Article Presentation Patho
description
Transcript of Article Presentation Patho
ARTICLE PRESENTATION
• THE MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTHYROIDISMBY
JAYNE A.FRANKLYN M.D,Ph.D.
IN THE NEW ENGLAND
JOURNAL OFMEDICINEEDITED BY
AlASTAIR J.J.Wood
Objectives
• At the end of this presentation learners will be able :-
• To understanding the knowledge given in the article about the management of hyperthroidism.
• To describe the antithyroid drugs,beta-antagonist and radioiodine therapy its effects,dosage and complications given in the article .
The Management of Hyperthyroidism
• Hyperthyroidism is common,affecting approx 2 percent of women and 0.2 percent of men
• There are three principle treatments• -Antithyroid drugs• -Radiodione• Surgery
INVESTIGATIONS
• Diagnosis should be confirmed by mseasurement of serum thyro-tropin and total of free thyroxine.
• If thryotropin level thyroxine level=Normal
• Serum triiodothyronine should be measured since the patient may have triiodothyronine toxicosis
Cont..
• Serum total thyrxine concentrations -in patients with increased serum
concentrations of thyroixine-binding globulin.
• Like pregnant women taking estrogens or persons with inherited increase thyroxine binding globulin having high affinity for thyroxine.
Investigation cont…
All the patients with these latter conditions are clinically euthyroid and have normal
serum concentrations of thyrotropin.
Cont..
• Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism
• It is obvious if a diffuse goiter and ophthalomopathy are present.
• Other causes ,a multinodular goiter,toxic thyroid adenoma and subacute thyroiditis.
• Should be evident from the history or by the measurement of uptake of radioiodine by the thyroid.
Antithyroid drugs
• Methimazole,carbimazole and propylthiouracil are the main drugs of antithyroid drug therapy.
• Their principle action is to inhibit the coupling of iodothronines and hence the synthesis of thyroid hormones.
Antithyroid drugs
• Methimazole has a longer duration of action ,although both of the drugs are effective for more than 5 hours as they accumulate in thyroid cells.
Indications for Antithyroid drug therapy and treatment Regimens
• The three main drugs are prescribed for Graves’ in the hope that the pt will have a remission during
the therapy.
• Our policy is to give an ant thyroid drug ,hope of achieving remission in pt(those 40 years old or
younger).before treating with radioiodine.
Cont..
• Treatment stared with 10 to 20 mg of methimazole once a day or 75 to 100 mg of propylthiouracil three times a day.
• The dose should be reduces after 4-6 weeks as improvement occurs and adjusted every 4-6 weeks to maintain normal thyroid secretions.
Side effects
• Serious effects occure in 3/1000 pt,whether they receive meth or propyl.
• Agranulocytosis is more common over 40 yrs old with fever & sore throat.
• Pt adviced to discontinue therapy and recover after 3 weeks after the drug is stopped/some had also rash and pruritus.
Outcome of Treatment
• In one study, the rate of remission one year after treatment was stopped was 31 percent among patients treated for 6 months and 82 percent among patients treated for 2 years.
• Relapse is most likely within the first six months after withdrawl of therapy and may occur years after.
Beta-Andrenergic-Antagonist Drugs
• They are useful adjunctive agents,in patents with Graves’ hyperthyroidism
• In this Propanolol,metoprolol,atenolol and nadolol are all effective in pt with hyperthyroidism
• Caution exercised in pt with asthma or heart failure.
Inorganic Iodide
• Iodine given as (Lugol’s solution) inhibits the release of thyroid hormones for few days or weeks.
• This drug is not used routinely but the short term therapy is useful in the prep of pt for surgery.
• The useful dose (5% iodine and 10 % potassium iodide in H2O) ,potassium iodide is 60 mg TDS.
Radioiodine Therapy
• The objective of this therapy is to destroy sufficient thyroid tissue to cure
hyperthyrodism.
• The regimens used include low doses (2 mCi),fixed doses of 5 to 10 mCi and doses on
the basis of size of the thyroid.
Post-Treatment Thyroid Function
• Hypothyroidism occurring within the first six months in 50 % of the pt given high doses by 1 year and in 50% of those given lower doses by 25 yrs.
Other Side Effects
Aside from radioiodine therapy ,it also has few adverse effects like radiation thyroiditis includes thyroid pain ,tenderness and swelling.
Opthalmopathy:A recent study of pt more than 35 years old treated with meth,surgery or radioiodine and the eye disease was higher among pt treated with radioiodine.
Subtotal Thyroidectomy
• Pt with Graves’ hyperthyroidism subtotal thyroideectomy is appropriate treatment only for those who refuse radioiodine therapy.
• Preoperative:-It includes methimazole combined with potassium iodide (60 mg TDS) for 10 days and short term therapy with propranolol.
Post Op Thyroid Function
• Relapse occurring atleast 10% of pt most often during the first 5 years after surgery.
• Pt with elevated serum thyrotropin level but a normal serum thyroxine concentration (subclinical hypothyroidism) within the 1 year should not be considered as permanent hypothyroidism.
Management of toxic Adenoma or Toxic Nodular Goiter a
• Hyperthyroidism due to thyroid nodular disease is permanent ,there are no spontaneous remission.
• The most appropriate therapy due to this disease is radioiodine.
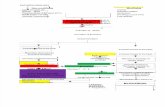
Prevelance of Hypothyroidism after treatment with radioiode or thyroidectomy
60
RADIOIODINE
40•
20
Thyroidectomy
Prevalence Of hypothyroidism%
0
0 2 5 10 15 20 25 Years after treatment
OVER ALL SUMMARYTHERAPEUTIC AGENT ACTIONS INDICATIONS
Antithyorid drugs-Propylthiouracil-Methimazole-Carbimazole
Inhibit thyroid hormone synthesis
First line therapy for graves’ hyperthyroidism
B-Andrenergic-antagonist drugsPropranolol,Metoprolol,Atenolol,Nadolol
Ameliorate action of thyroid hormone in tissues
Often only therapy required for thyroiditis
Iodine-containing compoundsLugol’s sol,potassium iodide
Inhibit T4 and T3 release Prep for surgery ,no routine indications
Miscellaneous agentsGlucocorticoidsPotassium PerchlorateLithium carbonate
Inhibit iodine transport and thyroid hormone synthesis
Thyrotoxic crisis.
References
• http://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJM199406163302407