4.4 LIPIDS
description
Transcript of 4.4 LIPIDS

4.4 LIPIDS



Lipids
• Consist of C,H and O• High hydrogen to
oxygen ratio• Non polar
hydrophobic compounds

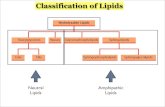
LIPIDSLIPIDS
FatsFats OilsOils
WaxesWaxes
PhospholipidsPhospholipids
SteroidsSteroids
• Fats & Oils are similar chemically• At room temperature, fats are solid and oils are liquid

Triglycerides (fats & oils)
•composed of a glycerol plus three fatty acids•“true” fats
FUNCTIONS •Serve as a good energy store•Stored under skin as insulator•Transport fat soluble vitamins

Phospholipids
•Composed of a diglyceride that bonded to phosphate group
FUNCTIONS •Most abundant lipids in plasma membrane
•Control cell permeability

Waxes
Insoluble
FUNCTIONS •Form a waterproof layer of cuticle on:
•Epidermis of plants•Exoskeleton of insects
•Feathers of bird•Fur of mammals

Steroids
CholesterolCholesterol
Makes the plasma membrane more rigid &
stable
Makes the plasma membrane more rigid &
stable
Sex hormones (testosterone,
oestrogen, progesterone)
Sex hormones (testosterone,
oestrogen, progesterone)
Control sexual development & body physiology
Control sexual development & body physiology
BileBile
Emulsifies fatsEmulsifies fats

Components of FatsComponents of Fats
GlycerolGlycerol Fatty AcidFatty Acid
• Colorless, odorless, sweet –tasting syrupy liquid
• 3 carbon and 3 hydroxyl group (OH)
• Colorless, odorless, sweet –tasting syrupy liquid
• 3 carbon and 3 hydroxyl group (OH)
• Organic acid• Molecular structure
• Long hydrocarbon tail with carboxyl (-COOH) at one end
• Different fatty acids have different hydrocarbon tails
• Organic acid• Molecular structure
• Long hydrocarbon tail with carboxyl (-COOH) at one end
• Different fatty acids have different hydrocarbon tails

Glycerol

Fatty Acid

Formation & breakdown of fats & oils

Source of Fats

Saturated fats vs unsaturated fats
Solid state at room temperature
Are in the liquid state (oil) at room temperature

Differences between saturated and unsaturated fats
Saturated fats Aspects that are different
Unsaturated fats
All covalent bonds between carbon atoms are single (C-C)
Type of chemical bond Existence of double covalent bonds between carbon atom (C=C)
Less reactive Reactivity More reactive because due to the double bonds
More tightly packed together
Packaging of the fat molecule
Less tightly packed due to the double bonds
Solid (fat) State of matter at room temperature
Liquid (oil)
Mainly from animal products: red meat, chicken skin, butter & coconut oil)
Source Mainly from plants: vegetable oils, palm oil, corn oil and olive oil
Increase level of “bad” cholesterol
Effects on blood cholesterol level
Increase levels of “good” cholesterol