.56/ 01.09.2010)
Proficiency Test - Objectives
![Page 93: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/93.jpg)
Proficiency Test
• Optional • Student may appear in one or all - English,
Hindi, Social Science, Mathematics and Science
• One test will be held on a single day.• Paper-pen test• May/June next year (2011) - the exact
schedule will be notified later.• Pay separate examination fee(500/- to
Rs.1000/-)• Joint certificate by CBSE and the collaborating
agency indicating percentile rank.
(Circular No.56/ 01.09.2010)
![Page 94: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/94.jpg)
Design of the Question Paper
• 2½ hours, 100 marks• No. of questions may vary one subject to another.• All MCQ’s with only single correct answer.• Negative marks will be awarded for wrong answers• The test will be based on classes IX-X syllabus in the
subject prescribed by CBSE• typology of questions - different from the type of
questions asked in conventional final examination conducted by the Board at the end of Class-X
![Page 95: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/95.jpg)
DIMENSIONS OF CO-
SCHOLASTIC LEARNING
![Page 96: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/96.jpg)
School Programmes
School Property Co-Scholastic
AreasEnvironment
Students/Peers
Towards Teachers
Attitudes and Values(5 POINT SCALE)
Emotional Skills
Social Skills
Co-Scholastic Areas(5 POINT SCALE)
Life Skills
(5 POINT SCALE)
Thinking Skills
1.Literary & Creative Skills2.Scientific & ICT Skills3.Visual & Performing Arts4.Organisational & Leadership
Skills
Health & Physical Education
(5 POINT SCALE)1. Sports/Indigenous Sports2. NCC/NSS 3. Scouting & Guiding4. Swimming 5. Gymnastics 6. Yoga 7. First Aid 8. Gardening/Shramdaan9.Work Experience
![Page 97: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/97.jpg)
How to calculate Grades in Co-Scholastic Areas
1. Each student will be graded on each of the 03 Life Skills, Work Education, Visual and Performaing Arts, 03 Attitudes, Values, 02 Co-curricular Activities and 02 Health and Physical Education (HPE) activities.
2. Maximum score for each Life Skill, Work Education and Visual and Performing Arts and Attitudes is 50, for Values is 200 and for Co-curricular Activities and HPE is 50.
3. Before assigning the Grades on each component using the conversion table, please calculate the average or grade points by dividing the total score obtained by a student by number of items in that component. For example, for a student who has a score of 35 in Thinking Skills; you need to divide it by the number of descriptors, i.e. 10; the average or grade point is 3.5; hence grade is B.
4. A Sample Sheet to calculate grades in Co-Scholastic Areas is given after the indicators.
![Page 98: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/98.jpg)
![Page 99: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/99.jpg)
4B. Value Systems
![Page 100: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/100.jpg)
![Page 101: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/101.jpg)
![Page 102: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/102.jpg)
![Page 103: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/103.jpg)
![Page 104: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/104.jpg)
![Page 105: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/105.jpg)
![Page 106: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/106.jpg)
![Page 107: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/107.jpg)
![Page 108: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/108.jpg)
![Page 109: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/109.jpg)
LIFE SKILLS EDUCATION
![Page 110: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/110.jpg)
Policy – (School Management)Policy – (School Management)
Health & Wellness Clubs
School Health & Wellness Programme
Health Education Life Skills
AEPClass IX & XIRevised Manuals (in process)
Integrated Components(Eco – Clubs – Peace & Value Education)
Teachers’ Manual - I – VIII
Teachers’ Manual - IX
Curriculum PlusClasses VI – VIIIRevised Teachers’ Manual for Class VI (2008-09)
Class 1 – 12Vol IVol IIVol IIIIVol IV
![Page 111: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/111.jpg)
Health Manuals
Comprehensive School Health Manuals (C.S.H.M) (under revision):
Holistic health ( physical, mental, emotional and psychological health).
Formal and informal approaches in curriculum pedagogy for health promotion.
Emphasis on providing a safe school environment.
![Page 112: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/112.jpg)
CSHP: COMPREHENSIVE SCHOOL HEALTH PROGRAMME
Food and Nutrition
Personal And Environmental
Hygiene
Physical Fitness
Being Safe AndResponsible
Knowing your body
Behaviour And Life Skills
![Page 113: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/113.jpg)
Teachers Manual on
Life Skills Class – IX - X
Under Revision
Graded Activities / Teachers Manuals
![Page 114: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/114.jpg)
Adolescence Education
Programme
→Addresses Inclusion
→Through Activities
![Page 115: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/115.jpg)
Panchkula -120 schools,378 Participants
Ajmer-167 schools,296 participants
Allahabad-133 Schools, 448 participants
Guwahati-30 schools,85 participants
Patna-96 schools,282 participants
Bhubaneshwar-52 schools 182 participants
Chennai-141 schools360 participants
AEP
![Page 116: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/116.jpg)
AEP-2010
• Master Trainers’ Workshops-5, one in each State
• Nodal Teachers’ Training Workshops-32
• Principal’s Advocacy Workshops-32• Peer Educators’ Workshops-5, one
in each State• Monitoring and Mentoring of AEP
through AEP Sahodaya system
![Page 117: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/117.jpg)
Ajmer-14 Rajasthan-7Madhya Pradesh-7
ChennaiMaharashtra-7
PatnaBihar-5
BhubaneswarOrissa-6
AEP States -
2010
![Page 118: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/118.jpg)
SECTION – III INITIATIVES
![Page 119: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/119.jpg)
Languages – Communicative Language Teaching
○ English ○ Japanese – VIII – 2008-09○ Sanskrit ○ German – VI – 2008-09○ French ○ Bahasa Maleyu – X – 2008-09
Mathematics Science Social Science I.T. Enrichment activities Examination Reforms
![Page 120: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/120.jpg)
FOREIGN LANGUAGES
• Arabic • Bhasha
Maleyu • English• French• German• Japanes
e• Nepali
• Portugese
• Persian • Russian• Spanish• Tibetan• Chinese
![Page 121: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/121.jpg)
• Upper Primary Level (VI-VIII) - Computer basics as
part of work experience.
