Autonomic Nervous System II Plants that affect the sympathetic nervous system.
-
date post
22-Dec-2015 -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
1
Transcript of Autonomic Nervous System II Plants that affect the sympathetic nervous system.

Autonomic Nervous System II
Plants that affect the sympathetic nervous system

Ganglionic blocking compounds
nicotine, lobeline

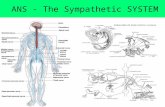
Peripheral Nervous System: Neurotransmitters & Receptors
CNS
nicotinic receptor
nicotinic receptor
muscarinic receptor
adrenergic receptor
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Somatic Motor
nicotinic and muscarinic receptors = cholinergic receptors

Ganglionic Blocking Compounds
• A high dose of nicotine or lobeline (nicotinic cholinergic receptor agonists) can overstimulate ganglionic receptors
• persistent depolarization of autonomic ganglia: autonomic ganglionic blocade
• triggers further release of epinephrine by adrenal medulla, which leads to vasoconstriction and potentiation of ganglionic blockade

Ganglionic Blocking Compounds
Two phases of autonomic ganglionic blocade:• Stimulatory phase:– constriction of capillaries and arterioles– increase in blood pressure– sweating
• Paralytic phase:– decrease in blood pressure…40 mg of nicotine (amount extracted from 2
cigarettes) can cause fatal ganglionic blocade if it is injected (when smoked most nicotine is degraded)

Nicotiana tabacum

Nicotiana tabacum
• Common name: tobacco• Origin: South America• Ethnomedical uses by
Native Americans:• leaves smoked and snorted
as sacred enebriant and CNS stimulant

Nicotiana tabacum
• Active compound: nicotine (alkaloid)
• Mechanisms of action:– CNS stimulant– stimulates acetylcholine
release in autonomic ganglia at juncture of pre- and post-ganglionic neurons

• Therapeutic uses of nicotine (not recommended due to the addictive nature of nicotine)– enhancement of athletic performance– improvement of short-term memory / mental
functioning
Nicotiana tabacum

Lobelia inflata

Lobelia inflata• Common name: Indian
tobacco• Plant family: Lobeliacae• Origin: North America• Habit: herbaceous plant on
forest floor• Ethnomedical uses by
Native Americans:• leaves used as a
respiratory expectorant and for chest conditions

Lobelia inflata
• Active compound: α-lobeline (alkaloid)
• Therapeutic uses:– expectorant– decongestant– smoking deterrant
(stimulates same receptors, but has a milder effect than nicotine)

Compounds That Target the Sympathetic Nervous System

Sympathetic Nervous System (Review)
• Catabolic system that expends (burns) energy• Nerves in this system originate from the thoraco-
lumbar regions• “Fight or flight” responses to danger:– increase in heart rate & force of ventricular contractions– shunting blood to muscles and heart– increase in sweat gland secretion– dilates pupils– dilates bronchial tubes– inhibits GI motility and secretions, contracts GI sphincters– stimulates secretion of adrenaline from adrenal medulla

Sympathetic Nervous System Adrenergic Receptors (Stimulated by Norepinephrine)
• alpha receptors – – reduce glandular secretions– reduce GI motility – increase constriction of certain arterioles and veins
• beta receptors – – increase heart rate, contractions– increase kidney renin secretion– relax trachea and bronchioles – dilate some arterioles and veins (not in skin or brain)– increase breakdown of glycogen / fats for energy

Adrenergic Agonists
Endogenous agonists of α and β adrenergic receptors:
• Epinephrine (adrenaline)– produced by adrenal medulla– released in increased amounts in response to stress– stimulates heart– dilates blood vessels going to skeletal muscle
• Norepinephrine– postganglionic adrenergic neurotransmitter– stimulates heart– constricts blood vessels in skin, mucosal surfaces, and
kidneys

Plant-Derived Adrenergic Agonists(Sympathomimetics)
• Ephedra• Citrus aurantia

Ephedra spp.

Ephedra spp.• Common names: Ephedra, Mormon tea, Ma
Huang• Plant family: Ephedraceae• Plant parts used: aerial parts• Ethnomedical uses: asthma, sinusitis, stimulant• Active compound: ephedrine (alkaloid)– stimulates both α and β receptors– releases stored catecholamines (epinephrine,
norepinephrine, and dopamine)– CNS stimulant– Bronchodilator

Ephedra spp.Chemical derivatives of ephedrine:• pseudoephedrine HCl (sudafed, isophedrine)– vasoconstrictor– decongestant– longer bronchial effect & less CNS stimulation than
ephedrine• phenylpropanolamine– vasoconstrictor– decongestant
• vaponephrine– bronchiodilator to treat asthma
• salbutamol (albuterol, proventil)– bronchodilator to treat asthma

Citrus aurantium (bitter orange)

Citrus aurantium (bitter orange)
• contains synephrine alkaloids and para-octopamine (typically cited as active ingredients)
• these compounds have α-adrenergic agonist properties, and may also stimulate β receptors in the sympathetic nervous system

Citrus aurantium (bitter orange)
• effects similar to Ephedra• often added to herbal weight loss
supplements (in place of banned Ephedra)• compound responsible for weight loss is most
likely para-synephrine, also called oxedrine

Anti-adrenergic Compounds
• Ephedrine chemical derivatives are also used to create postsynaptic adrenergic receptor blockade
• used to treat hypertensiontwo classes:• β1 receptor specific competitive blockers– lopressor & tenormin
• β1β2 receptor competitive blockers– corgard, timoptic (also treats glaucoma)

Other plant-derived adrenergic antagonists
• Rauvolfia serpentina• Pausinystalia johimbe

Rauvolfia serpentina

Rauvolfia serpentina
• Plant family: Apocynaceae• Origin: India, Indomalasia• Habit: climbing shrub• Plant part used: root• Ethnomedical uses in Ayurvedic medicine:– sedative– tranquilizer– antipsychotic– antihypertensive

Rauvolfia serpentina
• Active compounds:– reserpine, rescinnamine, ajmalicine
• Mechanism of action:– binds storage vesicles in peripheral and central
adrenergic neurons– dysfunctional storage vesicles cause nerve endings
to lose their ability to concentrate and store catecholamines (norepinephrine and dopamine)
– has similar effect on serotonin (in CNS)

Rauvolfia serpentina
Physiological effects of reserpine:
• reduced sympathetic effects
• reduced catecholamine levels in CNS, heart, and PNS
• reduced serotonin levels• lowered blood pressure
due to reduced norephinephrine levels

Rauvolfia serpentina
Therapeutic uses:• reserpine & rescinnamine – treat psychosis, mania and
hypertension
• ajmalicine– treats circulatory disorders

Pausinystalia johimbe
• Common name: yohimbe• Plant family: Rubiaceae• Origin: West Africa• Active compound: Yohimbine• Plant part used: bark

Pausinystalia johimbe• Ethnomedical uses: taken orally as an
aphrodisiac in West Africa by many different ethnolinguistic groups
• Mechanism of action: Yohimbine causes competitive blockade on adrenergic receptors
• Has highest affinity for α2 receptors
• Therapeutic use: yohimbine taken orally as an aphrodisiac and to treat impotence