4.3-Reproductive Strategies & Technologies SBI3U.
-
Upload
elizabeth-tucker -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
2
Transcript of 4.3-Reproductive Strategies & Technologies SBI3U.

4.3-Reproductive Strategies & Technologies
SBI3U

Reproductive Strategies in Agriculture1. Selective breeding: breeding plants and animals for
desirable traits. 2. Artificial insemination: transfer of semen into a
female’s reproductive tract. 3. Embryo transfer: fertilizing an egg artificially and
then transferring it into a recipient female.

Reproductive Technologies in Humans
1. Artificial insemination: sperm is collected and concentrated, then introduced into a woman’s reproductive organ.
2. In vitro fertilization (IVF): immature eggs are retrieved, joined with sperm in the lab, and embryos are inserted into the woman’s uterus. This is an option for women with blocked Fallopian tubes.
3. Pre-implantation genetic diagnosis: As an additional step to IVF, one of the cells of an embryo is removed and tested for specific genetic disorders before it is implanted in the uterus

Cloning
•Process that reproduces identical copies of genes, cells or organisms.
•There are 3 main types:
1) Gene Cloning2) Therapeutic Cloning3) Reproductive Cloning

1) Gene Cloning
•Manipulating DNA to produce multiple copies of a gene or another segment of DNA in foreign cells.
•The production of the protein insulin is an example of a certain piece of DNA.

1) Gene cloning procedure

2) Therapeutic Cloning
•Producing genetically identical cells which can treat various diseases.
•The cloned cell is used to grow new tissues and organs.

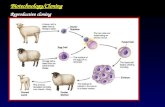
3) Reproductive Cloning•Process of producing genetically
identical organisms.
•This method is not very successful, only 0.5-6 % of cloned organisms are born.
•From those that are born only a small percentage of them survive.
•Dolly the sheep was the first successful clone

Stem cells•Stem cells: undifferentiated cells that can
develop into specialized cells in the body
3 different sources of stem cells:
1) Embryonic- obtained from embryos2) Adult- somatic cells that give rise to any type of cell. 3)Pluripotent – specialized adult stem cells that can produce only certain types of cells.

APPLICATIONS OF STEM CELLS

Transgenic organisms
•Organisms whose genetic material contains DNA from a different species.
•Genetically modified organisms (GMOs)
•Foreign DNA must be inserted into the organism in order for this to take place.
•Ex. plants and animals

Applications of Transgenic Plants
•Plants are continuously modified to increase resistance to herbicides, insects, pests or viruses
•Scientists help to use GMOs to increase nutritional value of plants ( ie. Golden rice).
•Insulin is now grown in safflower plants to produce a less expensive version of insulin for people with diabetes.

GOLDEN RICE
Note* 3 genes come from other plants and 1 from fungus

Applications of Transgenic Animals
•Different organisms are used to study diseases and medical procedures.
•Transgenic animals are used to produce medical proteins products. (e.g. goats- produce milk with Human growth hormone)
•Organisms can be developed to serve as organ donors to humans.

Ethical concerns with GMO
1) Environmental Threat: herbicide-resistant plants could encourage the use of stronger herbicides.
2) Health effects: not enough is known about the long-term effects of human consumption of transgenic foods and medicine
3) Social and Economic: the money spent is greater than the overall benefit.