Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
-
Upload
khairul-ikhwan -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
1/34
Antigen processing and
presentation
Dr Jacinta Kelly
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
2/34
Antigen processing and
presentation
Why is it needed?
How does it happen?
How are the pathways of endogenous andexogenous antigen kept apart?
What are the consequences?
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
3/34
T cell receptor: antigen receptor of T cells
Cannot recognise antigen in solution
Must have the antigen processedand presented to it
Specialised molecules present
antigens to T cells:
MHC molecules
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
4/34
Antigen presentation cells required
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
5/34
1.
3.
2
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
6/34
TCR
MHC
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
7/34
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
8/34
Antigen presentation by MHC
molecules
Two types of MHC molecules MHC class I
MHC class II
Two types of T cells CD4 T helper cells
CD8 T cytotoxic cells
Two types of antigen Endogenous (from within the cell)
Exogenous (from outside the cell)
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
9/34
Type of T cell activated
MHC class I activate CD8 T cytotoxic cells
Present endogenous (eg viral) antigens
Target cell is killed by CD8 cell
Any cell can become virallyinfected/neoplastic
Therefore: MHC class I is on all nucleated
cells
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
10/34
Cell expressing MHC class I
Ag
CD8+ T cell
CD 8 binds 3 domain
Stabilises interaction
MHC class I Ag presentation to CD8 T cell
Death of target
cell
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
11/34
CD8 CTL
Tumour cell
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
12/34
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
13/34
T cytotoxic cell
Endogenous antigenTCR MHC I
Death of target cell
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
14/34
Type of T cell activated
MHC class II activate CD4 T helper cells
Present exogenous (eg bacteria) antigens
CD4 T cells upregulate all immunefunctions
MHC class II found only on cells thatsample the extracellular environment
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
15/34
MHC class II-CD4 T cell
activation CD4 T helper cells up regulate immune
function
Stimulate Mactivation and phagocytosis,
B cell antibody production
Help to clear exogenous antigen
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
16/34
CD4+ T cell
CD 4 binds mainly 2 domain
Stabilises interaction
Cell expressing MHC class II
MHC class II Ag presentation to CD4 T cell
Upreglation of
Immune responses
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
17/34
T helper cell macrophage
cytokines
Bcell
antibodies
phagocytes
Exogenous antigenTCR MHC
II
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
18/34
Antigen: linearProtein fragments
How does antigen getInto MHC binding cleft
How does endogenousAg bind MHC class I?
How does exogenous ag
Bind MHC class II?
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
19/34
A question of language
Cells that express MHC class I, present
endogenous ag
Are killed by CD8+ cells
Are called Target cells
Cells that express MHC class II, present
exogenous ag
Activate the CD4 T cell response
Are called Antigen presenting cells
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
20/34
Target cells:
All nucleated cells express MHC class I
Can be a target cell if virally
infected/neoplastic
Antigen presenting cells
Limited number of cells express MHC class II
Must sample extracellular environment
Monocytes, M, B cells
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
21/34
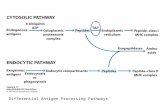
Antigen processing and
presentation Separate pathways for endogenous and
exogenous pathways
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
22/34
Endogenous antigen presentation
1
2
3
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
23/34
Exogenous antigen presentation
1
2
34
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
24/34
Loading of antigen to MHC
class I
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
25/34
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
26/34
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
27/34
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
28/34
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
29/34
Loading of antigen to MHC
class II
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
30/34
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
31/34
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
32/34
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
33/34
-
8/13/2019 Antigen Processing and Presentation 09
34/34
Useful textbooks
Kuby Immunology
Cellular and molecular immunology
(Abbas and Lichtman)
Janeways Immunobiology (Murphy,
Travers, Walport)