Adult Sepsis Nursing Competency
-
Upload
armando-holden -
Category
Documents
-
view
47 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Adult Sepsis Nursing Competency

Adult Sepsis Nursing Competency
Jonna Bobeck BSN, RN, CEN

Competency Instructions
• Listen to Competency• Read linked policies/guideline• Read article• Print test and complete. Return test to Clinical
Education

What is Sepsis?
• Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS)
• Sepsis• Severe Sepsis• Septic Shock

The Sepsis Continuum
A clinical response arising from a nonspecific insult, with 2 of the following: T >38oC or <36oC HR >90 beats/min RR >20/min WBC >12,000/mm3 or
<4,000/mm3 or >10% bands
SIRS with a presumed or confirmed infectious process
SepsisSIRSSevere Sepsis
SepticShock
Sepsis with organ failure
Refractoryhypotension

Epidemiology of Sepsis
• Sepsis in the United States• Major cause of Morbidity and Mortality
Leading cause of death in non-cardiac ICU in US 10th leading cause of death overall
Annually in >200,000 sepsis deaths Average cost per patient is $60,000 Average annual cost to health care system = 16.7 billion Average hospital length of stay is 19.6 days

Surviving Sepsis Campaign (SSC)
• A collaboration of three leading professional organizations
• Efforts to improve treatment and decrease mortality
• Click below to visit SSC website:
http://www.survivingsepsis.org/Pages/default.aspx

Early Goal Directed Therapy

SepsisSIRSSevere Sepsis
SepticShock
Insulin and tight glucose control
Early Goal Directed Therapy
Antibiotics and Source Control
Therapy Across the Sepsis Continuum

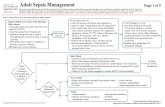
Sepsis Management Guidelines
• Initial resuscitation (first 6 hours) Begin immediately for elevated lactate or hypotension Resuscitation goals:
CVP 8-12 mmhg MAP > 65mmhg Urine output > 0.5 ml/kg/hr Central venous oxygenation > 70%, mixed venous
> 65%

Diagnosis
• Careful history and physical• Obtain appropriate cultures• Do not delay antibiotics

Antibiotic Therapy
• Begin as soon as possible• Broad-spectrum• Reassess• Duration

Source Identification and Control
• Site of infection• Evaluate for focus of infection• Source control measures• Remove infected devices

Safe Study and Fluid Therapy
• Resuscitate using crystalloids or colloids• CVP > 8mmhg• Use fluid challenge technique• Monitor for overload

PRH Fluid Therapy Instructions
• SIRS/Early Sepsis– Bolus 0.9 NS 20ml/kg
• Sepsis– If MAP less than 65 mmHg give 0.9 NS at 20ml/kg
as a bolus; repeat x 1 if MAP continues less than 65 mmHg

PRH Fluid Therapy Instructions
• Severe Sepsis/Septic Shock– If MAP less than 65 mmHg give 0.9 NS at 20ml/kg as a
bolus; repeat x 1 if MAP continues less than
65 mmHg. If MAP les than 65 mmHg following 40ml/kg
then begin:
Norepinephrine up to 20mcg/min to maintain MAP >65
Vasopressin 0.04 units/minute to maintain MAP >65

Vasopressors
• Maintain MAP > 65 mm Hg• Norepinephrine or dopamine

Inotropic Therapy
• Dobutamine in patients with myocardial dysfunction
• Combined inotrope/vasopressor

Glucocorticoids
• Low-dose glucocorticoids• Choice of steroid• Adrenal insuffieiency• Prolonged survival

Blood Transfusion
• PRBC’s• Oxygen delivery impairment• Target hemoglobin of 7.0 – 9.0 g/dL

Scv02
• Measure the mixed central venous 02 saturation (Scv02) by obtaining ABG from distal port of CVC line.– If Scv02 >70% - therapy achieved– If Scv02 is <70% check hematocrit and follow protocol

Mechanical Ventilation
• Mechanical ventilation of sepsis-induced acute lung injury (ALI)/ARDS
• Targets• Peep• Conservative fluid strategies