• Secondary Level ( IX & X) - I I T - Additional
Subject
• Senior Secondary Level (XI & XII) - 3 Electives
1. Computer Science2. Informatics Practices3. Multimedia & Web Technology
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY BASED SUBJECTS
![Page 122: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/122.jpg)
NEW ELECTIVES AT SENIOR SECONDARY LEVEL
Academics
• Creative Writing and Translation Studies: 2007– 08.
Reader – Class XI
Reader – Class XII
FIRST BOARD EXAM- 2009
Contd…
![Page 123: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/123.jpg)
• Heritage Crafts–XI - 2008-09–XII - 2009-10
• Graphic Design–XI - 2008-09–XII - 2009-10
Readers NCERT
Readers NCERT
NEW ELECTIVES AT SENIOR SECONDARY LEVEL
![Page 124: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/124.jpg)
VOCATIONAL
• FINANCIAL MARKET MANAGEMENT (FMM) – 2007-08
Contd…
(Contd…)
NEW ELECTIVES AT SENIOR SECONDARY LEVEL
![Page 125: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/125.jpg)
Health Care Sciences
• Class XI 2009 – 2010
• First Board Examination 2011
Joint certification with FICCI
![Page 126: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/126.jpg)
126
![Page 127: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/127.jpg)
127
![Page 128: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/128.jpg)
128
![Page 129: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/129.jpg)
129
![Page 130: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/130.jpg)
M & M : - CBSE Initiative
• Empowering Training and Goal Setting
• Project Approach to Problem Solving
• Institute leadership• Collaborate quality teams.• DO IT ALL OVER AGAIN
![Page 131: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/131.jpg)
Evaluate/Learn/Decide
Plan
Implement
Monitor
Reflect/Learn/
Decide/Adjust
Implement
Monitor
Reflect/Learn/
Decide/Adjust
Implement
SCOPE OF WORK
Identification of Mentoring Schools according to criteria’s laid down.
Capacity Building- setting expectations, implementation.
Evaluation.
Timelines for Implementation.
![Page 132: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/132.jpg)
MAJOR OBJECTIVES of M & M
• Implementation of CCE has to be in letter and spirit, not just a procedure fulfilled on paper.
• It involves working very closely with the actual resource base that can make CCE a worthwhile initiative – i.e., the teachers and school leaders, and that involves understanding them, their views and their constraints (and find ways to overcome them)
![Page 133: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/133.jpg)
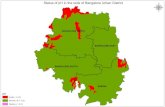
133
• STATES COVERED
• STATES YET TO BE
COVERED
• STATES PARTIALLY COVERED
STATUS OF M & M
![Page 134: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/134.jpg)
CCE AWARDS- 2010-11
One award for every 100 schools and each award shall consist of Rs. 25,000/- and a certificate
![Page 135: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/135.jpg)
MENTOR AWARDS 2010-11
One award on every 100 schools i.e. one award on every 10 to 15 mentors and each award shall consist of Rs. 10,000/- and a certificate
![Page 136: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/136.jpg)
VISION FOR THE FUTURE
THE ROAD AHEAD
![Page 137: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/137.jpg)
Plan schools as life-long, year-round community resource
centersInvest in your key resource: teachers as facilitators.
Change the assessment
system / pattern – follow
formative assessment
Use tomorrow’s technology.
Use your entire
community as a resource.
Give everyone the right to
choose.
Ask your students and
parents.
Guarantee success and satisfaction for parents
Cater to all intelligence traits and all
learning styles.
Use the world’s best
teaching, study and learning methods
![Page 138: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/138.jpg)
VISION FOR THE FUTURE
• Lifelong continual learning will be a fact of life for everyone.
• Inside the context, everyone should be encouraged to plan his or her own curriculum for life.
• While there is no one right way to teach or learn, there are many techniques to enable anyone to learn faster, better, smarter. And an open-minded search for nee ideas is central to tomorrow’s world and central to tomorrow’s schools.
![Page 139: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/139.jpg)
History’s newest revolution : the power to change your life -
Beliefs• World – hurtling – fundamental turning point in history.• We are living through a revolution – that is changing
the way we live, communicate, think and prosper.• Probably not more than one person in five knows how
to benefit fully from the hurricane of change – even in developed countries.
• Unless we find answers, an elite 20 percent could end up with 60 percent of each nation’s income, the poorest fifth with only 2 percent. That is a formula for guaranteed poverty, school failure, crime, drugs, despair, violence and social eruption.
• Need for a parallel revolution in lifelong learning to match the information revolution and for all to share the fruits of an age of potential plenty.
![Page 140: Bangalore Sahodaya-1 Updated Auto Saved]](https://reader037.fdocuments.us/reader037/viewer/2022102615/5470d515b4af9fbd058b4587/html5/thumbnails/140.jpg)