Glucose Control
• Hyperglycemia associated with poor outcomes• Target glucose 140 – 180mg/dL• NICE-SUGAR trial
PRH Insulin Order Guideline

DVT Prophylaxsis
• Low molecular weight heparin• Mechanical prophylaxis

Evaluation for Sepsis Screening Tool
• Press Ctrl and click link to view tool:
- Surviving Sepsis Campaign

Severe Sepsis Bundles
• Sepsis Resuscitation Bundle• Sepsis Management Bundle

Sepsis Resuscitation Bundle: (To be accomplished ASAP and scored over 6 hours)
• Serum lactate measured • Blood cultures obtained prior to antibiotic administration • From the time of presentation, broad-spectrum antibiotics
administered within 3 hours for ED admissions and 1 hour for non-ED ICU admissions
• In the event of hypotension and/or lactate > 4 mmol/L (36 mg/dl):
– Deliver an initial minimum of 20 ml/kg of crystalloid (or colloid equivalent)
– Apply vasopressors for hypotension not responding to initial fluid resuscitation to maintain mean arterial pressure (MAP) > 65 mm Hg
• In the event of persistent hypotension despite fluid resuscitation (septic shock) and/or lactate > 4 mmol/L (36 mg/dl):
– Achieve central venous pressure (CVP) of > 8 mm Hg – Achieve central venous oxygen saturation (SvO2) of > 70%

Sepsis Management Bundle: (To be accomplished ASAP and scored over 24 hours)
• Low-dose steroids• Activated Protien C - administered in
accordance with a standardized ICU policy • Glucose control maintained > lower limit of
normal, but < 180 mg/dl • Inspiratory plateau pressures maintained < 30
cm H2O for mechanically ventilated patients

Read Article and Take Test
Article
Test

References• Surviving Sepsis Campaign, Initials. (2009). Surviving sepsis campaign. Retrieved from
http://www.survivingsepsis.org/Pages/default.aspx• Angus, DC, Linde-Zwirble, WT, Lidicker, J, et al. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and
associated costs of care. Crit Care Med 2001; 29:1303.
• Bernard, GR, Wheeler, AP, Russell, JA, et al. The effects of ibuprofen on the physiology and survival of patients with sepsis. The Ibuprofen in Sepsis Study Group. N Engl J Med 1997; 336:912.
• McCloskey, RV, Straube, RC, Sanders, C, et al. Treatment of septic shock with human monoclonal antibody HA-1A. A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 1994; 121:1.
• Zeni, F, Freeman, B, Natanson, C, et al. Anti-inflammatory therapies to treat sepsis and septic shock: a reassessment. Crit Care Med 1997; 25:1095.
• Sasse, KC, Nauenberg, E, Long, A, et al. Long-term survival after intensive care unit admission with sepsis. Crit Care Med 1995; 23:1040. • Annane, D, Bellissant, E, Cavaillon, JM. Septic shock. Lancet 2005; 365:63. • Dellinger, RP, Levy, MM, Carlet, JM, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and sep
tic shock: 2008. Crit Care Med 2008; 36:296.
• Hollenberg, SM, Ahrens, TS, Annane, D, et al. Practice parameters for hemodynamic support of sepsis in adult patients: 2004 update. Crit Care Med 2004; 32:1928.
• Practice parameters for hemodynamic support of sepsis in adult patients in sepsis. Task Force of the American College of Critical Care Medicine, Society of Critical Care Medicine. Crit Care Med 1999; 27:639.
• Sessler, CN, Perry, JC, Varney, KL. Management of severe sepsis and septic shock. Curr Opin Crit Care 2004; 10:354. • Luce, JM. Pathogenesis and management of septic shock. Chest 1987; 91:883. • Ghosh, S, Latimer, RD, Gray, BM, et al. Endotoxin-induced organ injury. Crit Care Med 1993; 21:S19. • Rivers, E, Nguyen, B, Havstad, S, et al. Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med 200
1; 345:1368.